Abstract
Purpose
To determine retrospectively if a simultaneous frontalis suspension could change the result of undercorrection observed during levator resection in congenital ptosis patients with poor levator functions.
Methods
Eight eyes in the present study were from 5 infants, 4 infants had congenital ptosis and 1 infant had blepharophimosis. The average age was 3.3 years (range: 1.5 to 6.9 years). If the upper lid margin was not positioned on the superior limbus after performing levator resection under general anesthesia, the height of the upper lid margin was controlled by simultaneous frontalis suspension.
Results
The average follow-up period was 29.8 months. After surgery on both eyes, all 8 cases showed good results and sudden relapse did not occur. Exposed corneal erosion was observed in 6 eyes, but with artificial tears, eye drops, and ointment there were significant improvements within 1 month in all cases. At final examinations, 6 out of 8 eyes showed excellent or good results; undercorrection in 2 eyes was observed and the lateral portion of ptosis in 1 eye was observed as an eye complication.
Figures and Tables
Figure 1
The procedure of the simultaneous levator resection and frontalis suspension for congenital ptosis. The procedure was performed from A to H. The upper lid margin was positioned to superior limbus level.
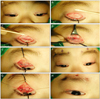
Figure 2
Photograph show excellent results in both eyes after performing our procedure for congenital ptosis. (A) Preoperative photograph. (B) Intraoperative photograph after the last procedure. (C) Postoperative photograph after 13 months.

References
1. Wilson ME, Johnson RW. Congenital ptosis. Long-term results of treatment using lyophilized fascia lata for frontalis suspensions. Ophthalmology. 1991. 98:1234–1237.
2. Leone CR Jr, Rylander G. A modified silicone frontalis sling for the correction of blepharoptosis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1978. 85:802–805.
3. Crawford JS. Recent trends in ptosis surgery. Ann Ophthalmol. 1975. 7:1263–1267.
4. Oh JY, Kim C, Chung HK, Khwarg SI. Frontalis sling operation using silicone rod in congenital blepharoptosis patients. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005. 46:573–580.
5. Korean Society of Ophthalmic Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. Ophthalmic Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2009. 2nd ed. Seoul: Naewae Haksool;128–145.
6. Mauriello JA, Wagner RS, Caputo AR, et al. Treatment of congenital ptosis by maximal levator resection. Ophthalmology. 1986. 93:466–469.
7. Lee UK, Chung WS. The effect of external levator resection in blepharoptosis with poor levator function. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1998. 39:1062–1068.
8. Leibsohn JM. Whitnall's ligament eyelid suspension for severe blepharoptosis. Ophthalmic Surg. 1987. 18:286–287.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download