Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the changes of anterior chamber depth (ACD), Axial length (AXL) after combined vitrectomy and cat-aract surgery and to analyze the association with refractive errors.
Methods
In 22 eyes who underwent combined vitrectomy and cataract surgery (PPV-Phaco group), 20 eyes who under-went vitrectomy-only (PPV-only group) and 28 eyes who underwent uncomplicated cataract surgery (Phaco-only group), ACD and AXL were measured with IOL master (Carl Zeiss Jena, Germany) preoperatively and 3 months postoperatively. We compared the preoperative desired refraction and postoperative 3 months refraction.
Results
ACD were increased in PPV-Phaco group and Phaco-only group (all, p < 0.001) and this change was more prom-inent in PPV-Phaco group ( p = 0.030). In PPV only group, ACD was decreased ( p < 0.001). The AXL after surgery was not significant different from the preoperative AXL in PPV-Phaco and PPV only groups ( p = 0.612, p = 0.090). But the AXL was decreased in Phaco-only group ( p = 0.022). Hyperopic shifting were noticed in PPV-Phaco and phaco-only groups, but my-opic shifting was noticed in PPV-only group. However, these changes were not statistically significant ( p = 0.292, p = 0.251, p = 0.068).
Go to : 
References
1. McElvanney AM, Talbot EM. Posterior chamber lens implantation combined with pars plana vitrectomy. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1997; 23:106–10.

2. Koenig SB, Han DP, Mieler WF, et al. Combined phacoemulsifica-tion and pars plana vitrectomy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1990; 108:362–4.

3. Smiddy WE, Mady M, Anagnoste S. Acrylic intraocular lens placement in conjunction with pars plana vitrectomy. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001; 131:748–50.

4. Scharwey K, Pavlovic S, Jacobi KW. Combined clear corneal phacoemulsification, vitreoretinal surgery, and intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1999; 25:693–8.

5. Chen WL, Yang CM, Chen YF, et al. Ciliary detachment after pars plana vitrectomy: an ultrasound biomicroscopic study. Retina. 2002; 22:53–8.
6. Hikichi T, Ohnishi M, Hasegawa T. Transient shallow anterior chamber induced by supraciliary fluid after vitreous surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 1997; 124:696–8.

7. Minamoto A, Nakano KE, Tanimoto S, et al. Ultrasound biomicro-scopy in the diagnosis of persistent hypotony after vitrectomy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1997; 123:711–3.

8. Shioya M, Ogino N, Shinjo U. Change in postoperative refractive error when vitrectomy is added to intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1997; 23:1217–20.

9. Kovács I, Ferencz M, Nemes J, et al. Intraocular lens power calcu-lation for combined cataract surgery, vitrectomy and peeling of epi-retinal membranes for macular oedema. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2007; 85:88–91.

10. Falkner-Radler CI, Benesch T, Binder S. Accuracy of preoperative biometry in vitrectomy combined with cataract surgery for patients with epiretinal membranes and macular holes: results of a pro-spective controlled clinical trial. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:1754–60.
11. Kim DH, Kim SK, Koh HJ, Kwon OW. Postoperative refractive er-ror in combined operation of vitrectomy and intraocular lens implantation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002; 43:1644–8.
12. Jeoung JW, Chung H, Yu HG. Factors influencing refractive out-comes after combined phacoemulsification and pars plana vi-trectomy: results of a prospective study. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:108–14.
13. Lee DK, Lee SJ, You YS. Prediction of refractive error in com-bined vitrectomy and cataract surgery with one-piece acrylic intra-ocular lens. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2008; 22:214–9.

14. Chung TY, Chung H, Lee JH. Combined surgery and sequential surgery comprising phacoemulsification, pars plana vitrectomy, and intraocular lens implantation: comparison of clinical outcomes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:2001–5.
15. Lam DS, Young AL, Rao SK, et al. Combined phacoemulsifica-tion, pars plana vitrectomy, and foldable intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:1064–9.

16. Heiligenhaus A, Holtkamp A, Koch J, et al. Combined phacoe-mulsification and pars plana vitrectomy: clear corneal versus scler-al incisions: prospective randomized multicenter study. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:1106–12.
17. Gu BY, Sagong M, Chang WH. Phacovitrectomy versus vi-trectomy only for primary rhegmatogenous retinal detachment repair. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2011; 52:537–43.

18. Patel D, Rahman R, Kumarasamy M. Accuracy of intraocular lens power estimation in eyes having phacovitrectomy for macular holes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:1760–2.

19. Manvikar SR, Allen D, Steel DH. Optical biometry in combined phacovitrectomy. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:64–9.

