Abstract
Purpose
To investigate clinical outcomes and to analyze the factors of successful treatment of conjunctiva-Müller muscle resection (CMMR) in patients with mild to moderate ptosis.
Methods
The medical records of 22 patients (30 eyes) with upper lid ptosis were retrospectively reviewed. All patients underwent conjunctiva-Müller muscle resections, and four patients (seven eyes) underwent concurrent upper lid blepharoplasty. The mean follow-up period was 81.62 ± 21 days. Pre- and post-operative MRD1, IPF and pupil to brow distance were measured using the Image J program. A preoperative phenylephrine test and a pathologic examination were performed to analyze the presence of Müller's muscle and the tear secreting glands from the CMMR specimens.
Results
The overall success rate of the procedure was 93%. Postoperatively, the MRD1 increased on average by 1.47 mm (p = 0.00) and increased by an average of 1.72 mm when the phenylephrine test response was greater than 2 mm and by 0.99 mm when the response less than 2 mm. The Müller muscle was observed in every specimen.
Go to : 
References
1. Fasanella RM, Servat J. Levator resection for minimal ptosis: another simplified operation. Arch Ophthalmol. 1961; 65:493–6.

2. Putterman AM, Urist MJ. Müller muscle-conjunctiva resection: technique for treatment of blepharoptosis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1975; 93:619–23.
3. Ben Simon GJ, Lee S, Schwarcz RM, et al. Müller's muscle– conjunctival resection for correction of upper eyelid ptosis: relationship between phenylephrine testing and the amount of tissue resected with final eyelid position. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2007; 9:413–7.
4. Weinstein GS, Buerger GF Jr. Modification of the Müller's muscle-conjunctival resection operation for blepharoptosis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1982; 93:647–51.
5. Karesh JW, Putterman AM, Fett DR. Conjunctiva-Müller's muscle excision to correct anophthalmic ptosis. Ophthalmology. 1986; 93:1068–71.

6. Escalas P. Ptosis treated by resection of the Muller muscle: analysis of a series of 51patients. J Fr Ophthalmol. 2006; 29:908–15.
7. Bae JS, Ha MS, Lee J-Y, et al. Results of conjunctiva-Müller muscle resection in mild eyelid ptosis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:1365–70.
8. Ha SW, Lee JM, Jeung WJ, Ahn HB. Clinical effects of con-junctiva-Müller muscle resection in Anophthalmic Ptosis. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2007; 21:65–9.

9. Michels KS, Vagefi MR, Steele E, et al. Müller muscle– Conjunctiva resection to correct ptosis in high risk patients. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007; 23:363–6.
10. Guyuron B, Davies B. Experience with the modified Putterman procedure. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1988; 82:775–80.

11. Dresner SC. Further modifications of the Müller's muscle conjunctival resection procedure for blepharoptosis. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1991; 7:114–22.
12. Mercandetti M, Putterman AM, Cohen ME, et al. Internal levator advancement by Müller's muscle-conjunctival resection: technique and review. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2001; 3:104–10.
13. Song WS, Lee SJ, Kim YH. Morphologic study of upper eyelid contour and functional evaluation of levator palpebrae. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2001; 42:1523–9.
14. Buckman G, Jakobiec FA, Hyde K, et al. Success of Fasanella-Servat operation independent of Müller's smooth muscle excision. Ophthalmology. 1989; 96:413–8.
15. Cahill KV, Buerger GF Jr, Johnson BL. Ptosis associated with fatty infiltration of Muller's muscle and levator muscle. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1986; 2:213–7.
16. Brown MS, Putterman AM. The effect of upper blepharoplasty on eyelid position when performed concomitantly with Muller muscle-conjunctival resection. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000; 16:94–100.
17. Kim JH, Lee JK. The change of eyebrow position after Upper lid blepharoplasty in patients With dermatochalasis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1141–5.

