Abstract
Purpose
To report a case of bilateral macular holes in a patient with bilateral macular telangiectasia (Mac Tel).
Case summary
A 61-year-old male presented with decreased central vision in both eyes. His best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) was 0.8 in the right eye and 0.6 in the left eye. On fundoscopy, fluorescein angiography (FAG), and optical coher-ence tomography (OCT), he was diagnosed with Mac Tel type 2 combined with stage 1A of the right eye and stage 1B im-pending macular hole in the left eye. Two years and 8 months later, the BCVA of both eyes was unchanged. On fundo-scopy, FAG and OCT, there were no definitive changes in both eyes. The patient was observed without treatment.
Go to : 
References
1. Gass JD, Blodi BA. Idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasis. Update of classification and follow-up study. Ophthalmology. 1993; 100:1536–46.
2. Yannuzzi LA, Bardal AM, Freund KB. . Idiopathic macular telangiectasia. Arch Ophthalmol. 2006; 124:450–60.

3. Chang YI, Lee JG, Kim TW, Lee EK. The clinical manifestations and treatment of parafoveal telangiectasis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2004; 45:576–84.
4. Park YS, Sohn JH, Lim HW, Lee BR. Intravitreal bevacizumab in-jection in adult Coats’disease. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:630–4.
5. Ryu JW, Kim JR, Lee WK. A case of combination therapy for sub-retinal neovascularization in bilateral acquired parafoveal telangiectasis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1423–6.

6. Lee SW, Kim SM, Kim YT, Kang SW. Clinical features of idio-pathic juxtafoveal telangiectasis in Koreans. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2011; 25:225–30.

7. Moon BG, Kim YJ, Yoon YH, Lee JY. Use of intravitreal bev-acizumab injections to treat type 1 idiopathic macular telangiectasia. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012; 250:1697–9.

8. Patel B, Duvall J, Tullo AB. Lamellar macular hole associated with idiopathic juxtafoveolar telangiectasia. Br J Ophthalmol. 1988; 72:550–1.

9. Olson JL, Mandava N. Macular hole formation associated with idi-opathic parafoveal telangiectasia. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2006; 244:411–2.

10. Charbel Issa P, Scholl HP, Gaudric A. . Macular full-thickness and lamellar holes in association with type 2 idiopathic macular telangiectasia. Eye. 2009; 23:435–41.

11. Koizumi H, Slakter JS, Spaide RF. Full-thickness macular hole for-mation in idiopathic parafoveal telangiectasis. Retina. 2007; 27:473–6.

12. Rishi P, Kothari AR. Parafoveal telangiectasia (PFT) has been as-sociated with changes in macular architecture and macular holes (lamellar and full thickness). Retina. 2008; 28:184–5. author reply 185-6.
13. Gregori N, Flynn HW Jr. Surgery for full-thickness macular hole in patients with idiopathic macular telangiectasia type 2. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2010; 41(Online):1–4.

14. Shukla D. Evolution and management of macular hole secondary to type 2 idiopathic macular telangiectasia. Eye (Lond). 2011; 25:532–3.

15. Shukla D, Venkatesh R. Spontaneous closure of full-thickness macular hole in type 2 idiopathic macular telangiectasia. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012; 250:1711–2.

16. Gupta V, Gupta A, Dogra MR, Agarwal A. Optical coherence to-mography in group 2A idiopathic juxtafoveolar telangiectasis. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2005; 36:482–6.

17. Albini TA, Benz MS, Coffee RE. . Optical coherence tomog-raphy of idiopathic juxtafoveolar telangiectasia. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2006; 37:120–8.

