Abstract
Purpose
To compare the corneal wetting properties of balanced salt solution (BSS) and ophthalmic viscosurgical device (OVD) during cataract surgery.
Methods
The patients with senile cataract were randomly assigned to receive either BSS or viscous dispersive OVD for maintaining optical clarity during phacoemulsification. Intraoperative factors (VAS pain score, occurrence of corneal punctate epithelial erosions (PEE)) and postoperative factors (visual acuity, Oxford staining score, changes in endothelial cell counts, corneal thickness and volume) were compared.
Results
Twenty-two eyes were assigned to the BSS group and; 33 eyes were assigned to the OVD group. There were no significant differences in demographic variable between the 2 groups. Intraoperative PEE was observed in 6 eyes in the BSS group and in 2 eyes in the OVD group. The incidence of PEE in the OVD group was significantly lower than in the BSS group (p = 0.045). There were no significant differences in other parameters (VAS pain score, postoperative factors).
Go to : 
References
1. Hoffman RS, Fine IH, Packer M. New phacoemulsification technology. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2005; 16:38–43.

2. Yee RW, Matsuda M, Schultz RO, Edelhauser HF. Changes in the normal corneal endothelial cellular pattern as a function of age. Curr Eye Res. 1985; 4:671–8.

3. Liu Y, Zeng M, Liu X. . Torsional mode versus conventional ultrasound mode phacoemulsification: randomized comparative clinical study. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:287–92.
4. Hayashi K, Hayashi H, Nakao F, Hayashi F. Risk factors for corneal endothelial injury during phacoemulsification. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1996; 22:1079–84.

5. Shah PA, Yoo S. Innovations in phacoemulsification technology. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2007; 18:23–6.

6. Mackool RJ, Brint SF. AquaLase: a new technology for cataract extraction. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2004; 15:40–3.

7. Edelhauser HF, Hine JE, Pederson H. . The effect of phenylephrine on the cornea. Arch Ophthalmol. 1979; 97:937–47.

8. Kalyanasundaram TS, Hasan M. Corneal-wetting property of lignocaine 2% jelly. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:1444–5.

9. Chen YA, Hirnschall N, Findl O. Comparison of corneal wetting properties of viscous eye lubricant and balanced salt solution to maintain optical clarity during cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:1806–8.

10. Nam MJ, Kim KS. Differences in control function of corneal hydration between older and younger. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1990; 31:1256–62.
11. Wessels IF, DeBarge R, Wessels DA. Salvaged viscoelastic reduces irrigation frequency during cataract surgery. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 1998; 29:688–91.

12. Nixon DR. Preoperative cataract grading by scheimpflug imaging and effect on operative fluidics and phacoemulsification energy. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:242–6.

13. Bron AJ, Evans VE, Smith JA. . Grading of corneal and conjunctival staining in the context of other dry eye tests. Cornea. 2003; 22:640–50.

14. Arshinoff SA, Khoury E. HsS versus a balanced salt solution as a corneal wetting agent during routine cataract extraction and lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1997; 23:1221–5.

15. Miller JJ, Scott IU, Flynn HW Jr. . Acute-onset endophthalmitis after cataract surgery (2000-2004):incidence, clinical settings, and visual acuity outcomes after treatment. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005; 139:983–7.
16. Oh TH, Lee SJ, Kim HS. Clinical outcomes of cataract surgery using torsional mode phacoemulsification and soft shell techinique. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1313–8.
17. Miyata K, Maruoka S, Nakahara M. . Corneal endothelial cell protection during phacoemulsification: low- versus high-molecular weight sodium hyaluronate. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:1557–60.
18. Miyata K, Nagamoto T, Maruoka S. . Efficacy and safety of the soft-shell technique in cases with a hard lens nucleus. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:1546–50.

19. Arshinoff SA, Jafari M. New classification of ophthalmic viscosurgical devices–2005. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:2167–71.

20. Oshika T, Bissen-Miyajima H, Fujita Y. . Prospective randomized comparison of Discovisc and Healon 5 in phacoemulsification and intraocular lens implantation. Eye (Lond). 2010; 24:1376–81.
21. Praveen MR, Vasavada AR, Koul A. . Subjective evaluation of intraoperative performance of DisCoVisc in complex ocular environments. Eye (Lond). 2010; 24:1391–5.

