Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the clinical efficacy of blepharotomy to treat upper eyelid retraction associated with thyroid eye disease.
Methods
A retrospective survey was performed with 9 eyes of 7 thyroid ophthalmopathy patients, who visited Korea University Medical Center from August 2009 to February 2011, and had undergone blepharotomy. The sex, age, change of upper eyelid retraction, postoperative complication, follow-up periods, and the surgical results were reviewed. To assess the efficacy of blepharotomy more objectively, the preoperative and postoperative pictures of patients were taken and the following lid parameters measured: marginal reflex distance 1, interpalpebral fissure height, total palpebral fissure area, upper nasal palpebral fissure area, and upper temporal palpebral fissure area.
Results
The mean age of patients was 37.4 years and mean follow-up period was 12.8 months. Five patients had undergone surgery unilaterally and 2 patients, bilaterally. Seven eyes of 6 patients had undergone full thickness blepharotomy and 2 eyes of 1 patient had undergone graded blepharotomy. According to the 3-month preoperative and postoperative picture analysis, all lid parameters improved significantly after blepharotomy (2.03 mm, 1.95 mm, 24.28 mm2, 12.98 mm2, and 16.21 mm2, respectively). Complications associated with blepharotomy included multiple and high folds in 2 eyes of 2 patients who had undergone full thickness blepharotomy. Re-operation was performed on only 1 eye and the result was satisfactory.
Figures and Tables
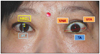 | Figure 1Pre and postoperative five lid parameters were measured by image J program. Marginal reflex distance 1 (MRD1, distance from the upper lid margin to the center of the pupil), interpalpebral fissure height (IPF, widest distance between the upper and lower lid margins), and total palpebral fissure area (TA) were measured. For defining the upper nasal area (UNA) and upper temporal area (UTA), a straight line connecting the medial and lateral canthi was drawn, and a perpendicular line passing through the center of the intercanthal line was drawn. |
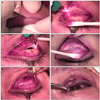 | Figure 2Intraoperative steps of blepharotomy in a patient with upper eyelid retraction. (A) Skin incision in the marked crease. (B) Meticulous dissection of orbital septum using a Desmarres retractor. (C) Transsection of levator complex and conjunctiva in the lateral third of the upper lid. (D) Upper eyelid after medial and lateral horizontal blepharotomy. (E) Dissection of the lateral horn. (F) Skin closure after tarsal fixation of subcutaneous tissue and skin. |
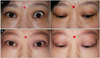 | Figure 3Improvement of left upper lid retraction after blepharotomy in a patient with thyroid eye disease. (A) Before blepharotomy. (B) After blepharotomy. |
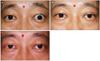 | Figure 4A patient with multiple high folds after blepharotomy. High folds was corrected successfully after re-operation. (A) Before blepharotomy. (B) After blepharotomy. (C) After re-operation for high fold. |
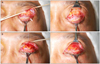 | Figure 5Re-operation procedure for multiple high folds after blepharotomy. (A) Release of scar tissue between orbicularis oculi muscle and septum and levator aponeurosis; arrow indicates the scar tissue. (B) Pull down preaponeurotic fat to suture upper tarsal plate. |
References
1. Bartley GB. The epidemiologic characteristics and clinical course of ophthalmopathy associated with autoimmune thyroid disease in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1994. 92:477–588.
2. Frueh BR, Musch DC, Garber FW. Lid retraction and levator aponeurosis defects in Graves' eye disease. Ophthalmic Surg. 1986. 17:216–220.
3. Chee E, Chee SP. Subconjunctival injection of triamcinolone in the treatment of lid retraction of patients with thyroid eye disease: a case series. Eye (Lond). 2008. 22:311–315.
4. Mancini R, Khadavi NM, Goldberg RA. Nonsurgical management of upper eyelid margin asymmetry using hyaluronic acid gel filler. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011. 27:1–3.
5. Ebner R. Botulinum toxin type A in upper lid retraction of Graves' ophthalmopathy. J Clin Neuroophthalmol. 1993. 13:258–261.
6. Putterman AM. Surgical treatment of thyroid-related upper eyelid retraction. Graded Müller's muscle excision and levator recession. Ophthalmology. 1981. 88:507–512.
7. Ceisler EJ, Bilyk JR, Rubin PA, et al. Results of Müllerotomy and levator aponeurosis transposition for the correction of upper eyelid retraction in Graves disease. Ophthalmology. 1995. 102:483–492.
8. Elner VM, Hassan AS, Frueh BR. Graded full-thickness anterior blepharotomy for upper eyelid retraction. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 2003. 101:67–73.
9. Elner VM, Hassan AS, Frueh BR. Graded full-thickness anterior blepharotomy for upper eyelid retraction. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004. 122:55–60.
10. Cruz AA, Coelho RP, Baccega A, et al. Digital image processing measurement of the upper eyelid contour in Graves disease and congenital blepharoptosis. Ophthalmology. 1998. 105:913–918.
11. Flynn TH, Rose GE, Shah-Desai SD. Digital image analysis to characterize the upper lid marginal peak after levator aponeurosis repair. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011. 27:12–14.
12. Hintschich C, Haritoglou C. Full thickness eyelid transsection (blepharotomy) for upper eyelid lengthening in lid retraction associated with Graves' disease. Br J Ophthalmol. 2005. 89:413–416.
13. Song WS, Kim YH, Lee SJ. Morphologic study of upper eyelid contour and functional evaluation of levator palpebrae superioris muscle in adult and young people. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2001. 42:1523–1529.
14. Lyons CJ, Rootman J. Orbital decompression for disfiguring exophthalmos in thyroid orbitopathy. Ophthalmology. 1994. 101:223–230.
15. Fatourechi V, Bergstralh EJ, Garrity JA, et al. Predictors of response to transantral orbital decompression in severe Graves' ophthalmopathy. Mayo Clin Proc. 1994. 69:841–848.
16. Henderson JW. A surgical procedure for retraction of eyelids in endocrine exophthalmos (a moving picture). Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1965. 63:70–74.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download