18. Haouchine B, Massin P, Gaudric A. Foveal pseudocyst as the first step in macular hole formation: a prospective study by optical co-herence tomography. Ophthalmology. 2001; 108:15–22.
Go to : 
 | Figure 1.(A, B, C, D) Fundus photographs and red free photographs of both eyes showed mild grayish discoloration of the temporal to foveal area at the initial visit. Also, the corresponding area presents loss of retinal transparency of both eyes. |
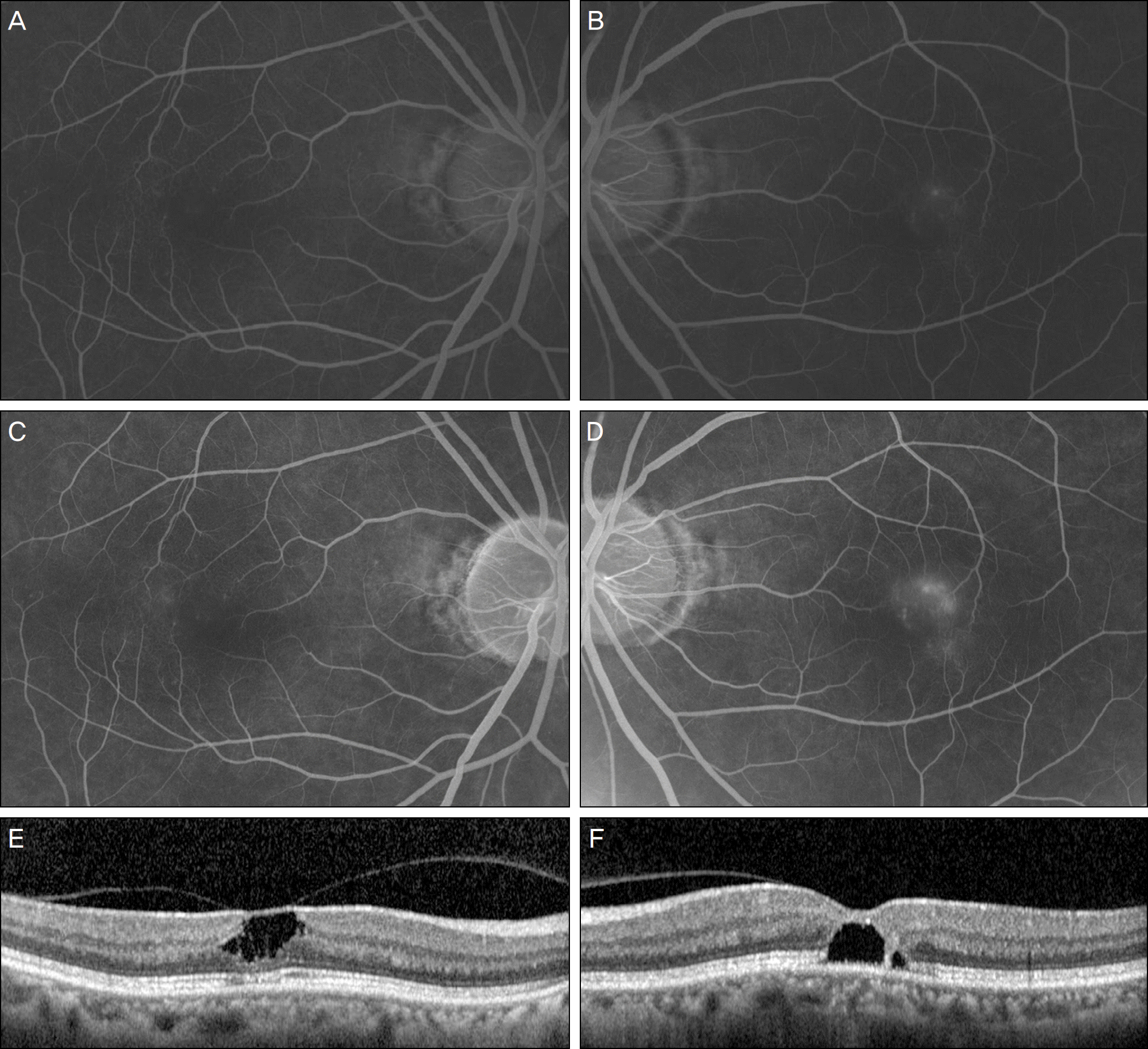 | Figure 2.(A, B) Early fluorescein angiography (FAG) of the right eye shows mild fluorescein stain of the capillary in the super-otemporal to the macula and FAG of the left eye shows telangiectatic changes in the superotemporal macula area at the initial visit. (C, D) Late FAG of both eyes show late leakage from the telangiectatic vessels at the initial visit. (E, F) Optical coherence tomo-graph (OCT) of the right eye reveals 1A impending macular hole and OCT of the left eye reveals stage 1B impending macular hole at initial visit. OCT horizontal scan through the fovea of the right eye shows that stage 1A macular hole was in fact characterized by an inner foveal cyst. The foveal floor is flat and the posterior hyaloid is still attached to the foveal center. The photoreceptor IS/OS (inner segment/outer segment) line may be intact but slightly depressed at the foveal center. OCT horizontal scan through the fovea of the left eye shows that stage 1B macular hole characterized by an foveal cyst is extending in the outer retina. There is a dis-ruption of the photoreceptor layer. The posterior hyaloid is still attached to the center of the fovea. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download