Abstract
Purpose
To compare clinical outcomes between different IOL sizes after microincisional cataract surgery.
Methods
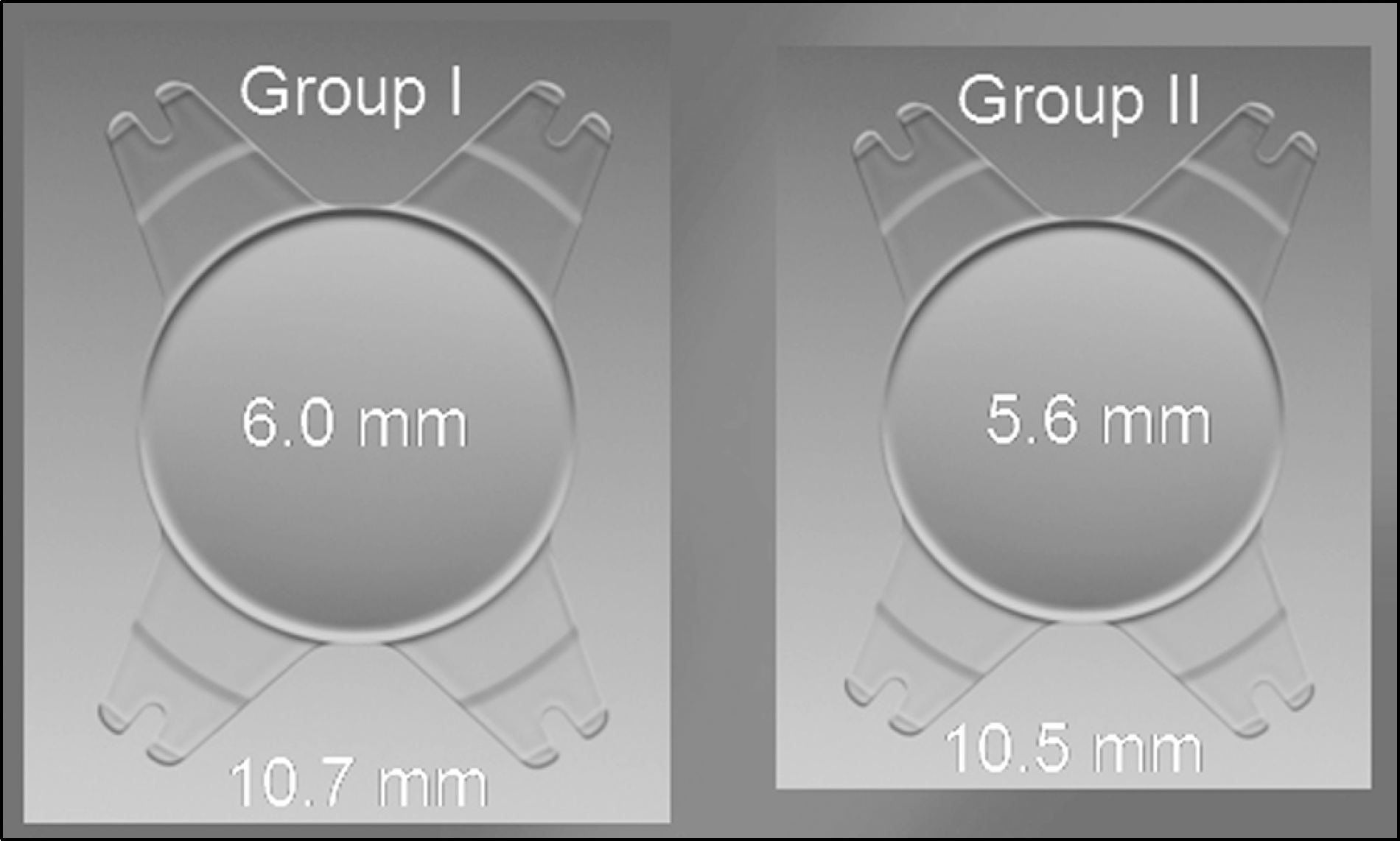
Retrospective chart review was done in 68 eyes of 68 patients who underwent phacoemulsification and implantation with two different-sized aspheric IOLs (AKREOS MI60 Bausch & Lomb, Inc., Rochester, NY). The patients were divided into 2 groups: group I consisted of 38 eyes between 15.5-22.0 diopter (D) (optic size 6.0 mm, overall size 10.7 mm), and group II consisted of 30 eyes between 22.5–30.0 D (optic size 5.6 mm, overall size 10.5 mm). The best corrected visual acuity (BCVA), refractive error, and anterior chamber depth (ACD) were measured preoperatively and post-operatively and were compared between groups.
Results
Postoperative 6 month BCVA was 0.08 ± 0.10 D in group I and 0.07 ± 0.11 D in group II. During the same period, the spherical equivalent was −0.32 ± 0.65 D in group I and −0.16 ± 0.59 D in group II (p > 0.05). There were no significant differences in ACD or refractive error during the postoperative period (p > 0.05).
Go to : 
References
1. Kershner RM. Topical anesthsia for small incision self sealing cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1993; 19(Suppl):290–2.
2. Siepser SB. Sutureless cataract surgery with radial transverse incision. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1991; 17(Suppl):716–8.

