Abstract
Purpose
To report a patient with Leber's idiopathic stellate neuroretinitis accompanying peripapillary sensory retinal detachment detected with optical coherence tomography.
Case summary
A 26-year-old woman complained of visual disturbance in her right eye for several months. Her best corrected visual acuity was 0.5 in the right eye and 0.9 in the left eye. A relative afferent papillary defect was present in the right eye. Severe disc swelling with retinal hemorrhage and stellate macular exudates were observed in the right eye. Fluorescein angiography revealed optic disc leakage. There appeared to be no leakage from the other retinal vessels or from the retinal pigment epithelium. OCT revealed outer nuclear-plexiform layer fluid accumulation in the papillomacular region. Eight weeks after steroid treatment, the best corrected visual acuity in the right eye had improved to 0.7, and the optic disc edema had improved. The OCT showed that the fluid in the outer nuclear-plexiform layer space had largely been absorbed.
References
1. Leber T. Die pseudonephritischen Netzhauterkrnakungen, die Retinitis stellata: Die Purtschersche Netzhautaffektion nach schwerer Schadelverletzung. Graefe AC, Saemishe T, editors. Graefe-Saemisch Handbuch der Gesamten Augerheikunde. 2nd ed.78. Leipzig: Engelmann;1916. p. 1319.
