Abstract
Purpose
To determine the factors affecting the outcome of silicone intubation for congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction.
Methods
A total of 233 eyes of 200 children that received silicone intubation were enrolled in a retrospective study.
Results
The overall success of silicone intubation was 193 of 233 eyes (82.8%). There was no significant difference in success rate between age groups. Tube retention time did not affect the success rates. Immediate tube dislocation as early as within 2 weeks did not lower the success rates (81.5%). Success rates were significantly lowered by persistent epiphora at the point of tube removal (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
The outcome of silicone intubation is determined by symptomatic improvement, which is not affected by tube retention time. Unplanned early tube dislocation may not affect the outcome of silicone intubation unless symptoms are persistent, and sufficient tube retention time does not ensure the success if symptoms are persistent.
Go to : 
References
1. Lee SY, Chung HS, Kim HB, et al. The incidence of congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction in korean neonates. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1989; 30:5–8.
2. Oh HS, Ahn Y. The incidence and medical treatment of congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction in Korean infants. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1995; 36:1007–13.
3. Paul TO. Medical management of congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1985; 22:68–70.

4. Petersen RA, Robb RM. The natural course of congenital obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1978; 15:246–50.

5. Mannor GE, Rose GE, Frimpong-Ansah K, Ezra E. Factors affecting the success of nasolacrimal duct probing for congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction. Am J Ophthalmol. 1999; 127:616–7.

6. Katowitz JA, Welsh MG. Timing of initial probing and irrigation in congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction. Ophthalmology. 1987; 94:698–705.

7. Welsh MG, Katowitz JA. Timing of Silastic tubing removal after intubation for congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1989; 5:43–8.

8. Cho KW, Lee SY, Kim SJ. Treatment of congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction using silicone intubation set. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1995; 36:553–8.
9. Yoon TJ, Na KS, Yoon WJ. The effect of silicone tube intubation in pediatric nasolacrimal duct obstruction. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002; 43:155–9.
10. Lim CS, Martin F, Beckenham T, Cumming RG. Nasolacrimal duct obstruction in children: outcome of intubation. J AAPOS. 2004; 8:466–72.

11. Peterson NJ, Weaver RG, Yeatts RP. Effect of short-duration silicone intubation in congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008; 24:167–71.

12. Pediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group. Primary treatment of nasolacrimal duct obstruction with nasolacrimal duct intubation in children younger than 4 years of age. J AAPOS. 2008; 12:445–50.
13. Dortzbach RK, France TD, Kushner BJ, Gonnering RS. Silicone intubation for obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct in children. Am J Ophthalmol. 1982; 94:585–90.

14. Kaufman LM, Guay-Bhatia LA. Monocanalicular intubation with Monoka tubes for the treatment of congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction. Ophthalmology. 1998; 105:336–41.

15. al-Hussain H, Nasr AM. Silastic intubation in congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction: a study of 129 eyes. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1993; 9:32–7.
16. Leone CR Jr, Van Gemert JV. The success rate of silicone intubation in congenital lacrimal obstruction. Ophthalmic Surg. 1990; 21:90–2.

17. Migliori ME, Putterman AM. Silicone intubation for the treatment of congenital lacrimal duct obstruction: successful results removing the tubes after six weeks. Ophthalmology. 1988; 95:792–5.

18. Engel JM, Hichie-Schmidt C, Khammar A, et al. Monocanalicular silastic intubation for the initial correction of congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction. J AAPOS. 2007; 11:183–6.

19. Paul TO, Shepherd R. Congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction: natural history and the timing of optimal intervention. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1994; 31:362–7.

20. Ahn DH, Lew H, Kim HY, Lee SY. The effect of probing for congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1998; 39:836–40.
21. Young JD, MacEwen CJ. Managing congenital lacrimal obstruction in general practice. BMJ. 1997; 315:293–6.
22. Kapadia MK, Freitag SK, Woog JJ. Evaluation and management of congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2006; 39:959–77.

23. Ghuman T, Gonzales C, Mazow ML. Treatment of congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction. Am Orthopt J. 1999; 49:163–8.

