Abstract
Purpose
To analyze the clinical features of patients who successfully discontinued correction with hyperopic glasses for refractive accommodative esotropia during a 10 year follow-up.
Methods
The authors of the present study analyzed 29 patients followed-up for a minimum of 10 years after diagnosis of accommodative esotropia. The patients were divided into 2 groups: patients who successfully discontinued correction with hyperopic glasses (10 patients, Group A), and patients who required constant use of hyperopic glasses (19 patients, Group B). The age at first visit, refractive error, deviated angle without correction, stereopsis, and follow-up duration were compared between the 2 groups.
Results
The mean age at first visit for all patients was 3.03 ± 1.46 years, and the follow-up duration was 11.3 ± 1.51 years. Patients in Group A discontinued the use of hyperopic glasses after 10.26 ± 2.08 years. There were no statistical differences in mean age at first visit, deviated angle without correction, stereopsis, follow-up duration, or the amount of change in hyperopia. The initial amount of hyperopia in Group A was 3.81 ± 1.54 D, significantly lower than the 5.12 ± 1.37 D in Group B.
Go to : 
References
1. Choi KS, Chang JH, Chang YH, Lee JB. Occurrence and risk factors of decompensation and additional treatment in refractive accommodative esotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:121–6.
2. Kim DJ, Chun BY, Kwon J-Y. Five-year follow-up results of refractive accommodative esotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:315–20.
3. Kang IS, Park SW, Park YG. Clinical features of refractive accommodative esotropia: lomg-term study. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:487–92.
4. The Korean Strabismus and Pediatric Ophthalmology Society. Current Concepts in Strabismus. 2nd ed.Seoul: Naewaehaksul;2008. p. 183–5.
5. Kim C, Hwang JM. The clinical course of esotropia associated with hypermetropia after initial wearing of glasses. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:134–43.
6. Yang H, Chang YH, Lee JB. Clinical features of refractive accommodative esotropia and partially accommodative esotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2004; 45:626–30.
7. Lee TY, Kim MM. Clinical characteristics of accommodative esotropia with successful wearing out of glasses. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:1699–705.

8. Hutcheson KA, Ellish NJ, Lambert SR. Weaning children with accommodative esotropia out of spectacles: a pilot study. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003; 87:4–7.

