Abstract
Purpose
To formulate an equation to estimate corneal spherical aberration using Orbscan (Bausch & Lomb Surgical, Rochester, NY, USA) parameters.
Methods
The study was carried out retrospectively. The participants were 76 eyes of 76 senile cataract patients with the mean age of 57.37 ± 17.63 years. Both Orbscan and KR-1W (Topcon Corp, Tokyo, Japan) were taken as preoperative examinations. Correlation analysis between various parameters from Orbscan and corneal spherical aberrations for a 6 mm pupil by KR-1W was performed. And multivariable linear regression was performed with the significantly correlated Orbscan parameters from the correlation analysis.
Results
The mean corneal spherical aberration from KR-1W system was 0.25 ± 0.08 µm. As a result of the multivariable linear regression, we could generate following equations. If the Q-value was available, estimated corneal spherical aberration = 0.389 × Q-value + (0.022 × Axial power 3 mm) - 0.633 (R2 = 0.436). If the Q-value was not available, estimated corneal spherical aberration = 0.184 × (Mean power 5 mm - Mean power 3 mm) + (0.02 × Axial power 3 mm) - 0.563 (R2 = 0.429). By using the equations, 93.4-94.7% of subjects were in the error range of 0.10 µm.
Figures and Tables
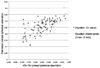 | Figure 1The scatter plot comparing the estimated corneal spherical aberrations with the corneal spherical aberrations measured by KR-1W. |
References
1. Trueb PR, Albach C, Montés-Micó R, Ferrer-Blasco T. Visual acuity and contrast sensitivity in eyes implanted with aspheric and spherical intraocular lenses. Ophthalmology. 2009. 116:890–895.
2. Pepose JS, Qazi MA, Edwards KH, et al. Comparison of contrast sensitivity, depth of field and ocular wavefront aberrations in eyes with an IOL with zero versus positive spherical aberration. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2009. 247:965–973.
3. Kim HS, Kim SW, Ha BJ, et al. Ocular aberrations and contrast sensitivity in eyes implanted with aspheric and spherical intraocular lenses. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008. 49:1256–1262.
4. Caporossi A, Martone G, Casprini F, Rapisarda L. Prospective randomized study of clinical performance of 3 aspheric and 2 spherical intraocular lenses in 250 eyes. J Refract Surg. 2007. 23:639–648.
5. Rocha KM, Soriano ES, Chalita MR, et al. Wavefront analysis and contrast sensitivity of aspheric and spherical intraocular lenses: a randomized prospective study. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006. 142:750–756.
6. Beiko GH, Haigis W, Steinmueller A. Distribution of corneal spherical aberration in a comprehensive ophthalmology practice and whether keratometry can predict aberration values. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007. 33:848–858.
7. Shimozono M, Uemura A, Hirami Y, et al. Corneal spherical aberration of eyes with cataract in a Japanese population. J Refract Surg. 2010. 26:457–459.
8. Chantra S, Pachimkul P, Naripthaphan P. Wavefront and ocular spherical aberration after implantation of different types of aspheric intraocular lenses based on corneal spherical aberration. J Med Assoc Thai. 2011. 94:Suppl 2. S71–S75.
9. Packer M, Fine IH, Hoffman RS. Aspheric intraocular lens selection based on corneal wavefront. J Refract Surg. 2009. 25:12–20.
10. Wang L, Koch DD. Age-related changes in corneal and ocular higher-order aberrations. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004. 138:897. author reply 897.
11. Athaide HV, Campos M, Costa C. Study of ocular aberrations with age. Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2009. 72:617–621.
12. Lim TH, Lee JR, Choi KY, Cho BJ. Anterior and posterior corneal spherical aberration measured with pentacam in the Korean. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010. 51:816–821.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download