20. Kunavisarut P, Poopattanakul P, Intarated C, Pathanapitoon K. Accuracy and reliability of IOL master and A-scan immersion bio-metry in silicone oil-filled eyes. Eye (Lond). 2012; 26:1344–8.

21. Arai M, Ohzuno I, Zako M. Anterior chamber depth after posterior chamber intraocular lens implantation. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh). 1994; 72:694–7.

22. Olsen T. Sources of error in intraocular lens power calculation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1992; 18:125–9.

23. Suzuki Y, Sakuraba T, Mizutani H, et al. Postoperative refractive error after simultaneous vitrectomy and cataract surgery. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 2000; 31:271–5.

24. Díaz Lacalle V, Orbegozo Gárate FJ, Martinez Alday N, et al. Phacoemulsification cataract surgery in vitrectomized eyes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1998; 24:806–9.
25. McDermott ML, Puklin JE, Abrams GW, Eliott D. Phacoemulsi- fication for cataract following pars plana vitrectomy. Ophthalmic Surg Lase. 1997; 28:558–64.
26. Yu AY, Lin ZD, Chen XQ, et al. Position of myopic iris-claw phak-ic intraocular lens by Scheimpflug photography and ultrasound biomicroscopy. Eye (Lond). 2008; 22:233–9.

