Abstract
Purpose
To report clinical and laboratory findings of toxic anterior segment syndrome (TASS) in seven patients following cataract surgery with intraocular lens (IOL) implantation.
Methods
The medical records of seven patients who underwent cataract surgery associated with postoperative decreased visual acuity, ocular pain, anterior chamber inflammation and corneal edema between Feb 2007 and Nov 2009 were retrospectively reviewed.
Results
All patients were over 60 years of age, four patients had diabetes and four patients had cardiovascular disease. Five patients had received hydrophilic IOL, and six patients underwent surgery later in order. All seven patients presented with increased anterior segment inflammation, acute decreased visual acuity, and severe corneal edema an average of 10.4 days (range 1 to 15 days) after surgery. Treatment of the seven patients included intensive topical and oral steroids, and improvement was noted in all patients.
Conclusions
The incidence of TASS after cataract surgery was 0.8%, and was significantly higher in cases of hydrophilic IOL insertion (5 of 284 cases, 1.76%) compared to cases of hydrophobic IOL insertion (2 of 581 cases, 0.34%) (p = 0.04). Five of the seven cases presented with TASS at postoperative day 14. Inflammation improved in all patients with steroid treatment.
References
1. Monson MC, Mamalis N, Olson RJ. Toxic anterior segment inflammation following cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1992; 18:184–9.

2. Breebaart AC, Nuyts RM, Pels E, et al. Toxic endothelial cell destruction of the cornea after routine extracapsular cataract surgery. Arch Ophthalmol. 1990; 108:1121–5.

3. Grimmett MR, Williams KK, Broocker G, Edelhauser HF. Corneal edema after miochol. Am J Ophthalmol. 1993; 116:236–8.

4. Duffy RE, Brown SE, Caldwell KL, et al. An epidemic of corneal destruction caused by plasma gas sterilization. The Toxic Cell Destruction Syndrome Investigative Team. Arch Ophthalmol. 2000; 118:1167–76.
5. Liu H, Routley I, Teichmann KD. Toxic endothelial cell destruction from intraocular benzalkonium chloride. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001; 27:1746–50.

6. Eleftheriadis H, Cheong M, Sandeman S, et al. Corneal toxicity secondary to inadvertent use of benzalkonium chloride preserved viscoelastic material in cataract surgery. Br J Ophthalmol. 2002; 86:299–305.

7. Mamalis N, Edelhauser HF, Dawson DG, et al. Toxic anterior segment syndrome. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:324–33.

8. West ES, Behrens A, McDonnell PJ, et al. The incidence of endophthalmitis after cataract surgery among the U.S. Medicare population increased between 1994 and 2001. Ophthalmology. 2005; 112:1388–94.

9. Wallin T, Parker J, Jin Y, et al. Cohort study of 27 cases of endophthalmitis at a single institution. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:735–41.

10. Montan P, Lundström M, Stenevi U, Thorburn W. Endophthalmitis following cataract surgery in Sweden. The 1998 national prospective survey. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2002; 80:258–61.
11. Werner L, Sher JH, Taylor JR, et al. Toxic anterior segment syndrome and possible association with ointment in the anterior chamber following cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:227–35.

12. Kim JH. Intraocular inflammation of denatured viscoelastic sub-stance in cases of cataract extraction and lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1987; 13:537–42.

13. Kreisler KR, Martin SS, Young CW, et al. Postoperative inflammation following cataract extraction caused by bacterial contamination of the cleaning bath detergent. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1992; 18:106–10.

14. Jehan FS, Mamalis N, Spencer TS, et al. Postoperative sterile endophthalmitis (TASS) associated with the memorylens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000; 26:1773–7.

