Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the knowledge and awareness level of diabetic retinopathy (DR) in type 2 diabetes patients.
Methods
A total of 437 participants with diabetes were recruited in the Seoul Metro-City Diabetes Prevention Program (SMC-DPP). Participants underwent clinical and laboratory examinations and questionnaire survey to evaluate diabetes complications. The DR was diagnosed by grading fundus photographs 5 standard fields taken per eye.
Results
The overall prevalence of any DR was 20.4% and only 6.6% of patients were aware of their DR. The DR patients who underwent an eye examination within the previous year were 42.3%, and 50.3% out of 437 patients enrolled were educated on diabetes. Of the survey participants, 83.8% answered positive to ‘Evaluation of diabetes mellitus complication must be performed every year', 61.1% answered positive to ‘Must control blood pressure and lipid level for diabetes management' and 28.4% believed ‘It takes a long time for complications of diabetes to develop'. The DR self awareness was 14.6% and an eye examination within the previous year was 50.6% among the 89 DR participants.
Go to : 
References
1. Park IB, Baik SH. Epidemiologic Characteristics of Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: Current Status of Diabetic Patients Using Korean Health Insurance Database. Korean Diabetes J. 2009; 33:357–62.

2. Thompson TJ, Engelgau MM, Hegazy M, et al. The onset of NIDDM and its relationship to clinical diagnosis in Egyptian adults. Diabet Med. 1996; 13:337–40.

3. Choi YJ, Kim HC, Kim HM, et al. Prevalence and Management of Diabetes in Korean Adults: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 1998–2005. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:2016–20.
4. Aamir AH. Targets for treating type 2 Diabetes and preventing its complications: can we achieve it? Pak J Med Res. 2004; 43:95–6.
5. Turner RC. The U.K Prospective Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care. 1998; 21:35–8.
6. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT) Research Group. N Engl J Med. 1993; 329:977–86.
7. Kim EJ. Aims of diabetes treatment and importance of diabetes education. Diabetes Metab J. 1985; 9:1–3.
8. Gill GS, Jeong IS. Knowledge, perceived seriousness and adherence to preventive behaviors on chronic complications of diabetes mellitus. Korean J Health Promot Dis Prev. 2005; 2:78–89.
9. Grading diabetic retinopathy from stereoscopic color fundus photographs an extension of the modified Airlie House classification. ETDRS report number 10. Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group. Ophthalmology. 1991; 98:786–806.
10. Nam JH, Lee SH, Lee HJ, et al. The prevalence of chronic complications in non-insulin dependent diabetic patients. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 1999; 23:702–14.
11. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care for patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 1994; 17:616–23.
12. Glasgow RE, Osteen VL. Evaluating diabetes education: Are we measuring the most important outcomes? Diabetes Care. 1992; 15:1423–32.

13. Anderson RM, Funnell MM, Butler PM, et al. Patient empowerment. Results of a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care. 1995; 18:943–49.

14. D'Eramo-Melkus GA, Wylie-Rosett J, Hagan JA. Metabolic impact of education in NIDDM. Diabetes Care. 1992; 15:864–9.
15. Kim JH, Chang SA. Effect of diabetes education program on glyce-mic control and self management for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Korean Diabetes J. 2009; 33:518–25.

16. Goudswaard AN, Stolk RP, Zuithoff NP, et al. Long-term effects of self-management education for patients with type 2 diabetes taking maximal oral hypoglycaemic therapy: a randomized trial in primary care. Diabet Med. 2004; 21:491–6.