2. Dreyer RF, Hopen G, Gass JDM, Smith JL. Leber's idiopathic stellate neuroretinitis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1984; 102:1140–5.

3. Stewart MW, Brazis PW, Barrett KM, et al. Optical coherence tomography in a case of bilateral neuroretinitis. J Neruoophthalmol. 2005; 25:131–3.

4. Ryo A, Yasuhiro S, Takuya N, et al. Central serous retinal detachment detected by optical coherence tomography in Leber's idiopathic stellate neuroretinitis. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2005; 49:547–58.

5. Kitamei H, Suxuki Y, Takahashi M, et al. Retinal angiography and optical coherence tomography disclose focal optic disc vascular leakage and lipid-rich fluid accumulation within retina in a patient with Leber idiopathic stellate neuroretinitis. J Neuroophthalmol. 2009; 29:203–7.
6. Choi SJ, You TY, Chung YT. A case of Leber's idiopathic stellate neuroretinitis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1994; 35:994–8.
7. Wade NK, Levi L, Jones MR, et al. Optic disc edema associated with peripapillary serous retinal detachment: an early sign of systemic Bartonella henselae infection. Am J Ophthalmol. 2000; 130:327–34.
Figure 1.
Fundus photographs of a 26-year-old woman with Leber's idiopathic stellate neuroretinitis. (A) Initial examinations showed serous retinal detachment with linear hemorrhage and yellowish exudates at the papillomacular region in the right eye but no specific findings in the left eye. (B) Eight weeks later, the optic disc swelling and serous retinal detachment resolved but a few hard exudates remained on the papillomacular bundle in the right eye.
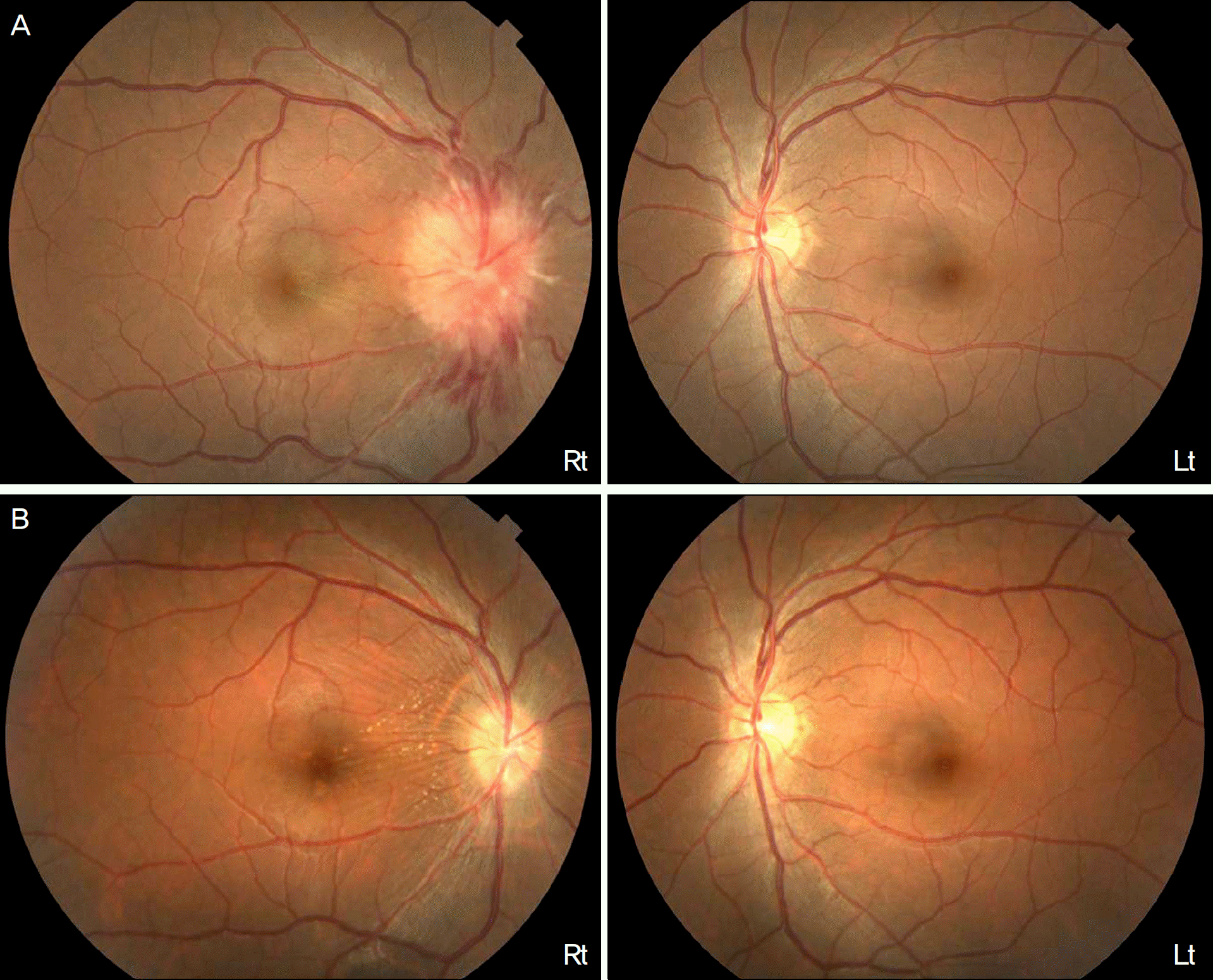
Figure 2.
(A) Initial fluorescein angiography shows leakage from multiple arterioles in the superficial layer of the optic disc during the arterial stage and slow diffusion of fluid over the optic disc and within the peripapillary retina. (B) Eight weeks later, fluorescein angiography shows reduced leakage from the optic disc during the arterial stage and staining of the peripapillary retina during the late arteriovenous stage.
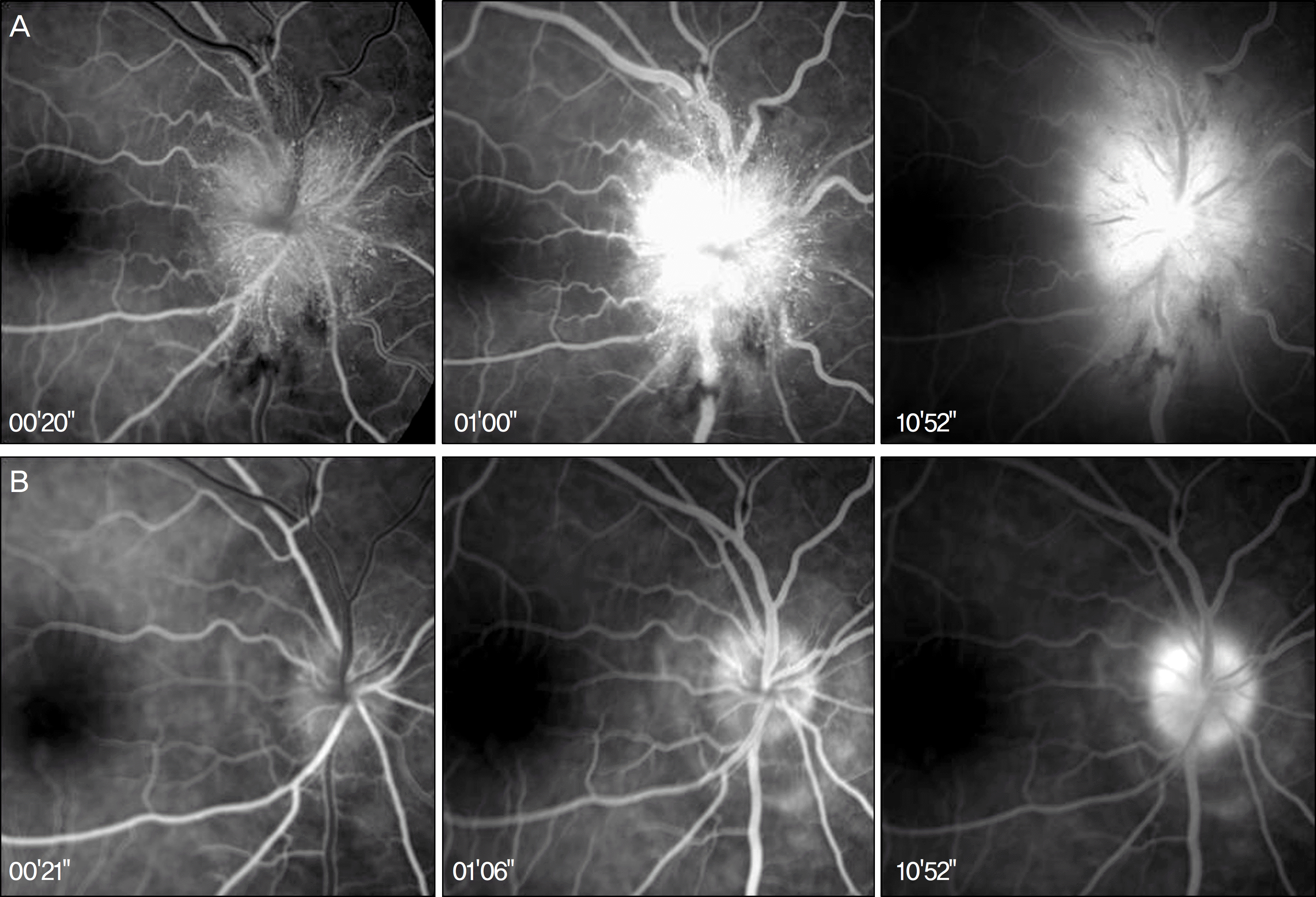
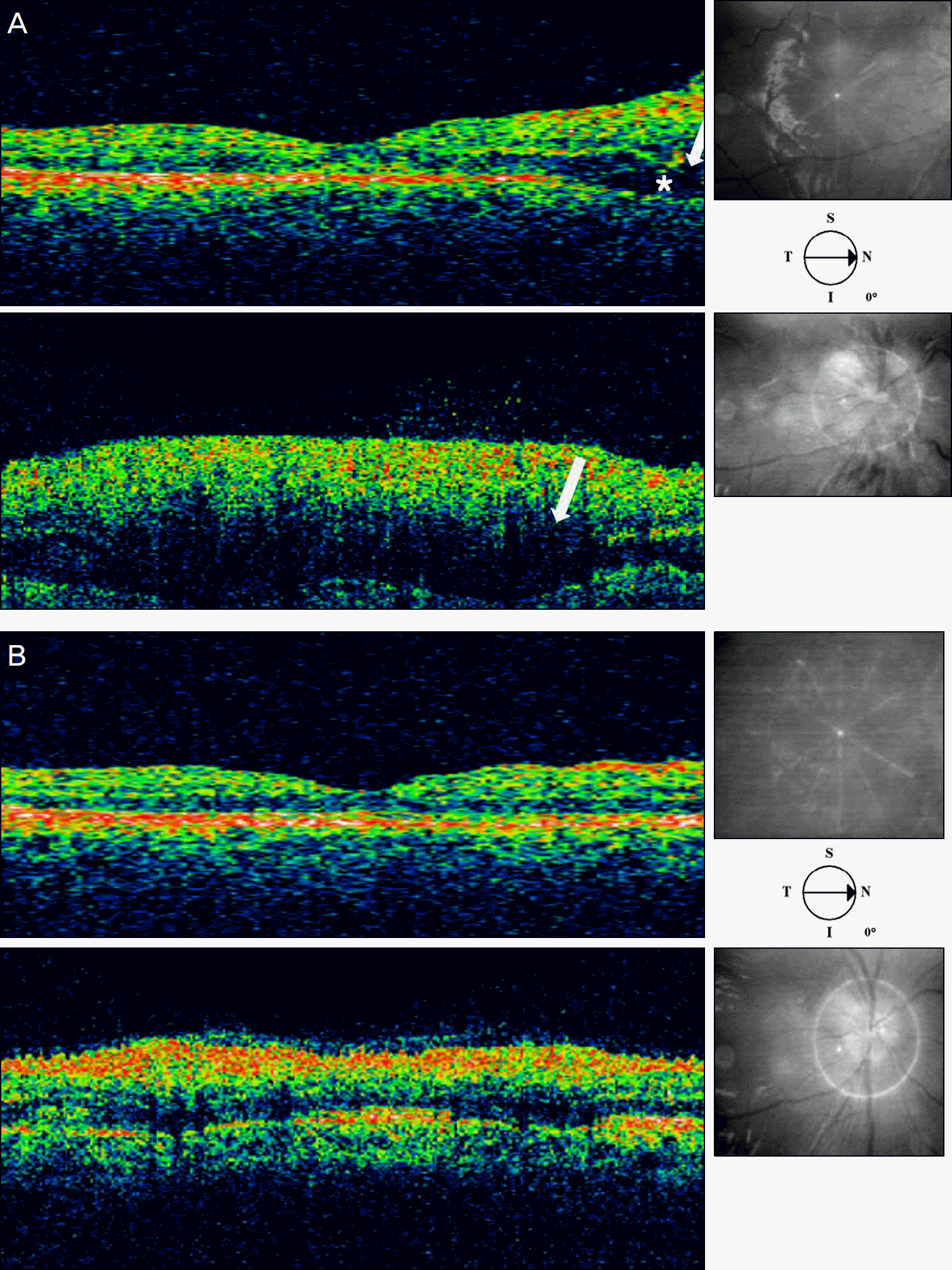
Figure 3.
(A) Initial optical coherence tomography shows shallow neurosensory detachment (asterisk) with significant outer nuclear-plexiform space (arrow) swelling at the peripapillary area. (B) Eight weeks later, Optical coherence tomography shows resolved serous detachment and marked resolution of outer retina edema.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download