9. Kwon J-Y, Lee DE, Song HC. Clinical studies on accommodative esotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1997; 38:687–91.
11. Raab EL. Hypermetropia in accommodative esodeviation. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1984; 21:P64–8.
12. Chang JH, Kim MM. Refractive accommodative esotropia associated with mild hyperopia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:1547–54.
13. Yang H, Jang YH, Lee JB. Clinical features of refractive accommodative esotropia and partially accommodative esotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2004; 45:626–30.
Go to : 
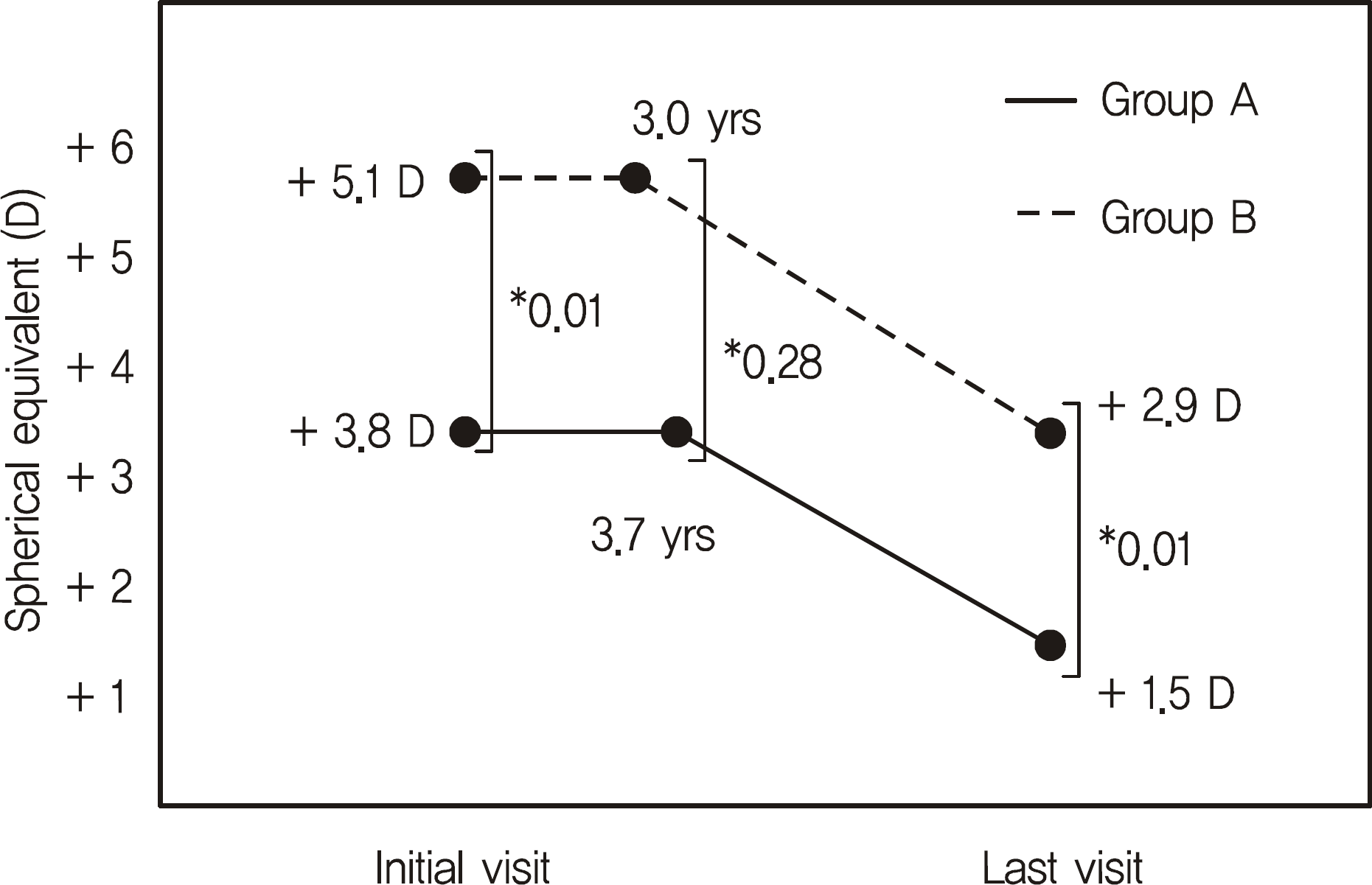 | Figure 1.The change of refractive error. Group A = patients who successfully discontinued correction with hyperopic glasses; Group B = patients who needed persistent wearing of hyperopic glasses; Refractive error was maintained for 3.7 years in Group A, 3.0 years in Group B then began to decrease.* p-value. |
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics
| | Group A (n = 10) | Group B (n = 19) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (n) | | | 0.058* |
| Male | 2 | 11 | |
| Female | 8 | 8 | |
| Age (mean ± SD, yr) | 3.42 ± 1.87 | 2.83 ± 1.19 | 0.597† |
| Follow up (mean ± SD, yr) | 12.08 ± 1.86 | 10.89 ± 1.15 | 0.114† |
Table 2.
Distribution of refractive error
| | Group A (20 eyes) | Group B (38 eyes) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spherical equivalent (D) | | | |
| 1.5–4 | 11 | 8 | |
| 4–6 | 7 | 17 | 0.047* |
| 6–8 | 2 | 12 | |
| 8–10 | 0 | 1 | |
| Interocular difference of spherical equivalent (mean ± SD, D) | 0.52 ± 0.61 | 0.61 ± 0.57 | 0.513† |
Table 3.
Deviated angle at far distance
| | Group A (n = 10) | Group B (n = 19) | p-value* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deviated angle without correction (mean ± SD, PD) | | | |
| Initial | 21.70 ± 6.75 | 28.68 ± 9.26 | 0.056 |
| Last | 1.20 ± 4.73 | 16.05 ± 10.36 | 0.001 |
Table 4.
Amblyopia treatment
| | Group A (n = 10) | Group B (n = 19) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amblyopia (n) | 5 | 9 | 0.893* |
| Amblyopia treatment | | | 0.505† |
| Occlusion (n) | 5 | 7 | |
| Atropine penalization (n) | 0 | 2 | |
| Successful treatment (n) | 5 | 7 | 0.505† |
Table 5.
Annual decrease in hyperopia
| | Group A (n = 20) | Group B (n = 38) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decreasing amount of hyperopia per year (mean ± SD, D/yr) | 0.20 ± 0.14 | 0.17 ± 0.19 | 0.676* |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download