Abstract
Purpose
To assess clinical features and efficacy of spectacles and low vision devices in pediatric patients with albinism.
Methods
A retrospective study was performed of 15 pediatric patients with albinism for whom glasses and low vision devices had been prescribed to determine subjective satisfaction and objective improvement in visual acuity (VA), strabismus, contrast sensitivity, number of reading letters during 1 minute with refractive correction and low vision devices.
Results
The median refractive correction was +0.12 ± 5.45 diopter (D) spherical equivalent with -0.71 ± 3.62 D astigmatism. Most patients complained of reading difficulty and photophobia. Hand-held magnifier and Keplerian telescope were commonly prescribed low vision devices. In addition, VA, strabismic deviation, contrast sensitivity and number of reading letters during 1 minute significantly improved after wearing glasses and low vision devices.
Conclusions
The present study showed a significant improvement in corrected VA, alignment and subjective symptoms in pediatric patients with albinism by wearing glasses and low vision devices. Additionally, high compliance can improve final patients’ satisfaction through using training of low vision devices.
Go to : 
References
1. Dorey SE, Neveu MM, Burton LC, et al. The clinical features of albinism and their correlation with visual evoked potentials. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003; 87:767–72.

2. Castronuovo S, Simon JW, Kandel GL, et al. Variable expression of albinism within a single kindred. Am J Ophthalmol. 1991; 111:419–26.

3. Abadi RV, Dickinson CM, Pascal E, Papas E. Retinal image quality in albinos. A review. Ophthalmic Paediatr Genet. 1990; 11:171–6.

4. Carden SM, Boissy RE, Schoettker PJ, Good WV. Albinism:modern molecular diagnosis. Br J Ophthalmol. 1998; 82:189–95.
5. Summers CG, King RA. Ophthalmic features of minimal pigment oculocutaneous albinism. Ophthalmology. 1994; 101:906–14.

6. Collewijn H, Apkarian P, Spekreijse H. The oculomotor behaviour of human albinos. Brain. 1985; 108:1–28.

7. Han GC, Lee JH, Paik HJ. Two cases of oculocutaneous albinism with congenital nystagmus. Korean J Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2004; 47:683–91.
Go to : 
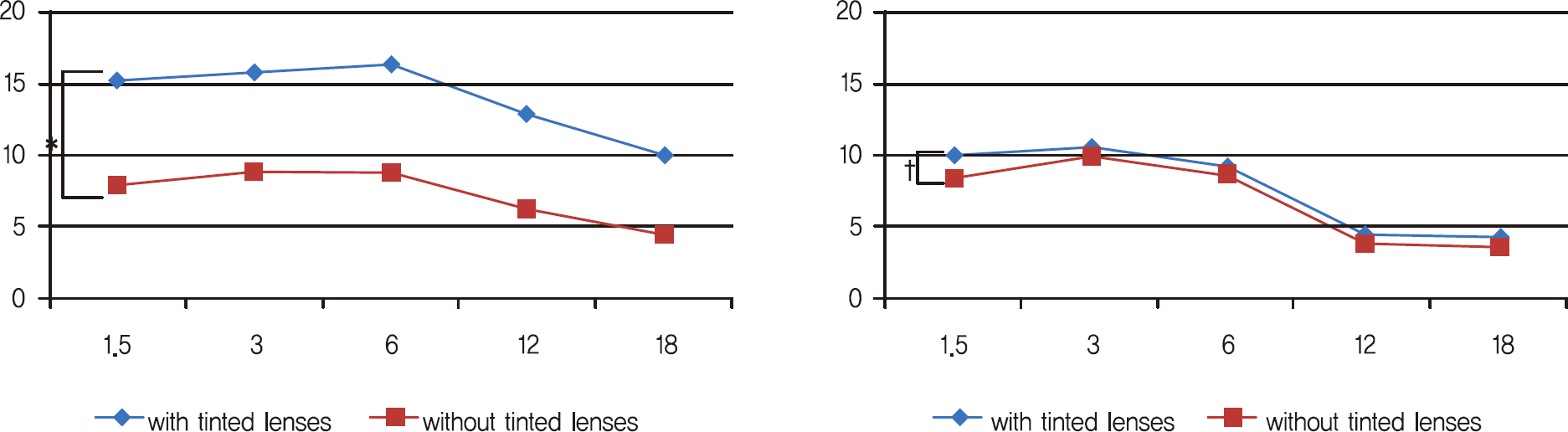 | Figure 1.Comparisons of mean contrast sensitivity according to wearing of tinted lenses at two conditions. *p<0.05 comparison between without tinted-lenses group and with tinted-lenses group in day condition (Mann-Whitney U-test); † p>0.05 comparison between without tinted-lenses group and with tinted-lenses group in day condition (Mann-Whitney U-test). |
Table 1.
Clinical characteristics in pediatric patients with albinism
Table 2.
Visual acuity results with low vision devices




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download