Go to : 
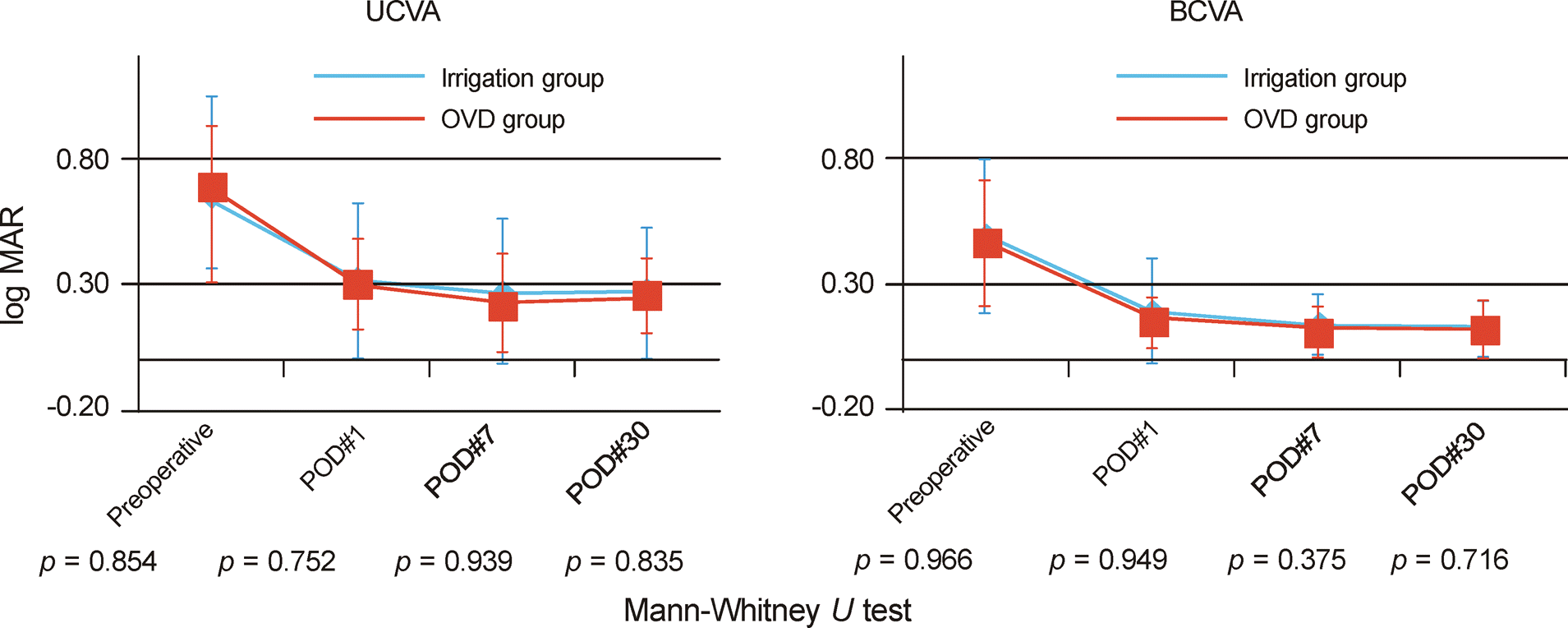 | Figure 1.Time course of visual acuity (log MAR) after cataract surgery. POD = postoperative day; UCVA = uncorrected visual acuity; BCVA = best corrected visual acuity; OVD = ophthalmic viscosurgical devices. |
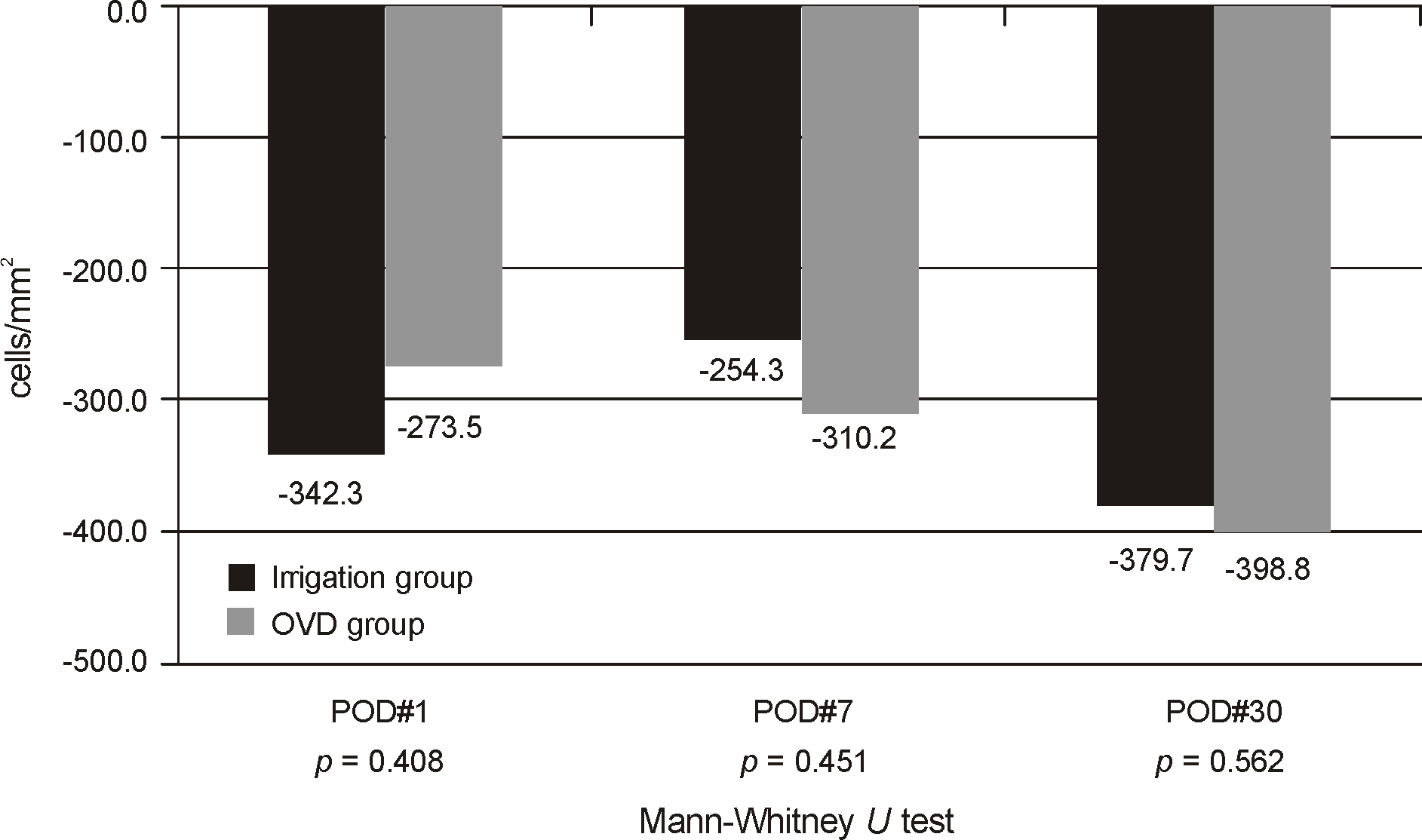 | Figure 2.Change in endothelial cell count