Abstract
Purpose
To identify the muscle weakening effect and the change of muscle tension according to degree of superior rectus Z-myotomy in rabbits.
Methods
After dissection of superior rectus in 15 rabbits (30 eyes), marking was done on 10 mm apart from muscle insertion. Then, Z-myotomy was done on 2 mm and 8 mm apart from muscle insertion which are two different positions on apposite sides. 25%, 50% and 75% Z-myotomy were defined as group 1 (10 eyes), group 2 (10 eyes) and group 3 (10 eyes). After Z-myotomy, the change of muscle lengthening between muscle insertion and marking, and muscle tension were measured. At 4 weeks after Z-myotomy, all parameters were re-measured.
Results
After Z-myotomy all markings moved posteriorly, and showed result as 10.83 ± 0.13 mm in group 1, 11.02 ± 0.17 mm in group 2 and 12.01 ± 0.23 mm in group 3 respectively. Muscle tension result showed as 3.98 ± 0.22 mm in group 1, 3.54 ± 0.18 mm in group 2 and 2.87 ± 0.25 mm in group 3. In comparison of three groups, group 2 and group 3 showed the significant results ( p < 0.05). At 4 weeks after Z-myotomy the markings showed result as 10.55 ± 0.14 mm, 10.85 ± 0.20 mm, 11.91 ± 0.14 mm respectively, and in group 2 and group 3 the significant changes were seen ( p < 0.05). Muscle ten-sions were 4.01 ± 0.31 mm, 3.88 ± 0.53 mm, 3.12 ± 0.42 mm respectively. There were significant results in group 2 and group 3 ( p < 0.05).
References
1. Almeida HC, Alvares MA. Split lengthening of the inferior oblique muscles. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1988; 226:181–2.

2. Toosi SH, von Noorden GK. Effect of isolated inferior oblique muscle myectomy in the management of superior oblique muscle palsy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1979; 88(3 Pt 2):602–8.

3. von Noorden GK. Binocular Vision and Ocular Motility: theory and management of strabismus, 5th ed. St. Louis: Mosby;1996. p. 535.
4. Mellott ML, Scott WE, Ganser GL, Keech RV. Marginal myotomy of the minimally overacting inferior oblique muscle in asymmetric bilateral superior oblique palsies. J AAPOS. 2002; 6:216–20.

5. Lee SY, Cho HK, Kim HK, Lee YC. The effect of inferior oblique muscle Z-myotomy in patients with inferior oblique overaction. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2010; 47:366–72.
6. Helveston EM. Atlas of strabismus surgery, 3rd ed. St. Louis:: CV Mosby;1985. p. 254–9.
8. Helveston EM, Cofield DD. Indications for marginal myotomy and technique. Am J Ophthalmol. 1970; 70:574–8.

