Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the clinical features of retinopathy in chronic hepatitis B patients treated with peginterferon.
Methods
Chronic hepatitis B patients treated with peginterferon were evaluated during regular routine ophthalmic examinations including fundus examination before and during the 1-year follow-up after treatment. A total of 88 patients were included in the study.
Results
Retinopathy developed in 11 (12.5 %) out of 88 patients at a mean of 7 weeks after initiation of treatment. Peginterferon treatment was continued in all patients and retinal abnormalities including cotton wool spot, retinal hemorrhage and microaneurysm resolved without visual impairment. The incidence of hypertension between the retinopathy group and the group without retinopathy was significantly different (P = 0.020).
Go to : 
References
1. Chae HB, Kim JH, Kim JK, Yim HJ. Current status of liver diseases in Korea: Hepatitis B. Korean J Hepatol. 2009; 15:S13–24.

2. Shin JW, Park NH. Treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Korean J Med. 2009; 77:265–74.
3. Okuno H, Hirota T, Shiozaki Y, et al. Interferon-associated retinopathy. Nippon Rinsho. 1994; 52:1919–23.
4. Kawano T, Shigehira M, Uto H, et al. Retinal complications during interferon therapy for chronic hepatitis C. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996; 91:309–13.
5. Wilkins T, Zimmerman D, Schade RR. Hepatitis B: diagnosis and treatment. Am Fam Physician. 2010; 81:965–72.
6. Lim JW, Shin MC. Pegylated-interferon-associated retinopathy in chronic hepatitis patients. Ophthalmologica. 2010; 224:224–9.

7. d'Alteroche L, Majzoub S, Lecuyer AI, et al. Ophthalmologic side effects during alpha-interferon therapy for viral hepatitis. J Hepatol. 2006; 44:56–61.
8. Kang HY, Lim JW, Shin MC. Pegylated interferon associated retinopathy in chronic hepatitis patients. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:383–9.

9. Hayasaka S, Nagaki Y, Matsumoto M, Sato S. Interferon associated retinopathy. Br J Ophthalmol. 1998; 82:323–5.

10. Bedossa P, Poynard T. An algorithm for the grading of activity in chronic hepatitis C. The METAVIR Cooerative Study Group. Hepatology. 1996; 24:289–93.
11. Malik NN, Sheth HG, Ackerman N, et al. A prospective study of change in visual function in patients treated with pegylated interferon alpha for hepatitis C in the UK. Br J Ophthalmol. 2008; 92:256–8.

12. Ogata H, Suzuki H, Shimizu K, et al. Pegylated interferon-associated retinopathy in chronic hepatitis C patients. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2006; 50:293–5.

13. Zandieh I, Adenwalla M, Cheong-Lee C, et al. Retinal vein thrombosis associated with pegylated-interferon and ribavirin combination therapy for chronic hepatitis C. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12:4908–10.

14. Goncalves LL, Farias AQ, Gonçalves PL, et al. Branch retinal vein thrombosis and visual loss probably associated with pegylated interferon therapy of chronic hepatitis C. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12:4602–3.
15. Wei YH, Wang IH, Woung LC, Jou JR. Anterior ischemic optic neuropathy associated with pegylated interferon therapy for chronic hepatitis C. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2009; 17:191–4.

16. Cuthbertson FM, Davies M, McKibbin M. Is screening for interferon retinopathy in hepatitis C justified? Br J Ophthalmol. 2004; 88:1518–20.

17. Nadir A, Amin A, Chalisa N, van Thiel DH. Retinal vein thrombosis associated with chronic hepatitis C: a case series and review of the literature. J Viral Hepat. 2000; 7:466–70.

18. Chisholm JA, Williams G, Spence E, et al. Retinal toxicity during pegylated alpha-interferon therapy for chronic hepatitis C: a multifocal electroretinogram investigation. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005; 21:723–32.

19. Guyer DR, Tiedeman J, Yannuzzi LA, et al. Interferon-associated retinopathy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1993; 111:350–6.

20. Andrade RJ, González FJ, Vázquez L, et al. Vascular ophthalmological side effects associated with antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis C are related to vascular endothelial growth factor levels. Antivir Ther. 2006; 11:491–8.
21. Pawlotsky JM, Ben Yahia M, Andre C, et al. Immunological disorders in C virus chronic active hepatitis: a prospective case-con-trol study. Hepatology. 1994; 19:841–8.

22. Nagaoka T, Sato E, Takahashi A, et al. Retinal circulatory changes associated with interferon-induced retinopathy in patients with hepatitis C. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007; 48:368–75.

23. Fried MW. Side effects of therapy of hepatitis C and their management. Hepatology. 2002; 36:S237–44.

24. Kim ET, Kim LH, Lee JI, Chin HS. Retinopathy in hepatitis C patients due to combination therapy with pegylated interferon and ribavirin. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2009; 53:598–602.