after cataract surgery. POD = postoperative day; OVD = ophthalmic viscosurgical devices. |
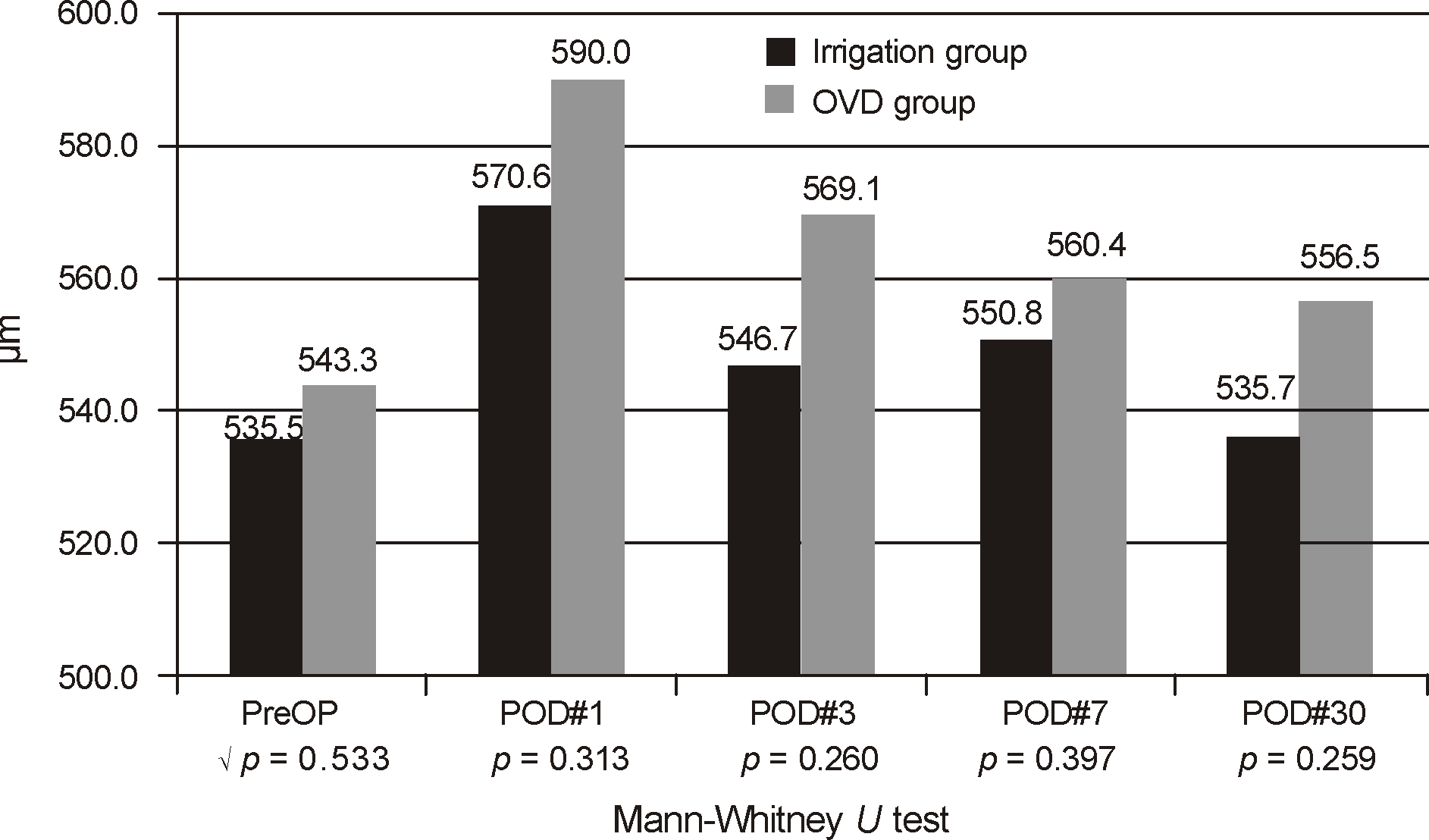 | Figure 3.Change in central corneal thickness after cataract surgery. POD = postoperative day; OVD = ophthalmic viscosurgical devices. |
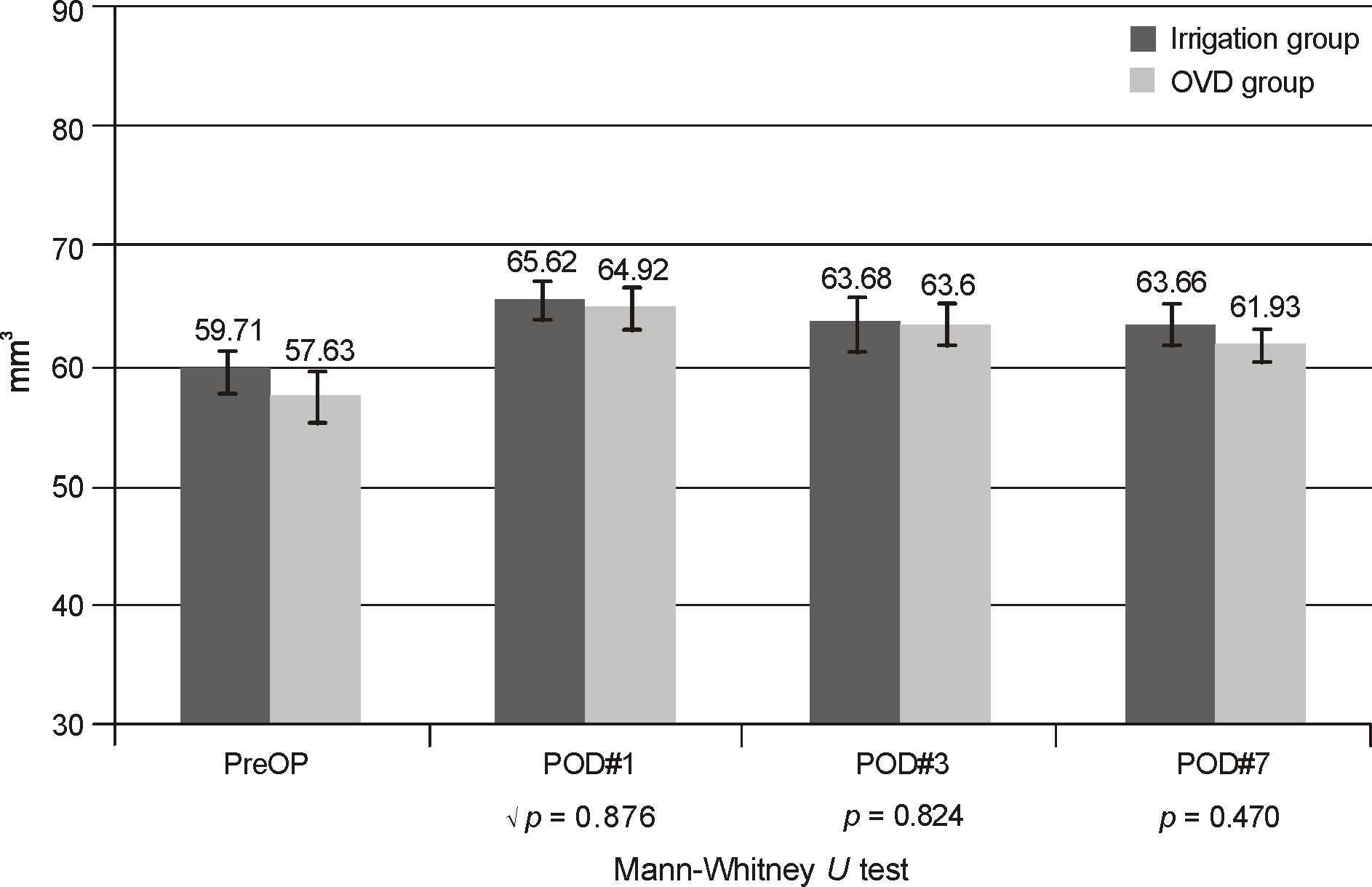 | Figure 4.Change of cornea Volume