9. von Noorden GK. Binocular Vision and Ocular Motility: theory and management of strabismus, 6th ed. St. Louis: Mosby;2002. p. 101–7.
Figure 1.
Photographs of superior rectus according to the degree of Z-myotomy. (A) 25% Z-myotomy of muscle width. (B) 50% Z-myotomy of muscle width. (C) 75% Z-myotomy of muscle width.
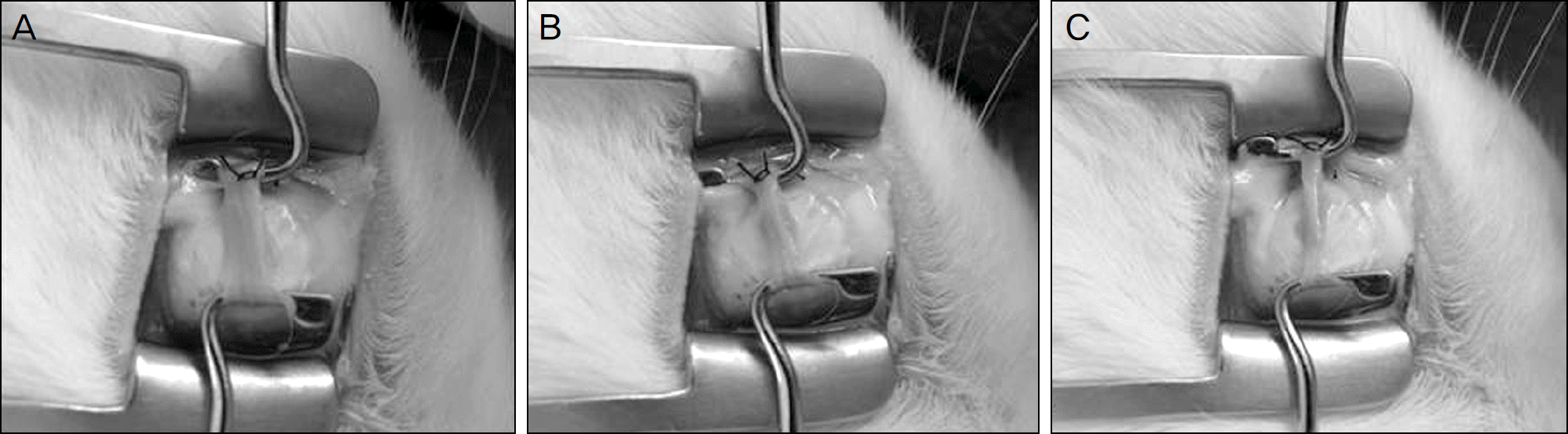
Figure 2.
Histologic findings of Z-myotomy site (75% Z-my-otomy of muscle width) at 4 weeks after surgery (Masson’s tri-chrome stain). Distorted muscle structures and collagen fiber proliferations (arrows) between muscle fibers were shown.
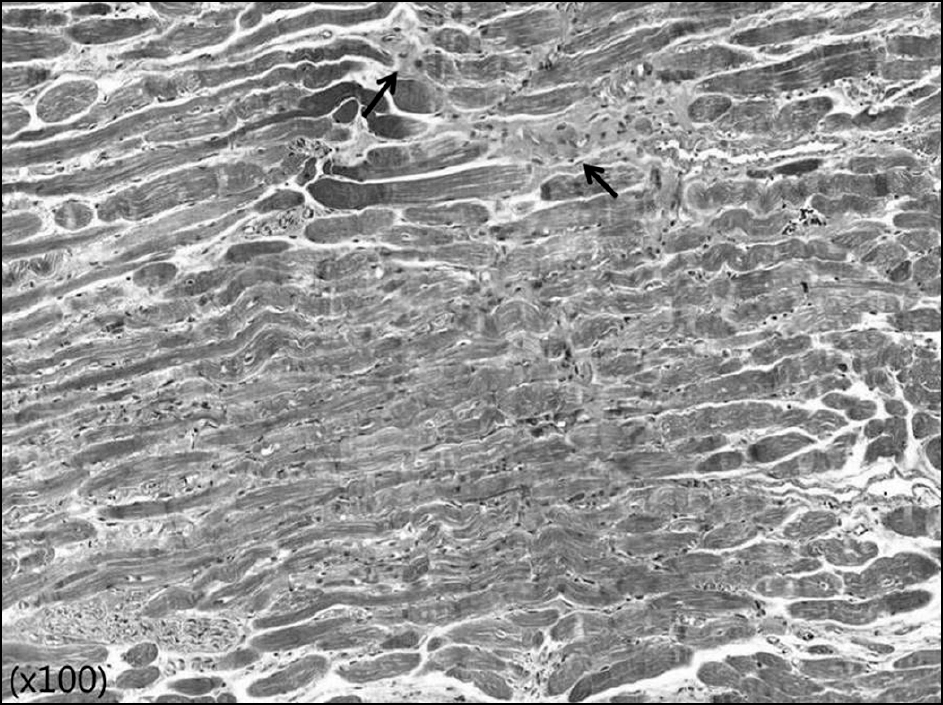
Table 1.
The location of mark on superior rectus muscle before and after Z-myotomy (initial position of mark is on 10.0 mm from muscle insertion site)
| Before Myotomy (A) | After Z-myotomy | * p-value (A-C) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immediately (B) | * p-value (A-B) | 4 weeks after (C) | |||
| Group 1† | 10 mm | 10.83 ± 0.13 mm | >0.05 | 10.55 ± 0.14 mm | >0.05 |
| Group 2‡ | 10 mm | 11.02 ± 0.17 mm | <0.05 | 10.85 ± 0.20 mm | <0.05 |
| Group 3§ | 10 mm | 12.01 ± 0.23 mm | <0.05 | 11.91 ± 0.14 mm | <0.05 |
| Comparison between groups (Π p-value) | <0.05 | <0.05 | |||
Table 2.
The change of the eyeball position after traction with 50 g tension to opposite direction of muscular action
| Before Myotomy (A) | After Z-myotomy | * p-value (A-C) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immediately (B) | * p-value (A-B) | 4 weeks after (C)* | |||
| Group 1† | 4.32 ± 0.21 mm | 3.98 ± 0.22 mm | >0.05 | 4.01 ± 0.31 mm | >0.05 |
| Group 2‡ | 4.36 ± 0.22 mm | 3.54 ± 0.18 mm | <0.05 | 3.88 ± 0.53 mm | <0.05 |
| Group 3§ | 4.30 ± 0.21 mm | 2.87 ± 0.25 mm | <0.05 | 3.12 ± 0.42 mm | <0.05 |
| Comparison between groups (Π p-value) | >0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | ||




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download