Abstract
Case summary
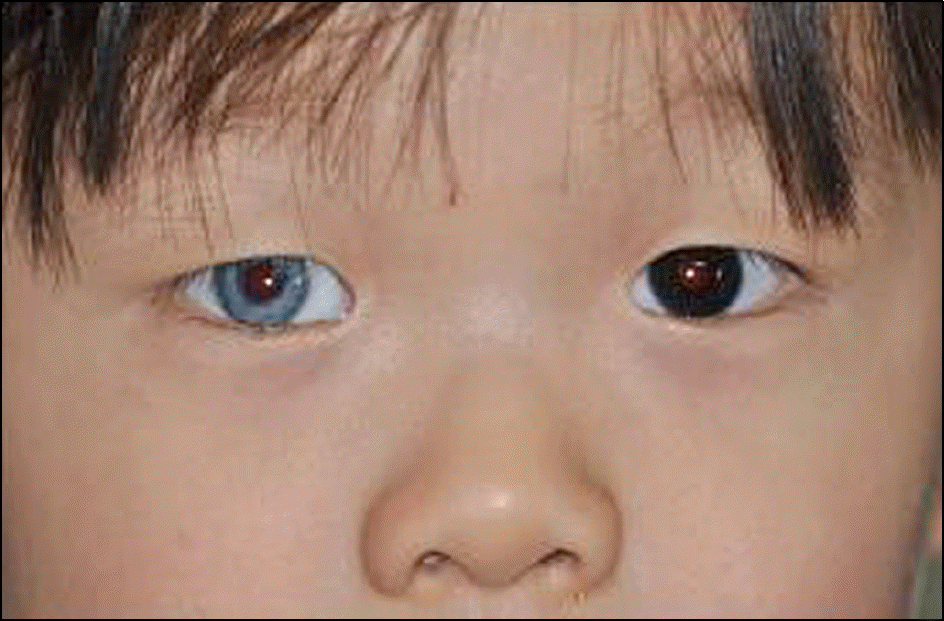
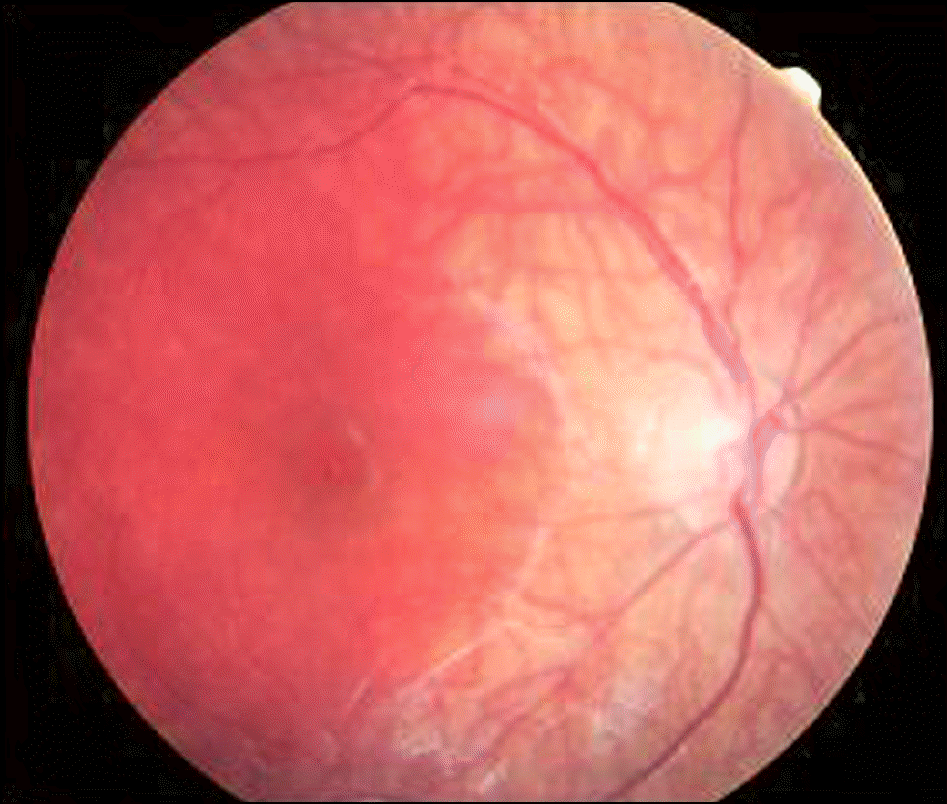
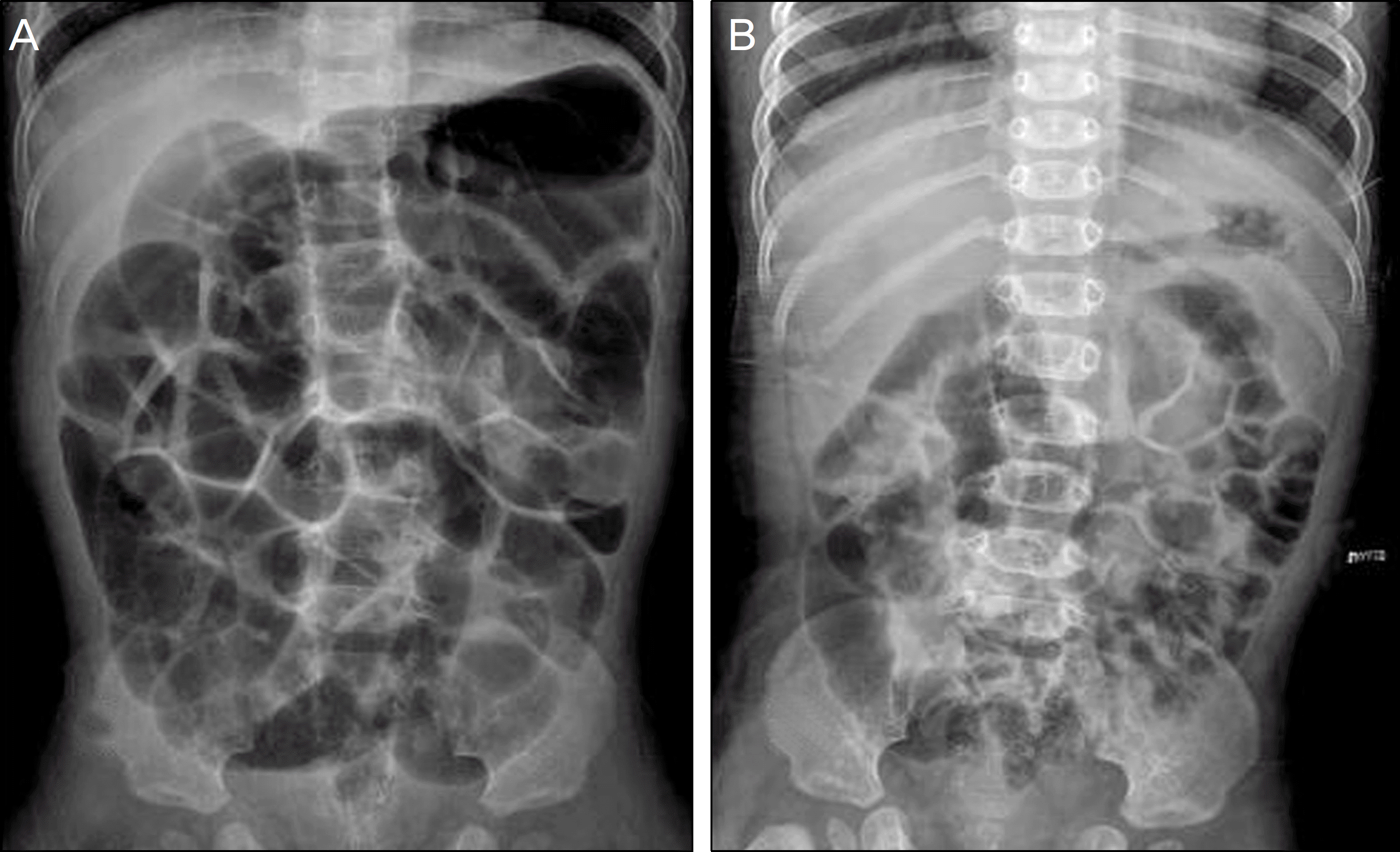
A 3-year-old boy visited our clinic to have his abnormal right eye iris color checked. The patient had a previous operation Hirschsprung's disease. In addition, his older sister and aunt showed similar ocular findings. A general physical examination, hearing test, and fundus examination were performed. On examination, hypochromic heterochromic iridum, albinism of the posterior pole upon ipsilateral fundus, and dystopia canthorum were found. There was no abnormal finding in the hearing test.
References
1. Waardenburg PJ. A new syndrome combining developmental anomalies of eyelids, eyebrows and nose root with pigmentary abdominal of the iris and head hair and with congenital deafness. Am J Hum Genet. 1951; 3:195–253.
2. Arias S. Genetic heterogeneity in the Waardenburg syndrome. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1971; 7:87–101.
3. Hageman MJ. Audiometric findings in 34 patients with Waardenbug's syndrome. J Laryngol Otol. 1977; 91:575–84.
4. Kim DK, Kim JH. A case of Waardenburg's syndrome. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1981; 22:687–91.
5. Lee OY, Choi YJ, Jung NH. A case of type 2 Waardenburg abdominal with open angle glaucoma. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:3532–5.
6. Kee SY, Le YC, Lee SY. Type 3 Waardenburg syndrome. J Korean Ophthalmol soc. 2005; 46:726–30.
7. Edery P, Attié T, Amiel J, et al. Mutation of the endothelin-3 gene in Waardenburg-Hirschsprung disease (Shah-Waardenburg abdominal). Nat Genet. 1996; 12:442–4.
8. Mallory SB, Wiener E, Nordlund JJ. Waardenburg's syndrome with Hirschsprung's disease: a neural crest defect. Pediatr Dermatol. 1986; 3:119–24.