after cataract surgery. POD = postoperative day; OVD = ophthalmic viscosurgical devices. |
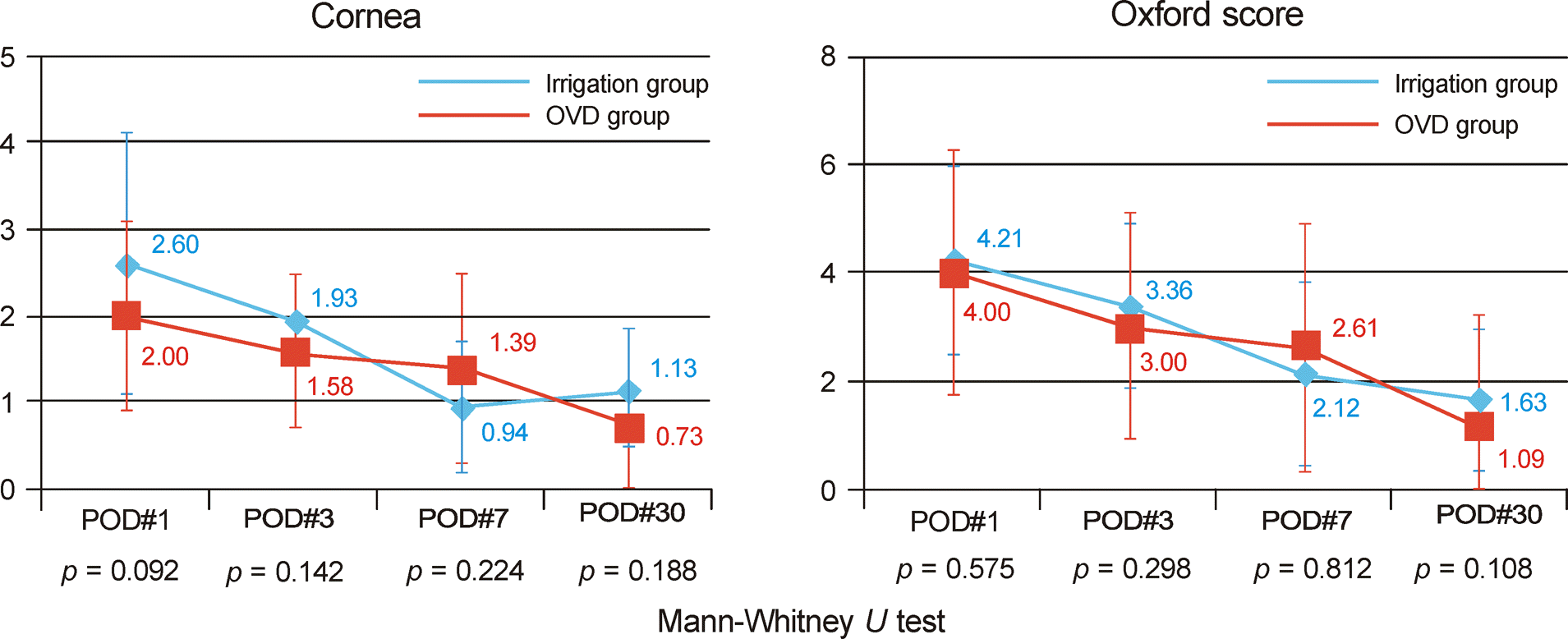 | Figure 5.Change in Oxford staining score after cataract surgery. POD = postoperative day; OVD = ophthalmicviscosurgical devices. |
Table 1.
Preoperative patient characteristis
| Irrigation | OVD | p-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 22 | 33 | ||
| Age (years) | 63.14 ± 12.8 | 67.33 ± 9.8 | 0.175* | |
| Sex (M:F) | 13 : 9 | 14 : 19 | 0.226‡ | |
| Lens grade | NO | 3.14 ± 0.77 | 3.39 ± 0.75 | 0.235† |
| NC | 3.09 ± 0.81 | 3.45 ± 0.83 | 0.201† | |
| C | 2.90 ± 1.45 | 2.75 ± 1.50 | 0.663† | |
| P | 1.85 ± 1.63 | 2.16 ± 2.02 | 0.671† | |
| UCVA (log MAR) | 0.648 ± 0.29 | 0.685 ± 0.37 | 0.854† | |
| BCVA (log MAR) | 0.490 ± 0.30 | 0.463 ± 0.25 | 0.966† | |
| CCT (μm) | 535.5 ± 21.0 | 543.3 ± 39.2 | 0.382* | |
| ECD (cell/mm2) | 2649 ± 444 | 2573 ± 346 | 0.446† | |
| Cornea volume (mm3) | 59.7 ± 5.1 | 57.6 ± 8.4 | 0.713† |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download