24. Espinoza GM, Lueder GT. Outcomes in children with nasolacrimal duct obstruction: Significance of persistent symptoms while stents are in place. J AAPOS. 2007; 11:187–8.

Go to : 
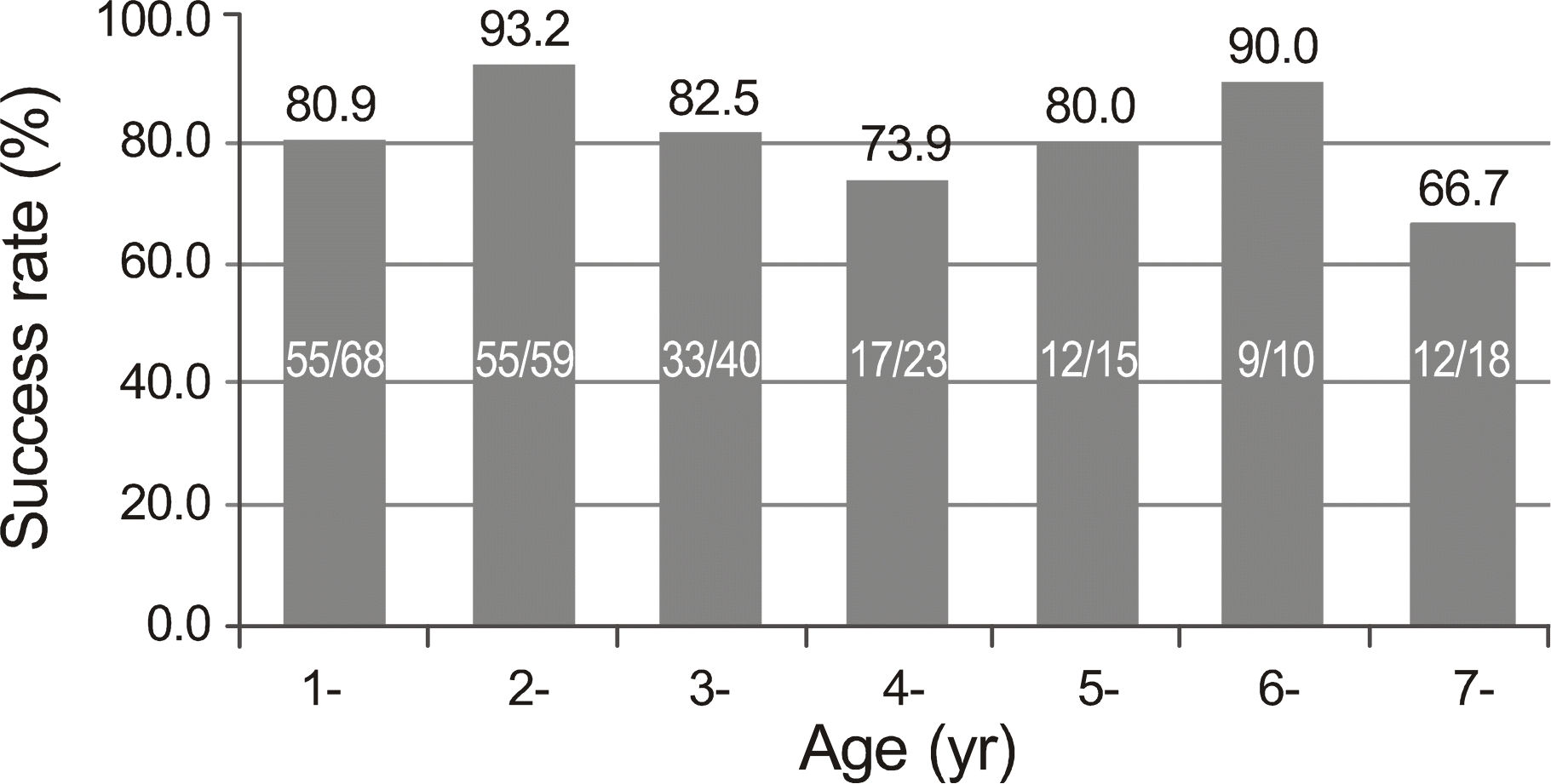 | Figure 1.The success rate for patients of different age groups. There is no significant difference in the success rate for patients of different age groups (p = 0.138; ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparisons). |