9. Omenn GS, McKusick VA. The association of Waardenburg abdominal and Hirschsprung megacolon. Am J Med Genet. 1979; 3:217–23.
10. Hageman MJ, Delleman JW. Heterogeneity in Waardenburg syndrome. AM J Hum Genet. 1977; 29:468–85.
11. Klein D. Albinisme partiel (leucisme) accompagne de surdi-mu-tite, d'osteomyodysplasie, de rideurs articulaires congenitales multiples et d'autres malformations congenitales. Arch Julius Klaus Stift Vererb Forsch. 1947; 22(3–4):336–42.
13. Goldberg MF. Waardenburg's syndrome with fundus and other anomalies. Arch Ophthalmol. 1966; 76:797–810.

14. O'Donnell FE, Green WR. The eye in albinism. Duan TD, editor. Clinical Ophthalmology. Philadelphia: Harper & Row Pubilshers;1983. chap. 38.
16. Hageman MJ. Audiometric findings in 34 patients with Waardenburg's syndrome. J Laryngol Otol. 1977; 91:575–84.

17. Tassabehji M, Newton VE, Liu XZ, et al. The mutational spectrum in Waardenburg syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 1995; 2131–7.

18. Lim JO, Chung GW, Cho BC. A case of Waardenburg's syndrome. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1986; 27:271–5.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download