3. Jee DH, Lee PY, Joo CK. The comparison of astigmatism according to the incision size in cataract operation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:594–8.
4. Kim HJ, Kim JH, Lee DH. Endothelial cell damage in micro-incison cataract surgery and coaxial phacoemulsification. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:19–26.
5. Dogru M, Honda R, Omoto M, et al. Early visual results with the rollable ThinOptX intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:558–65.

6. Pandey SK, Werner L, Agarwal A, et al. Phakonit. cataract removal through a sub-1.0 mm incision and implantation of the ThinOptX rollable intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:1710–3.

7. Alio J, Rodriguez-Prats JL, Galal A, Ramzy M. Outcomes of microincision cataract surgery versus coaxial phacoemulsification. Ophthalmology. 2005; 112:1997–2003.

8. Packer M, Fine IH, Hoffman RS. Aspheric intraocular lens selection: the evolution of refractive cataract surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2008; 19:1–4.

9. Kohnen T, Klaproth OK. [Aspheric intraocular lenses]. Ophthalmologe. 2008; 105:234–40.
10. Can I, Takmaz T, Bayhan HA, Bostanci Ceran B. Aspheric microincision intraocular lens implantation with biaxial microincision cataract surgery: efficacy and reliability. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:1905–11.

11. Choi JA, Kim CY, Na KS, et al. Clinical results after implantation of a spherical aberration-free intraocular lens: effect of contrast sensitivity and wavefront aberration–a clinical comparative study. Ophthalmologica. 2009; 223:320–5.
12. Mun GH, Im SK, Park HY, Yoon KC. Comparison of clinical results between two spherical aberraion-free intraocular lenses. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010; 51:670–6.

13. Lee SY, Chung JL, Hong JP, el al. Comparative study of two aspheric, aberration-free intraocular lenses in cataract surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1520–6.

14. Mun GH, Im SK, Park HY, Yoon KC. Comparison of visual function between two aspheric intraocular lenses after microcoaxial cataract surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010; 51:333–9.

15. Oshika T, Nagata T, Ishii Y. Adhesion of lens capsule to intraocular lenses of polymethylmethacrylate, silicone, and acrylic foldable materials: an experimental study. Br J Ophthalmol. 1998; 82:549–53.

16. Chang DF. Comparative rotational stability of single-piece open-loop acrylic and plate-haptic silicone toric intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:1842–7.

17. Kim JH, Lee D, Cha YD, et al. The analysis of predicted capsular bag diameter using modified model of capsule measuring ring in Asians. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2008; 36:238–44.

18. Lim SJ, Kang SJ, Kim HB, Apple DJ. Ideal size of an intraocular lens for capsular bag fixation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1998; 24:397–402.

19. Tana P, Belmonte J. Experimental study of different intraocular lens designs implanted in the bag after capsulorhexis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1996; 22:1211–21.
Go to : 
Table 1.
Characteristics of the IOL
| Overall diameter (mm) | Optic body diameter (mm) | Diopter range (dpt) |
|---|---|---|
| 11.0 | 6.2 | 10.0 to 15.0 |
| 10.7 | 6.0 | 15.5 to 22.0 |
| 10.5 | 5.6 | 22.5 to 30.0 |
Table 2.
Characteristics of the different-sized IOL groups
Table 3.
Postoperative best corrected visual acuity and refractive error according to different-sized IOL groups
| | | Group I | Group II | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCVA* | 1 month (log MAR) | 0.11 ± 0.11 | 0.10 ± 0.09 | 0.719 |
| 3 months (log MAR) | 0.09 ± 0.10 | 0.09 ± 0.11 | 0.900 | |
| 6 months (log MAR) | 0.08 ± 0.10 | 0.07 ± 0.11 | 0.562 | |
| Refractive error | 1 month (Diopter) | −0.34 ± 0.67 | −0.31 ± 0.56 | 0.829 |
| 3 months (Diopter) | −0.34 ± 0.66 | −0.19 ± 0.60 | 0.334 | |
| 6 months (Diopter) | −0.32 ± 0.65 | −0.16 ± 0.59 | 0.317 |
Table 4.
Postoperative change of anterior chamber depth and refractive error




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download