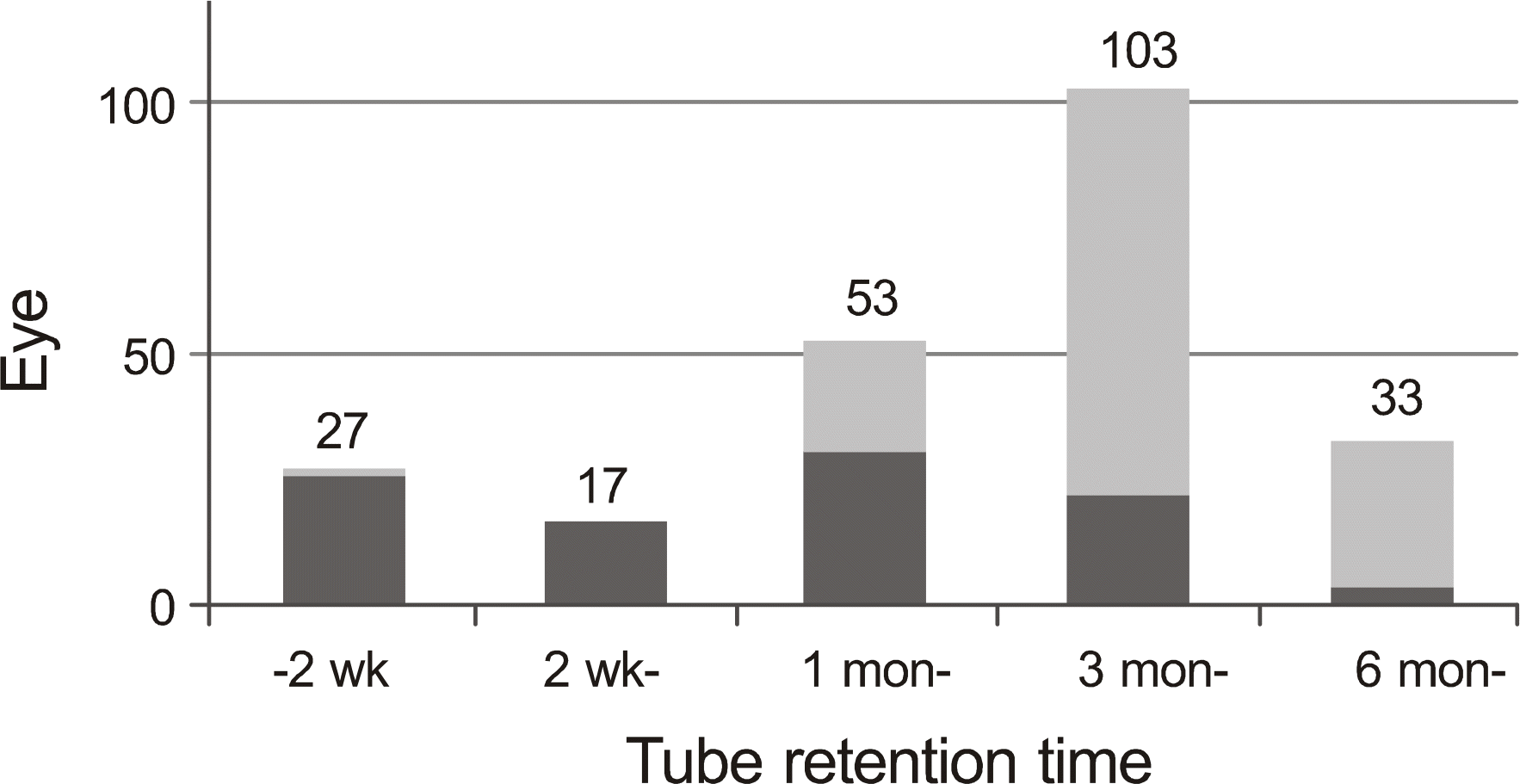 | Figure 2.The distribution of tube retention time and the proportion of unexpectedly dislocated tubes. The tube retention time of 103 of 233 eyes (44.2%) was between 3 to 6 months, and was between 1 to 3 months for 53 of 233 eyes (22.7%). The proportion of unexpectedly removed tubes is marked off with dark gray boxes. |