Go to : 
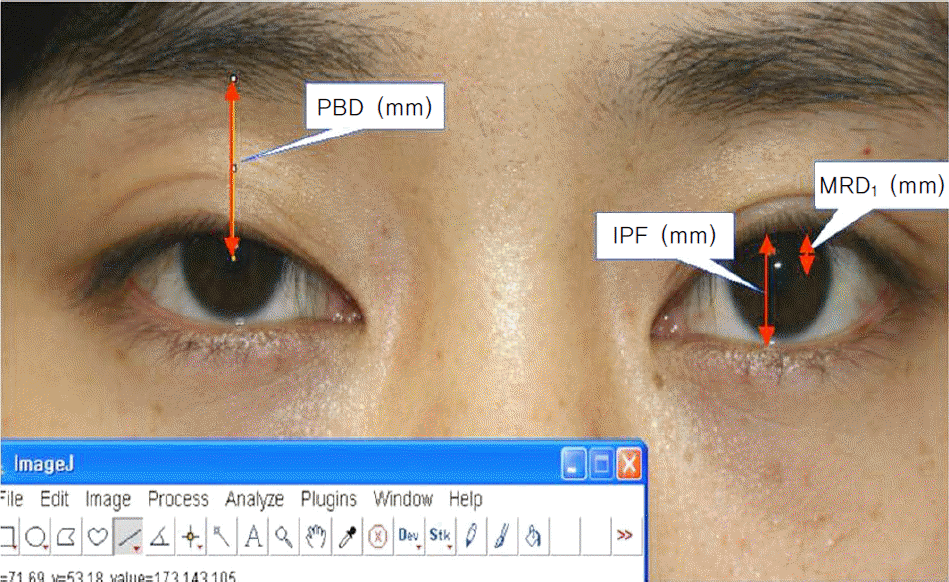 | Figure 1.Pre and post operative MRD1, IPF, PBD are measured by image J program. MRD1 = marginal reflex distance; IPF = interpalpebral fissure; PBD = pupil to brow distance. |
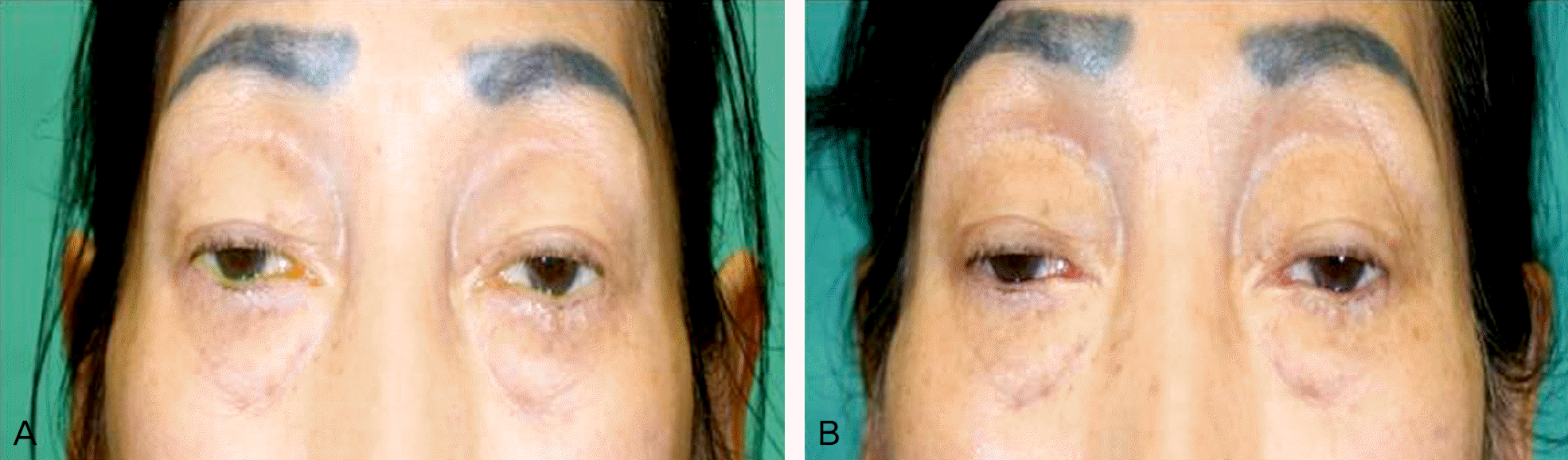 | Figure 2.A muscular dystrophy patient with bilateral ptosis was not corrected after CMMR. (A) Pre-op, (B) Post-op 1 month. CMMR = conjunctiva-Mller muscle resection. |
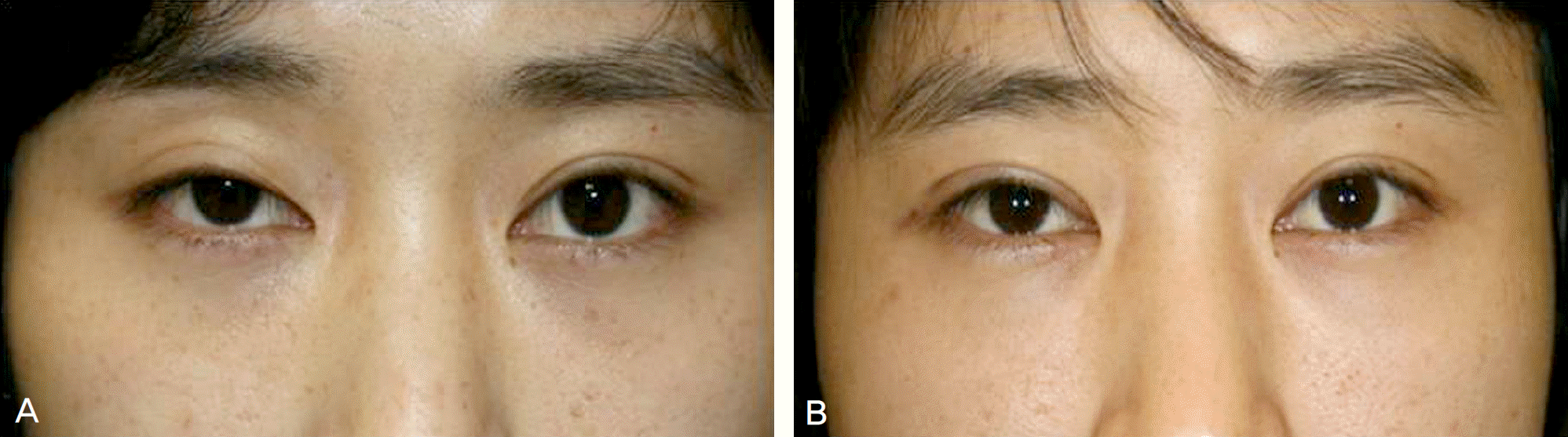 | Figure 3.A patient with right eye ptosis was corrected successfully. (A) Pre-op, (B) Post-op 3 year. |
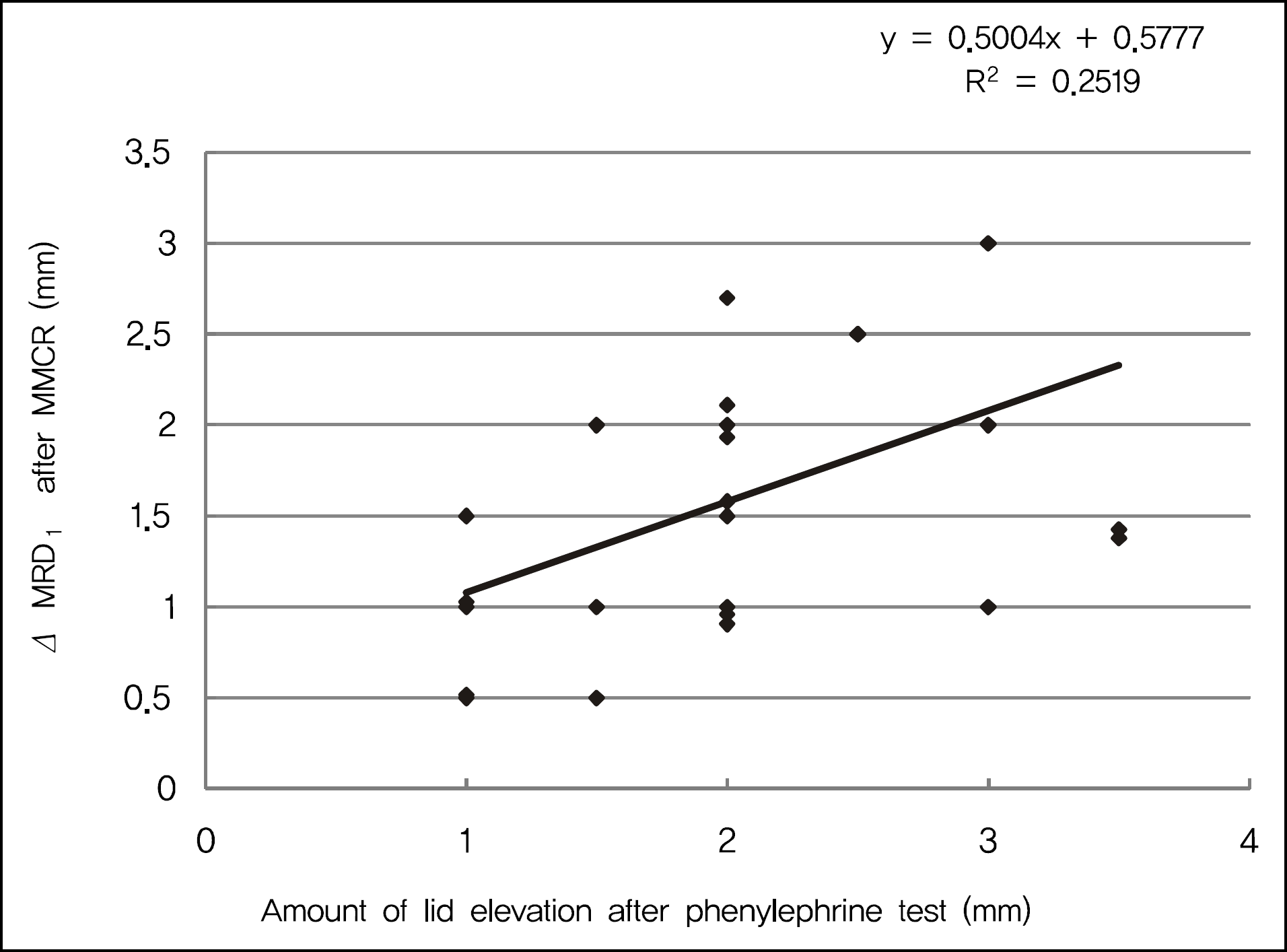 | Figure 4.Amount of lid elevation after phenylephrine test (mm) and Δ MRD1 after conjunctiva-Müller muscle resection (mm) shows linear correlation. Δ = post – pre value; MRD1 = marginal reflex distance. |