27. Nishigaki S, Kida Y, Uchida H. Refractive changes after triple pro-cedure for diabetic macular edema. Jpn J Clin Ophthalmol. 1998; 52:1135–7.
Go to : 
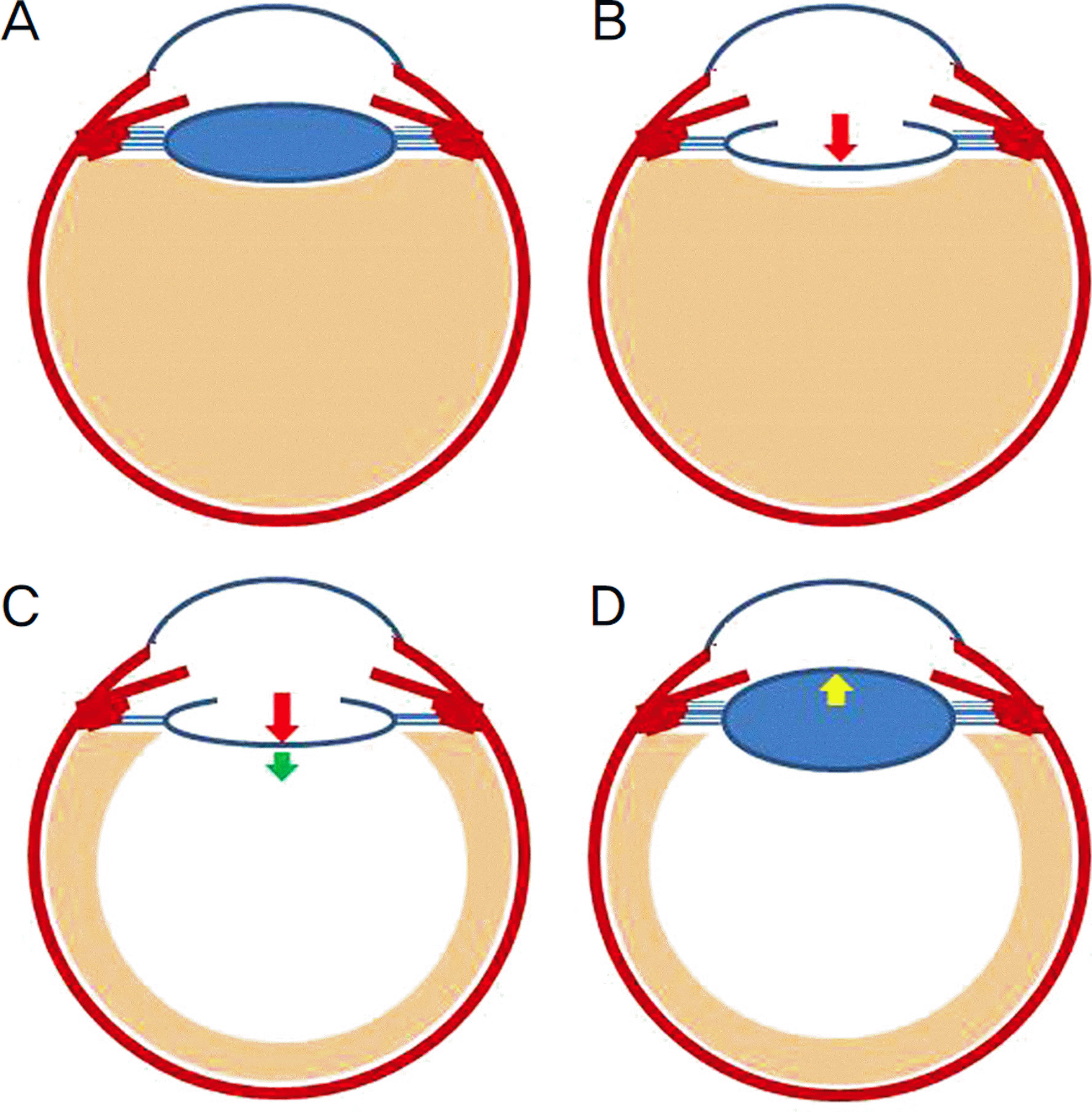 | Figure 1.(A) A diagram representing a normal anatomy of the eye. (B) After phacoemulsification, anterior chamber depth deepening effect caused by IOL replacement. (C) After com-bined vitrectomy, anterior chamber depth deepening by IOL replacement and decrease positive vitreous pressure. (D) After vitrectomy, decrease of adherence between zonule and vitre-ous makes zonule loose. Lens moves toward anterior chamber. |
Table 1.
Clinical features of enrolled pati ents
| Parameter | Group | p-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPV-Phaco (n = 22) | PPV-only (n = 20) | Phaco-only (n = 28) | ||
| Age (year) | 62.54 ± 9.74 | 49.14 ± 12.67 | 66.21 ± 10.87 | <0.001* |
| Gender (Male, %) | 45.5% | 60% | 25% | 0.129 |
| Indication (n) | ||||
| Vitreous hemorrhage (PDR) | 12 | 10 | ||
| Vitreous opacity (uveitis) | 2 | 2 | ||
| Epiretinal membrane | 8 | 7 | ||
| Terson’s syndrome | 1 |
Table 2.
Comparison of changes in anterior chamber depth and axial length following PPV-Phaco, vitrectomy-only and Phacoemulsification-only
| Parameter | Group | p-value† | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPV-Phaco (n = 22) | PPV-only (n = 20) | Phaco-only (n = 28) | |||
| ACD (mm) | |||||
| Preoperative | 3.08 ± 0.40 | 3.30 ± 0.47 | 3.10 ± 0.38 | 0.113 | |
| Postoperative | 4.64 ± 0.63 | 3.23 ± 0.46 | 3.99 ± 0.73 | <0.001‡ | |
| Changes | 1.56 ± 0.72 | -0.07 ± 0.07 | 0.88 ± 0.61 | <0.001§ | |
| p-value* | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| AXL (mm) | |||||
| Preoperative | 23.05 ± 0.84 | 23.27 ± 1.14 | 23.88 ± 2.00 | 0.466 | |
| Postoperative | 23.02 ± 0.85 | 23.38 ± 1.11 | 23.77 ± 2.02 | 0.398 | |
| Changes | -0.03 ± 0.27 | 0.11 ± 0.29 | -0.11 ± 0.24 | <0.001Π | |
| p-value* | 0.612 | 0.090 | 0.022 | ||
| Refraction | |||||
| Target (preoperative) | -0.44 ± 0.40 | (-0.46 ± 0.35) | -0.76 ± 0.84 | 0.493 | |
| Postoperative | -0.37 ± 0.34 | -0.64 ± 0.43 | -0.70 ± 0.82 | 0.159 | |
| Changes | 0.07 ± 0.31 | -0.19 ± 0.45 | 0.06 ± 0.27 | 0.032# | |
| p-value* | 0.292 | 0.068 | 0.251 |
Values are presented as mean ± SD. PPV = pars plana vitrectomy; Phaco = phacoemulsification and intraocular lens implantation; ACD = anterior chamber depth; AXL = axial length.
‡ PPV-only VS Phaco-only : p = 0.001, PPV-only VS PPV-Phaco: p < 0.001, PPV-Phaco vs Phaco-only: p = 0.030
§ PPV-only VS Phaco-only : p < 0.001, PPV-only VS PPV-Phaco: p < 0.001, PPV-Phaco vs Phaco-only: p = 0.001
Table 3.
Distributions of refractive errors after combined vitrectomy and cataract surgery
| Parameter | Refractive prediction error (D)* | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| -1.0 to -0.5 | -0.5 to 0.5 | 0.5 to 1.0 | |
| Combined vitrectomy (%) | 13.6 | 68.2 | 18.2 |
| Cataract surgery (%) | 14.3 | 71.4 | 14.3 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download