Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the primary indications, surgical outcomes, causes and risk factors for graft failure in patients with three or more penetrating keratoplasty (PKP) surgeries.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed indications for the initial corneal graft, survival periods, causes and risk factors for failure in 25 patients (26 eyes) who had undergone three or more PKP with minimum followup periods of nine months.
Results
The most common primary indications were herpes simplex keratitis (26.9%), followed by fungal keratitis (19.2%) and bacterial keratitis (11.5%). The average survival period of graft in three or more PKP was 12.9 ± 9.1 months. As the frequency of PKP increased, the survival period became shorter; the survival period was the longest in pseudophakic bullous keratopathy and the shortest in herpes simplex keratitis. The most common cause of graft failure was allograft rejection (82.8%), and the risk factors for graft failure were short interval between penetrating keratoplasties and corneal neovascularization.
Go to : 
References
1. Choi SH, Lee YW, Kim HM, et al. Epidemiologic Studies of Keratoplsty in Korea. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:538–47.
2. Boisjoly HM, Tourigny R, Bazin R, et al. Risk factors of corneal graft failure. Ophthalmology. 1993; 100:1728–35.

3. Kim EC, Kim MS. Graft rejection in penetrating keratoplasty. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:289–95.
4. Weisbrod DJ, Sit M, Naor J, Slomovic AR. Outcomes of repeat penetrating keratoplasty and risk factors for graft failure. Cornea. 2003; 22:429–34.

5. Yildiz EH, Hoskins E, Fram N, et al. Third or greater penetrating keratoplasties: indications, survival, and visual outcomes. Cornea. 2010; 29:254–9.

6. Tchah HW, Ha DW, Kim CK, et al. Penetrating keratoplasty results in 275 cases. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2001; 42:20–9.
7. Yoon KC, Park YK, Park YG. Surgical results of repeat penetrating keratoplasty and risk factors for graft failure. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2004; 45:1827–32.
8. Djalilian AR, Nussenblatt RB, Holland EJ. Immnunosuppressive therapy in ocular surface transplantation. Holland EJ, Mannis MJ, editors. Ocular Surface Disease Medical and Surgical Management. 1st ed.New York: Springer;2002. 1:chap. 22.
9. Halberstadt M, Machens M, Gahlenbek KA, et al. The outcome of corneal grafting in patients with stromal keratitis of herpetic and non-herpetic origin. Br J Ophthalmol. 2002; 86:646–52.

10. Robinson CH. Indications, complications and prognosis for repeat penetrating keratoplasty. Ophthalmic Surg. 1979; 10:27–34.
11. Rapuano CJ, Cohen EJ, Brady SE, et al. Indications for and outcomes of repeat penetrating keratoplasty. Am J Ophthalmol. 1990; 15:689–95.

12. Maeno A, Naor J, Lee HM, et al. Three decades of corneal transplantation: indications and patient characteristics. Cornea. 2000; 19:7–11.

13. MacEwen CJ, Khan ZU, Anderson E, MacEwen CG. Corneal re-graft: indications and outcome. Ophthalmic Surg. 1988; 19:706–12.

14. Patel NP, Kim T, Rapuano CJ, et al. Indications for and outcomes of repeat penetrating keratoplasty, 1989-1995. Ophthalmology. 2000; 107:719–24.

15. Vanathi M, Sharma N, Sinha R, et al. Indications and outcome of repeat penetrating keratoplasty in india. BMC Ophthalmol. 2005; 5:26.