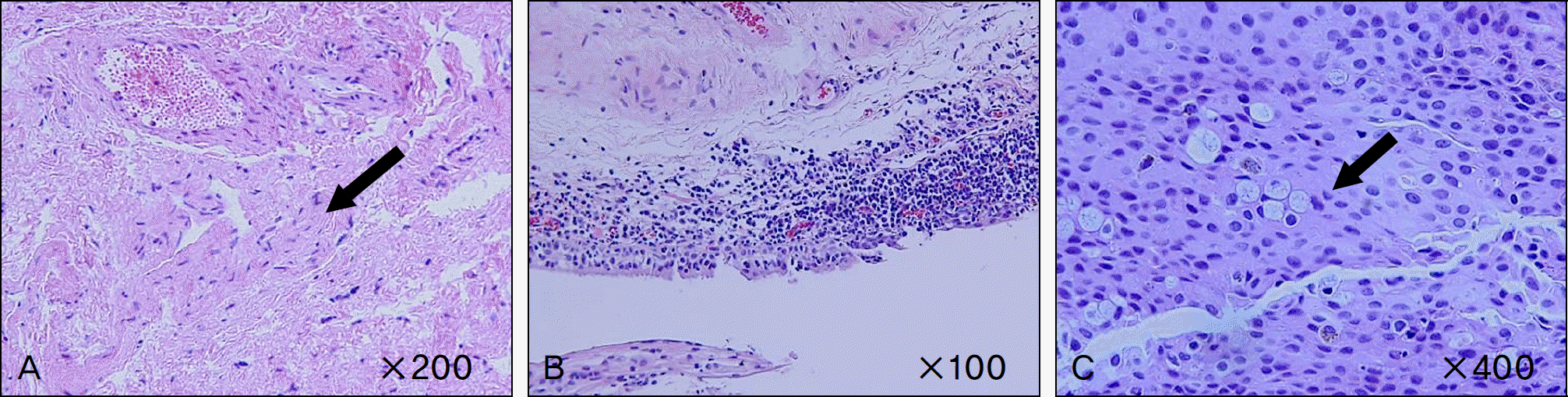 | Figure 5.(A) Müller's muscle (arrow) (H&E stain, ×200). (B) Conjunctival inflammation. Diffuse infiltration of many lymphocytes is noted (H&E stain, ×100). (C) Goblet cells (arrow) (H&E stain, ×400). |
Table 1.
Clinical outcomes of conjunctiva-Müller muscle resection
| | Preoperative (mm) | Post operative (mm) | Difference (mm) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRD1 | 0.87 ± 1.16 | 2.35 ± 0.67 | 1.47 | 0.000* |
| IPF | 5.62 ± 1.94 | 7.31 ± 1.58 | 1.68 | 0.000* |
| PBD | 23.14 ± 5.48 | 23.25 ± 5.50 | 0.11 | 0.872 |
Table 2.
The results of phenylephrine test in the patients for conjunctiva-Müller muscle resection
| Amount of lid elevation at phenylephrine test | ≥2 mm (n = 22) | <2 mm (n = 8) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Δ MRD1 | 1.74 ± 0.85 | 0.99 ± 0.61 | 0.030* |
| Δ IPF | 2.21 ± 1.06 | 1.09 ± 0.64 | 0.050 |
| Δ PBD | 0.41 ± 0.94 | 0.61 ± 0.92 | 0.635 |
Table 3.
The clinical outcomes of the patients treated with conjunctiva-Müller muscle resection using two hemostat clamps or Putterman clamps
Table 4.
The clinical outcomes of the patients treated with conjunctiva-Müller muscle resection or concurrent blepharoplasty
| | Δ MRD1 | Δ IPF | Δ PBD |
|---|---|---|---|
| CMMR (n = 23) | 1.45 ± 1.06 | 1.67 ± 1.46 | 0.13 ± 1.40 |
| CMMR+ blepharoplasty (n = 7) | 1.49 ± 0.57 | 1.68 ± 1.88 | 0.12 ± 1.51 |
| p-value | 0.345 | 0.465 | 0.468 |
| Total (n = 30) | 1.47 | 1.68 | 0.11 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download