Figure 1.
Photograph, 14 days after cataract surgery of case 1. Diffuse corneal edema, severe anterior chamber inflammation (A), and severe anterior capsule contracture (B) are observed.
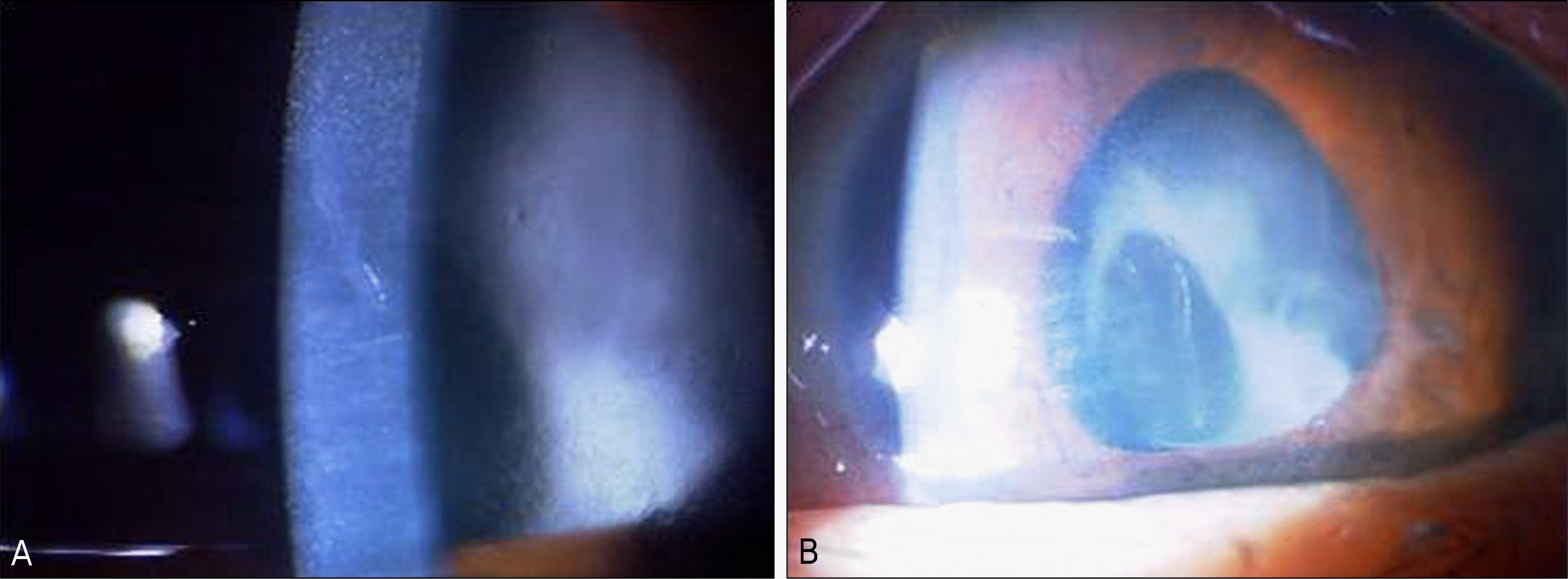
Figure 2.
Photograph, 1 day after cataract surgery of case 6. Diffuse corneal edema, severe anterior chamber inflammation, membranous deposit on the lens surface and hypopyons are observed.
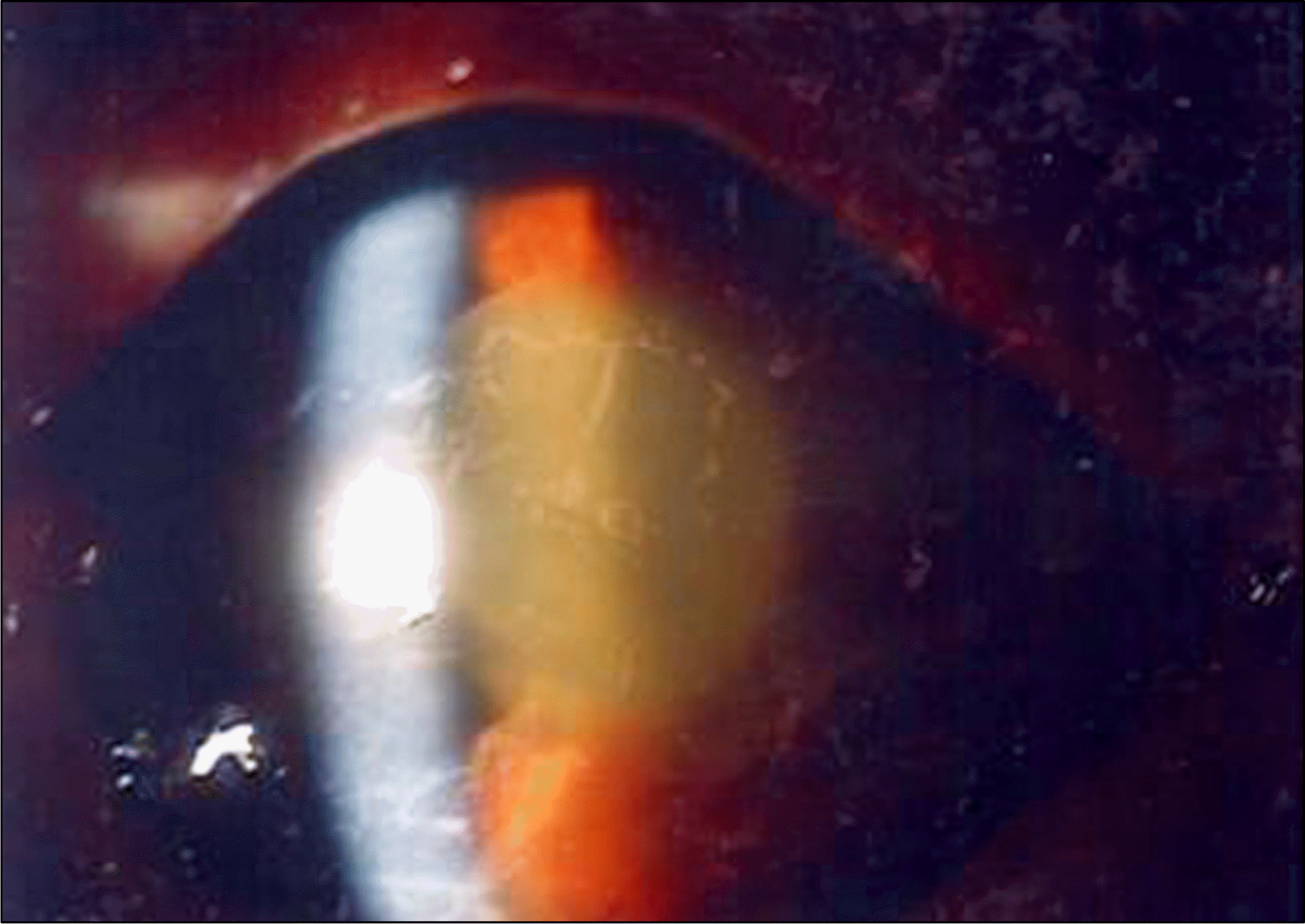
Table 1.
Summary of the patients and outcomes
| Case | Age/ Sex | Underlying disease | Original surgery | IOL* manufacturer | Anesthesia | Clinial presentation | Diagnostics/ Intervensions | Final outcomes | Preoperative ECC† | Postoperative ECC | ECC loss rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 73/ Female | Diabetes | Phaco/IOL OS‡ | Hydrophilic one piece IOL | Retrobulbar block | POD§ 14 Mild pain; VAΠ 20/1000; mod edematous cornea; ant. Capsular contracture; 3+ cell | Topical & systemic steroids, cycloplegics | POD 44 VA 20/100 Postop day 169 VA 20/25 | 2237 | 1748(POD 20 mon) | 22% |
| 2 | 67/ Male | Diabetes Hypertension Cerebrovascular accident(+) | r Phaco/IOL OS | Hydrophobic one piece IOL | Retrobulbar block | POD 15 Pain; VA 20/1000; mod edematous cornea | Topical & systemic steroids | POD 68 VA 20/40 normal exam | 2538 | 2070(POD 18 mon) | 18% |
