Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the clinical manifestations, management, and ophthalmologic complications of orbital roof fractures and zygoma fractures.
Methods
A retrospective survey of 119 patients who visited Korea University Medical Center from June 2009 to June 2010 was performed. The sex, age, causes, fracture characteristics, neurologic injury, ocular injury, and combined facial bone fractures of patients who were diagnosed with orbital roof fracture and zygoma fracture were statistically analyzed.
Results
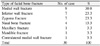
The mean age of patients with orbital roof fracture was 33.0 years old. The most common cause of orbital roof fracture was traffic accident (36.1%) with 6 patients receiveing surgical treatement (9.8%). Among the ophthalmologic diagnoses of the patients with orbital roof fracture, traumatic iridocyclitis was the most common (7 eyes) followed by eyeball rupture (2 eyes). The mean age of patients with zygoma fracture was 36.6 years old. The most common cause of zygoma fracture was traffic accident (32.8%), with 51 patients receiving surgical treatement (87.9%). Among the ophthalmologic diagnoses of the patients with zygoma fracture, traumatic iridocyclitis was the most common (6 eyes), followed by commotio retina (4 eyes).
Figures and Tables
References
1. Fulcher TP, Sullivan TJ. Orbital roof fractures: management of ophthalmic complications. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003. 19:359–363.
2. Rinna C, Rocchi G, Ventucci E, et al. Bilateral orbital roof fracture. J Craniofac Surg. 2009. 20:737–742.
3. Piotrowski WP, Beck-Mannagetta J. Surgical techniques in orbital roof fractures: early treatment and results. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 1995. 23:6–11.
4. Guly CM, Guly HR, Bouamra O, et al. Ocular injuries in patients with major trauma. Emerg Med J. 2006. 23:915–917.
5. Haug RH, Van Sickels JE, Jenkins WS. Demographics and treatment options for orbital roof fractures. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002. 93:238–246.
6. Obuekwe O, Owotade F, Osaiyuwu O. Etiology and pattern of zygomatic complex fractures: a retrospective study. J Natl Med Assoc. 2005. 97:992–996.
7. Haug RH. Management of the trochlea of the superior oblique muscle in the repair of orbital roof trauma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000. 58:602–606.
8. Trivellato PF, Arnez MF, Sverzut CE, Trivellato AE. A retrospective study of zygomatico-orbital complex and/or zygomatic arch fractures over a 71-month period. Dent Traumatol. 2011. 27:135–142.
9. Calderoni DR, Guidi Mde C, Kharmandayan P, Nunes PH. Seven-year institutional experience in the surgical treatment of orbito-zygomatic fractures. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2011. 39:593–599.
10. Bae YC, Lee J, Kim JH, Jeong SH. A clinical study of fracture of the zygomatic bone. J Korean Soc Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997. 24:86–99.
11. Evans BG, Evans GR. MOC-PSSM CME article: Zygomatic fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008. 121:1 Suppl. 1–11.
12. Kelley P, Hopper R, Gruss J. Evaluation and treatment of zygomatic fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007. 120:7 Suppl 2. 5S–15S.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print







 XML Download
XML Download