16. Al-Mezaine H, Wagoner MD, King Khaled Eye Specialist Hospital Cornea Transplant Study Group. Repeat penetrating keratoplasty: indication, graft survival, and visual outcome. Br J Ophthalmol. 2006; 90:324–7.
Go to : 
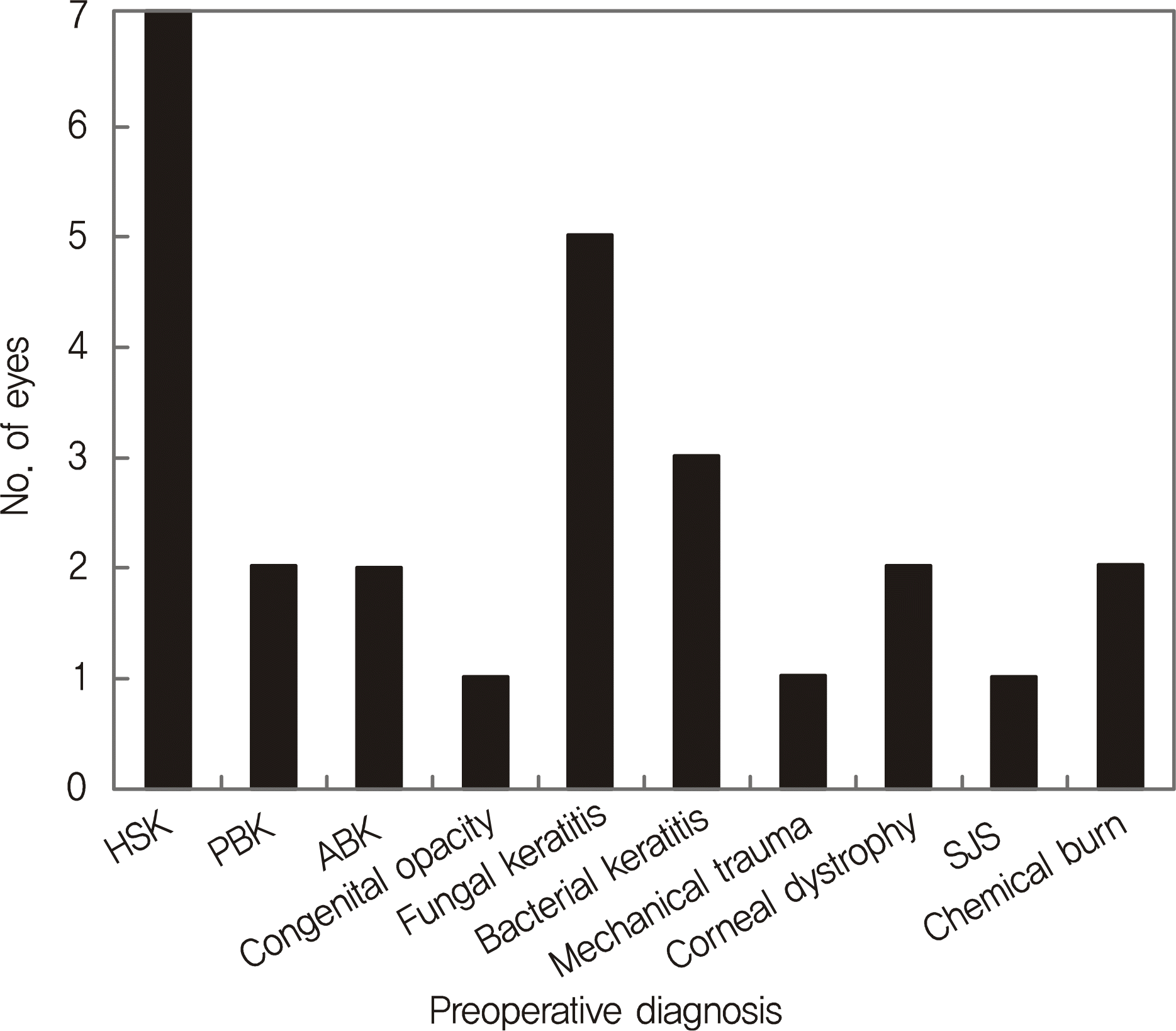 | Figure 1.The indications of the primary penetrating keratoplasty in patients undergoing three or more penetrating keratoplasties. HSK = herpes simplex keratitis, PBK = pseudophakic bullous keratopathy, ABK = aphakic Bullous keratopathy, SJS = Stevens-Jonson syndrome. |
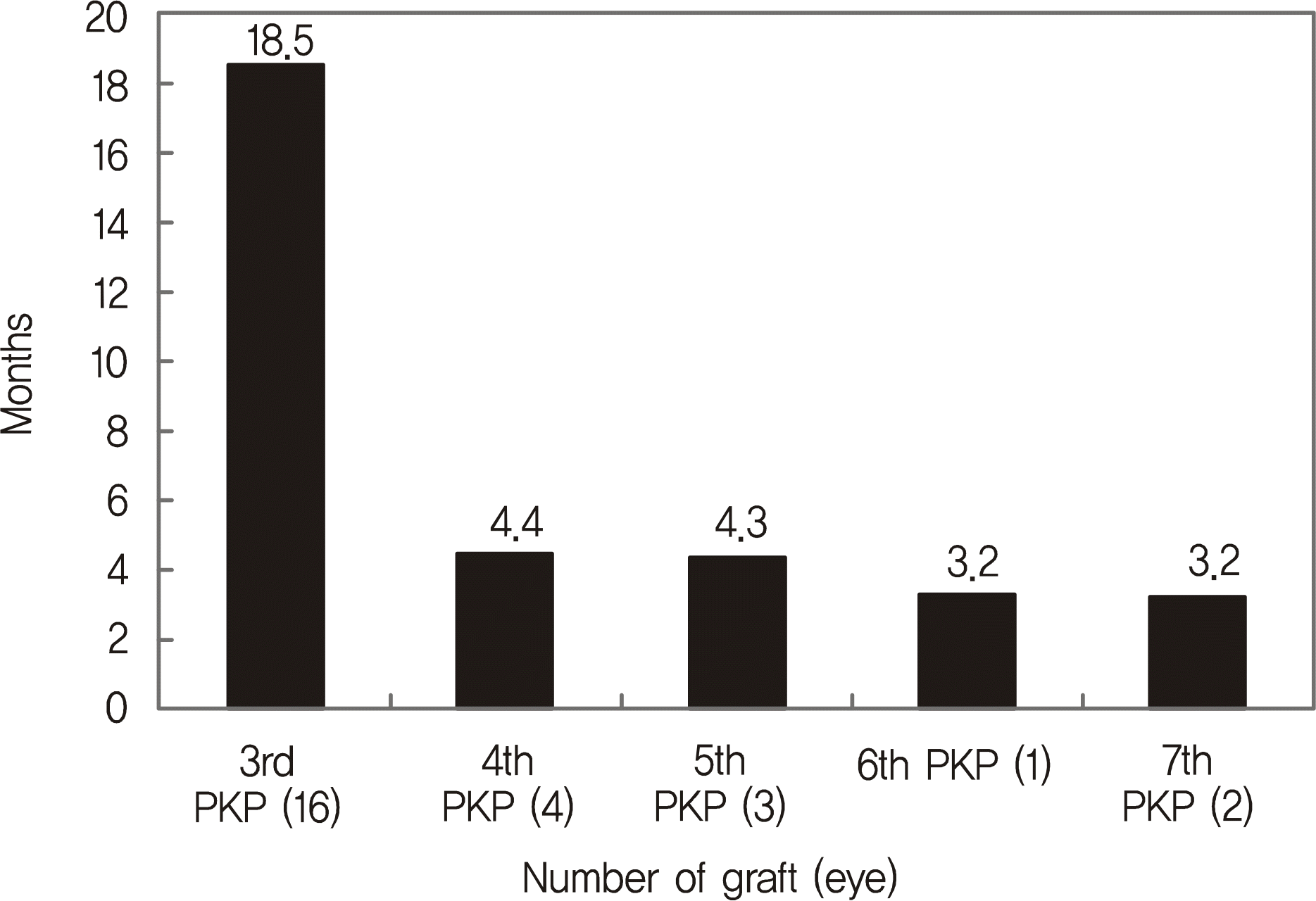 | Figure 2.Mean survival period of three or more penetrating keratoplasties. PKP = penetrating keratoplasty. |
Table 1.
Causes of graft failure in three or more penetrating keratoplasties
| Causes | No. of grafts (%) |
|---|---|
| Allograft rejection | 24 (82.8) |
| Endothelial failure | 3 (10.4) |
| Postoperative glaucoma | 1 (3.4) |
| Recurrence of host disease | 1 (3.4) |
| Total | 29 (100) |
Table 2.
Univariate analysis of risk factors for graft failure in patients with three or more penetrating keratoplasties
Table 3.
Multivariate analysis of risk factors for graft failure in patients with three or more penetrating keratoplasties




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download