Go to : 
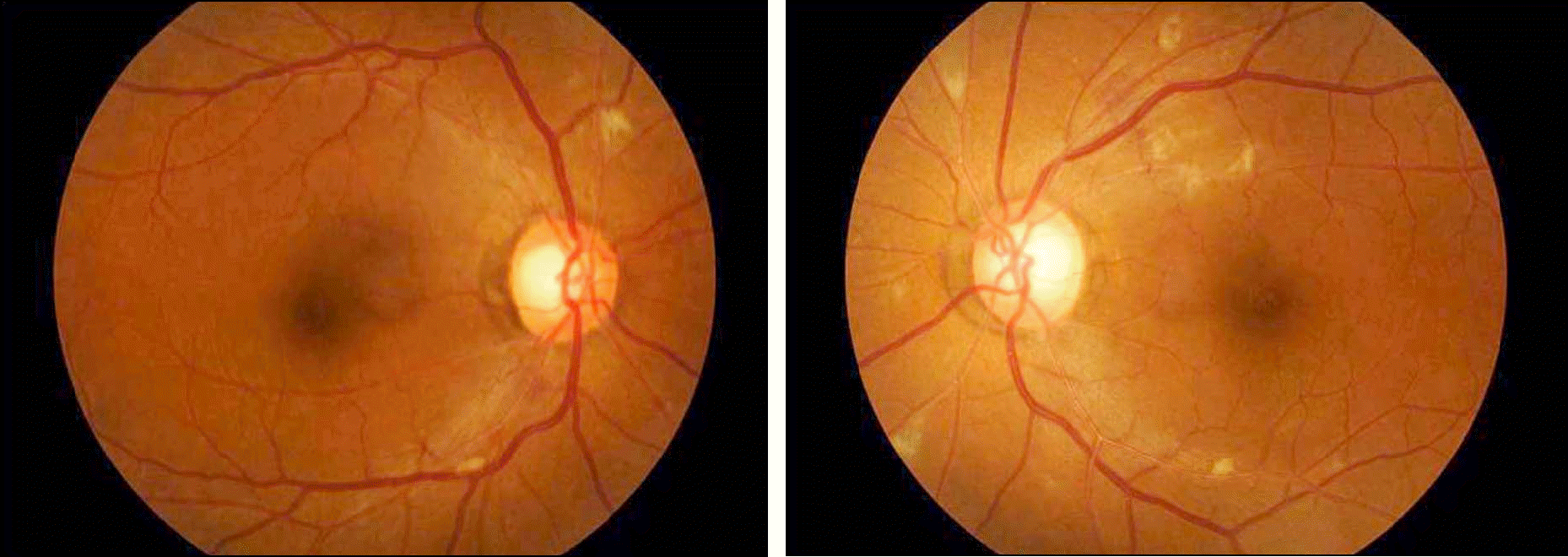 | Figure 1.The fundus photographs of peginterferon-associated-retinopathy in 36-year-old male patient. He started with peginterferon for treatment of chronic hepatitis B. After 1 month, cotton-wool spots with fluffy margin were noted at posterior fundus around the optic disc on both eyes. After 3 months, the lesions were completely disappeared without cessation of peginterferon. |
Table 1.
Comparison of characteristics in chronic hepatitis B patients with and without peginterferon-associated-retinopathy
| Variables | With retinopathy (n = 11) | Without retinopathy (n = 77) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yr) | 36.4 ± 8.0 | 37.5 ± 10.1 | 0.738* |
| Gender male: female | 6:5 | 40:37 | 0.207† |
| Antiviral combination therapy | 0 | 10 | 0.204† |
| Alanine aminotransferase (IU/L) | 143.2 ± 98.4 | 258.8 ± 121.2 | 0.209‡ |
| HBV-DNA (×106 copies/mL) | 58.0 ± 45.9 | 40.3 ± 30.8 | 0.301‡ |
| Liver biopsy Grade∏ 1:2:3:4 | 6:4:1:0 | 27:30:18:2 | 0.171§ |
| Hypertension | 2 (18.2%) | 2 (2.5%) | 0.020§ |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0 | 2 (2.5%) | 0.589§ |
| Cholesterol (mg/dl) | 169.7 ± 39.1 | 169.1 ± 28.9 | 0.948* |
| Hemoglobin (g/dl) | 13.2 ± 2.1 | 16.9 ± 3.0 | 0.442‡ |
| WBC (×106/uL) | 4.76 ± 2.8 | 5.17 ± 2.9 | 0.525‡ |
| Platelet (×103/uL) | 184.2 ± 78.9 | 213.5 ± 89.4 | 0.102‡ |
| Creatine (mg/dl) | 0.88 ± 0.15 | 0.94 ± 0.12 | 0.261‡ |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download