17. Norris SL, Lau J, Smith SJ, et al. Self-management education for adults with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of the effect on glyce-mic control. Diabetes Care. 2002; 25:1159–71.
Go to : 
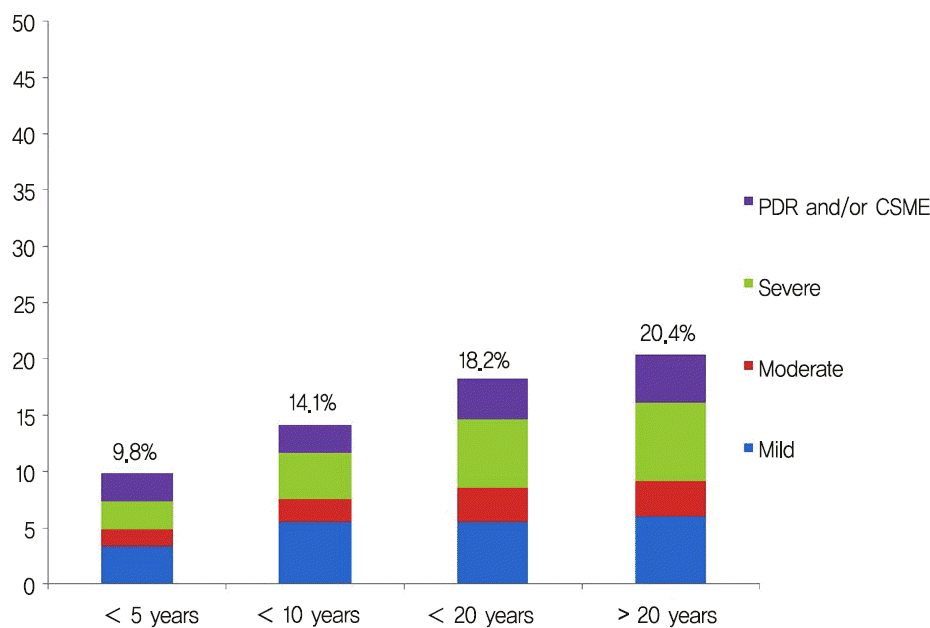 | Figure 1.Cumulative incidence ratio of diabetic retinopathy according to the duration of diabetes. CSME = clinically significant macular edema. |
Table 1.
The eligibility criteria for study
| Eligibility criteria |
|---|
| Inclusion criteria |
| (1) Patients with type 2 DM*, Seoul residence |
| (2) 30–65 years old |
| Exclusion criteria |
| (1) Patients with type 1 DM, Secondary DM |
| (2) Patients with other medical problem |
| ① Malignancy |
| ② Major cardiovascular disease: ex) angina |
| ③ Under hemodialysis |
Table 2.
Demographics and bio-physical profile of the study participants
| Characteristics | Value | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Duration of diabetes (mean ± SD*, yr) | 6.2 ± 5.4 | 0–30 |
| Age (mean ± SD, yr) | 55.4 ± 6.5 | 30–65 |
| Gender | | |
| Male | 240 (54.9%) | |
| Feale | 197 (45.1%) | |
| Diabetic retinopathy | 89 (20.4%) | |
| Mild | 26 (5.9%) | |
| Moderate | 14 (3.2%) | |
| Severe | 30 (6.9%) | |
| Proliferative and/or CSME† | 19 (4.3%) | |
| Diabetes medication | | |
| No | 75 (17.2%) | |
| Yes | 361 (82.6%) | |
| No response | 1 (0.2%) | |
| Hypertension medication | | |
| No | 104 (23.8%) | |
| Yes | 185 (42.3%) | |
| No response | 148 (33.9%) | |
| Hyperlipidemia medication | | |
| No | 152 (34.8%) | |
| Yes | 107 (24.5%) | |
| No response | 178 (40.7%) | |
| Systolic blood pressure (mean ± SD, mm Hg) | 124.3 ± 14.6 | 90–185 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mean ± SD, mm Hg) | 76.4 ± 9.2 | 50–100 |
| Body mass index (mean ± SD, kg/m2) | 24.6 ± 3.1 | 16.8–37.5 |
| Fast blood glucose level (mean ± SD, mg/dL) | 152.3 ± 38.2 | 51–484 |
| Postprandial glucose2 (mean ± SD, mg/dL) | 196.8 ± 60.1 | 82–856 |
| HbA1C (mean ± SD, %) | 7.4 ± 1.4 | 5–15.4 |
| Triglyceride (mean ± SD, mg/dL) | 162.6 ± 116.8 | 33–1034 |
| HDL‡-Cholesterol (mean ± SD, mg/dL) | 49.6 ± 16.6 | 6–265 |
| LDL§-Cholesterol (mean ± SD, mg/dL) | 110.7 ± 33.9 | 20–230 |
| Total cholesterol (mean ± SD, mg/dL) | 190.4 ± 43.7 | 8.89–537 |
| Albumin to creatinine ratio (ARC) (mean ± SD, mg/g) | 30.8 ± 42.1 | 3–276 |
| ACR<30 | 320 (73.2%) | |
| 30 < ACR < 300 | 111 (25.4%) | |
| ACR > 300 | 6 (1.4%) | |
Table 3.
Awareness level of diabetic retinopathy and eye examination
Table 4.
Percentage distribution of respondent's knowledge level of diabetes
| |
Answers (%) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Knowledge regarding diabetes control | Yes | No | | No response |
| I know what is glycosylated hemoglobin level | 30.4 | 69.4 | | 0.2 |
| I know the goal of my glucose level control | 9.4 | 90.4 | | 0.2 |
| I know the goal of my blood pressure level control | 4.1 | 95.2 | | 0.7 |
| I know the goal of my bad cholesterol (LDL*) level control | 1.1 | 98.9 | | 0.0 |
| Knowledge regarding complications of diabetes | Yes | No | Don't know | No response |
| Evaluation of diabetes mellitus complication must be performed every year | 83.8 | 2.7 | 12.8 | 0.7 |
| Must be control blood pressure and lipid level for diabetes management | 61.1 | 19.2 | 19.5 | 0.2 |
| It takes a large time to make have complications of diabetes | 38.0 | 28.4 | 33.2 | 0.4 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download