| 3 | 83/ Male | Hypertension | Phaco/IOL OD# | Hydrophilic one piece IOL | Retrobulbar block | POD 14. VA 20/60 mild edematous cornea; 3+ cell; | Topical steroids | POD 112 VA 20/32 normal exam | 2551 | NM** | − |
| 4 | 79/ Female | Diabetes | Phaco/IOL OD | Hydrophilic one piece IOL | Retrobulbar block | POD 14 Pain; VA 20/125; mod edematous cornea; Keratic precipitate; 3+ cell; membrane | Topical & systemic steroids, Hypertonic saline | POD 108 VA 20/32 normal exam | 2695 | 2564(POD 36 mon) | 5% |
| 5 | 79/ Female | Diabetes | Phaco/IOL OS | Hydrophilic one piece IOL | Retrobulbar block | POD 14 Pain; VA 20/125; mod edematous cornea; 3+ cell; membrane | Topical & systemic steroids, Hypertonic saline | POD 185 VA 20/22 normal exam | 2375 | NM | − |
| 6 | 68/ Male | Hypertension | Phaco/IOL OD | Hydrophilic one piece IOL | Topical | POD 1 pain; VA 20/1000; mod edematous cornea; 3+ cell; 2+ flare; hypopyon | Topical & systemic steroids, cycloplegics Subconj. dexamethasone injection | POD 35 VA 20/40 normal exam Culture(−), | 2288 | 2277(POD 36 mon) | 0.5% |
| 7 | 65/ Female | Arrhythmia | Phaco/IOL OS t | Hydrophobic three piece IOL | Topical | POD 1 VA 20/40; mild edematous cornea; + cell; thick membrane | Topical steroids | POD 41 VA 20/30;- cell | 2304 | NM | − |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download