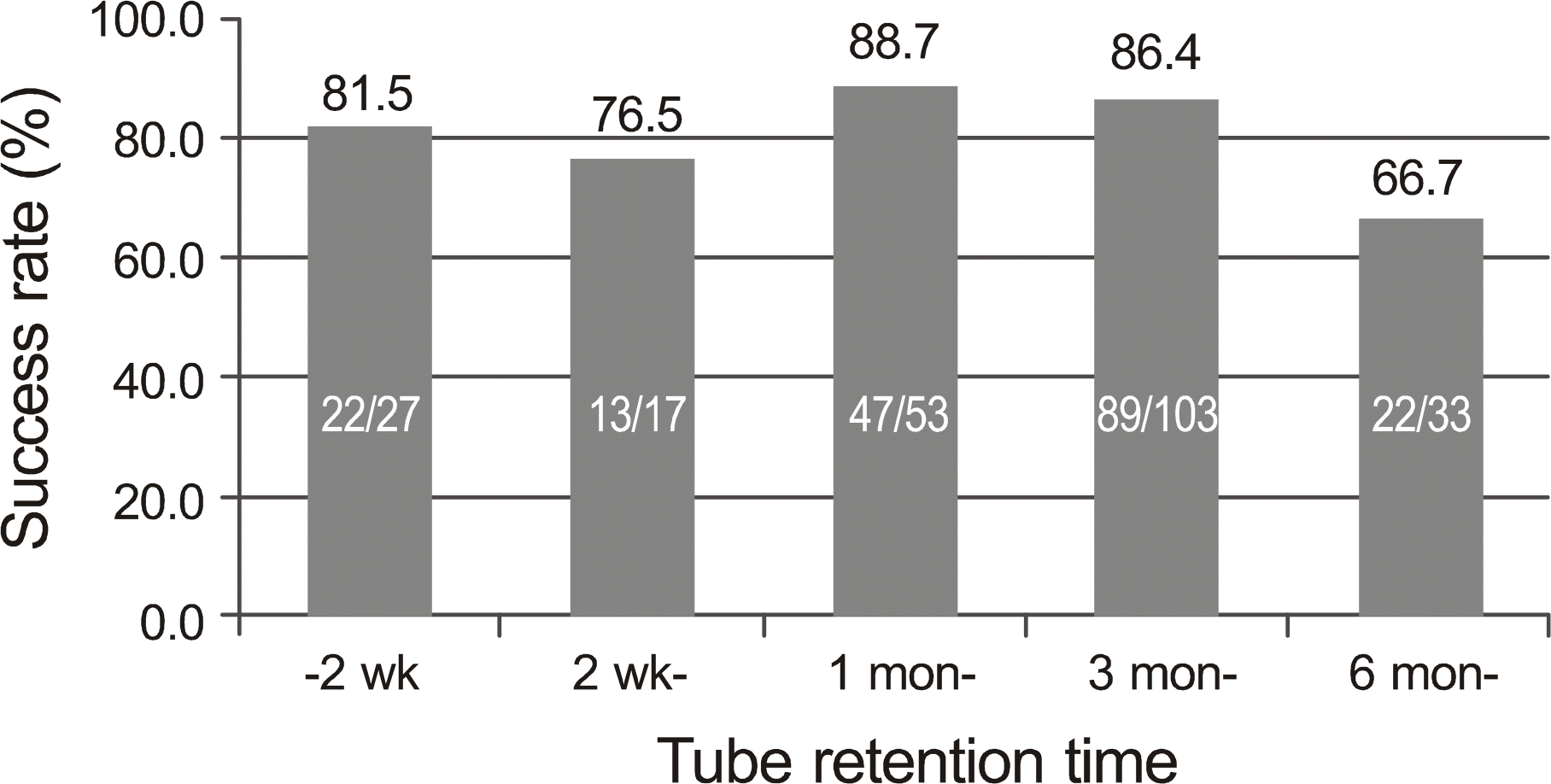 | Figure 3.The success rate according to the tube retention time. Each group, even the group in which tube retention time was less than 2 weeks, shows no significant difference in success rate (p = 0.066; ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparisons). |
Table 1.
Demographics




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download