Abstract
Purpose
To determine the extent of vertical rectus muscle correction in hypertropia showing good prognosis.
Methods
A retrospective study was performed with a total of 16 patients who underwent superior or inferior rectus muscle recession surgery with a follow-up of more than 6 months. Vertical muscle recession of 1 mm per 2.5 to 3.0 prism diopters was performed according to the surgeon's discretion.
Results
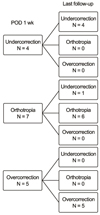
At 1 week after surgical correction, undercorrection, orthophoria, and overcorrection was observed in 4, 7 and 5 cases, respectively. At the final examination, ocular deviation was decreased in the undercorrected cases and maintained orthophoric except in 1 case where only a small amount of deviation recurred. However, in the cases of postoperative overcorrectionn, ocular deviation increased; 2 cases required surgical correction for consecutive hypertropia.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Jampolsky A. Strabismus reoperation techniques. Trans Sect Ophthalmol Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1975. 79:704–717.
2. Wisnicki HJ, Repka MX, Guyton DL. Reoperation rate in adjustable strabismus surgery. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1988. 25:112–114.
3. Franklin SR, Hiatt RL. Adjustable sutures in strabismus surgery. Ann Ophthalmol. 1989. 21:285–289.
4. Kenneth WW, Laurie EC, Monte AD, et al. Color Atlas of Ophthalmic Surgery: Strabismus. 1991. 1st ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott;241–242.
5. Pratt-Johnson JA, Tilson G. Management of Strabismus and Amblyopia : A Practical Guide. 1994. 1st ed. New York: Thieme Medical Publishers;211.
6. Sprunger DT, Helveston EM. Progressive overcorrection after inferior rectus recession. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1993. 30:145–148.
7. Lueder GT, Scott WE, Kutschke PJ, Keech RV. Long-term results of adjustable suture surgery for strabismus secondary to thyroid ophthalmopathy. Ophthalmology. 1992. 99:993–997.
8. Scotcher SM, O'Flynn EA, Morris RJ. Inferior rectus recession--an effective procedure? Br J Ophthalmol. 1997. 81:1031–1036.
9. Keech RV, Scott WE, Christensen LE. Adjustable suture strabismus surgery. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1987. 24:97–102.
10. Lorenz B, Raab I, Boergen KP. Dissociated vertical deviation: What is the most effective surgical approach? J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1992. 29:21–29.
11. Cho IO, Lee SY. The surgical correction of vertical deviation after superior rectus muscle recession in patients with hypertropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005. 46:688–692.
12. Von Noorden GK. Binocular Vision & Ocular Motility : Theory and Management of Strabismus. 1990. 4th ed. St. Louis: CV Mosby Co;85–100.
13. Parks MM. Duane TD, editor. Vergences. Clinical Ophthalmology. 1983. v. 1:revised ed. Philadelphia: Harper and Row;chap. 7.
14. Pickwell D. Binocular Vision Anomalies, Investigation and Treatment. 1984. London; Boston: Butterworths;33–34.
15. Lee GY, Kim YY. Horizontal and vertical fusional amplitudes in normal eyes. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1991. 32:1116–1122.
16. McNeer KW. Adjustable sutures of the vertical recti. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1982. 19:259–264.
17. Weston B, Enzenauer RW, Kraft SP, Gayowsky GR. Stability of the postoperative alignment in adjustable-suture strabismus surgery. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1991. 28:206–211.
18. Eustis HS, Leoni R. Early reoperation after vertical rectus muscle surgery. J AAPOS. 2001. 5:217–220.
19. Isenberg SJ, Abdarbashi P. Drift of ocular alignment following strabismus surgery. Part 2: using adjustable sutures. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009. 93:443–447.
20. Kim SJ, Kim SJ. Operations on vertical rectus muscles: Their influence on horizontal strabismus. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005. 46:462–465.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download