Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate clinical features and binocular function of long-standing intermittent exotropia detected for the first time in patients older than 16 years of age.
Methods
We retrospectively evaluated adult exotropic patients older than 16 years of age who were first diagnosed between March 2001 and February 2010. A total of 73 patients with exotropia who had not undergone ophthalmologic management for at least 10 years were included in the present study.
Results
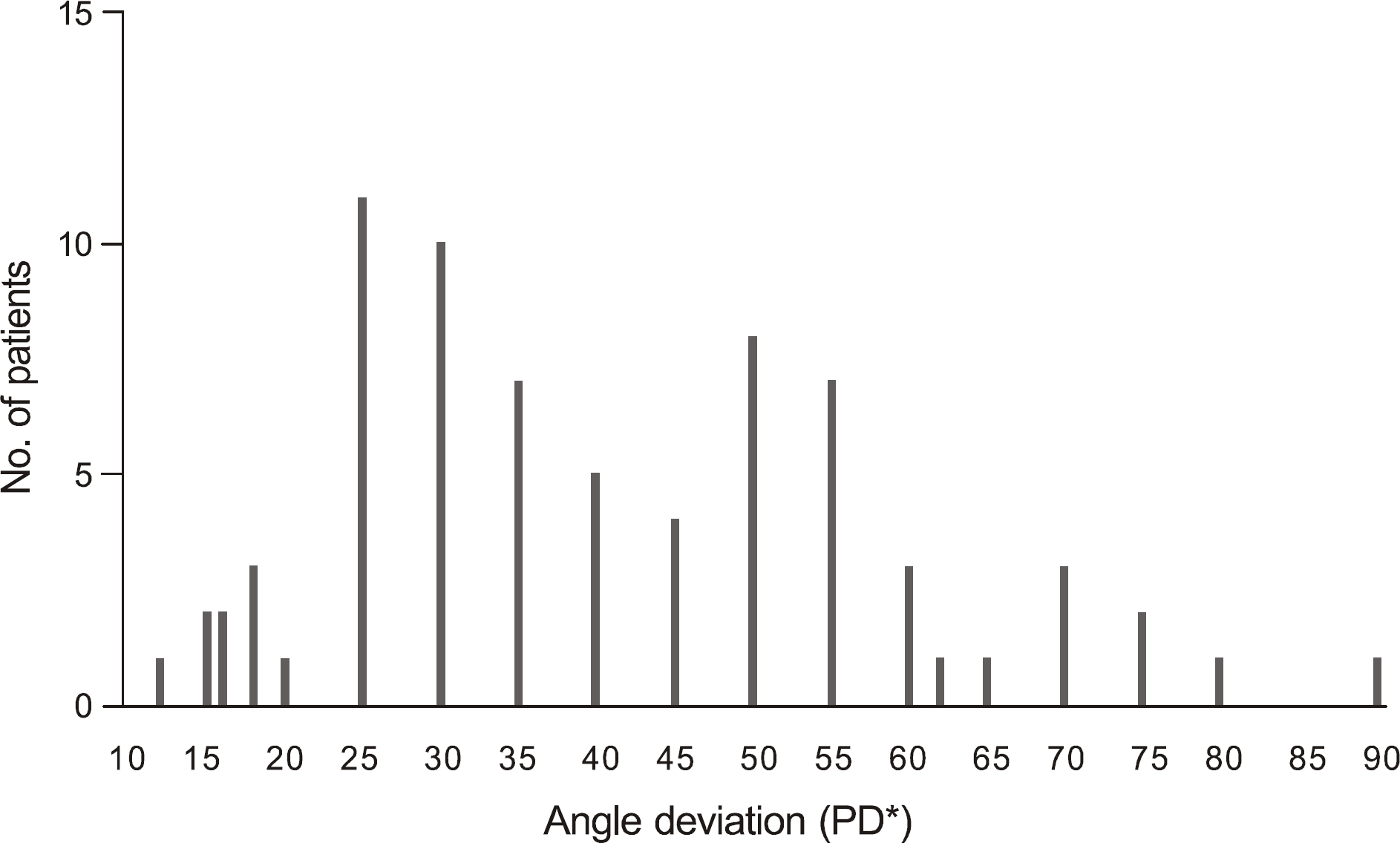
The mean age was 29.47 ± 12.13 years and 42 (57.5%) patients were male. The mean angle of deviation was 40.68 ± 17.75 prism diopter (PD); 46.58% of patients were between 30 to 50 PD and 26% were over 55 PD. Out Of 64 the intermittent exotropic patients, 17 patients had poor fusion at distance. Abnormal findings in binocular function such as poor stereoacuity, suppression at distance, reduced binocular visual acuity at distance, diplopia, panoramic vision, anomalous retinal correspondence, and accommodative spasms were observed. All 20 patients received surgery. Postoperatively, 59.90% of the patients showed improvement in near stereoacuity, and 78.57% improved in suppression at distance.
Conclusions
According to the present study, exotropia may cause subjective and objective deteriorations in mo-tor/sensory function without appropriate medical or surgical intervention during childhood. In addition, the potential for improvement in binocular function after surgery was demonstrated even in adults. Therefore, we recommend surgical treatment for untreated, long-standing exotropia in adults.
Go to : 
References
1. Korean Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus. Exodeviations. Current Concepts in Strabismus. 2nd ed.Seoul: Naewaehaksool;2008. p. 214–32.
2. Rah SH, Jun HS, Kim SH. An epidemiologic survey of strabismus among school-children in Korea. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1997; 38:2195–9.
3. von Noorden GK, Campos EC. Exodeviations. Binocular Vision and Ocular Motility. 6th ed.St Louis: Mosby;2002. p. 356–76.
5. van Selm JL. Primary infantile-onset esotropia–20 years later. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1988; 226:122–5.
6. Murray AD, Orpen J, Calcutt C. Changes in the functional binocular status of older children and adults with previously untreated infantile esotropia following late surgical realignment. J AAPOS. 2007; 11:125–30.

7. Seo YS, Kyung SE, Chang MH. Results of surgical treatment for paralytic strabismus. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1377–85.

8. Sanders SK, Kawasaki A, Purvin VA. Long-term prognosis in patients with vasculopathic sixth nerve palsy. Am J Ophthalmol. 2002; 134:81–4.
9. Wu H, Sun J, Xia X, et al. Binocular status after surgery for constant and intermittent exotropia. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006; 142:822–6.

10. Yoon SC, Paik HJ. The postoperative changes of stereopsis in adult strabismus. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:1807–11.

11. Lee KS, Cho YA, Roh GH. Stereopsis after surgery in longstanding adult horizontal strabismus. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:1656–62.
12. Cho Y, Lee DS, Kim EJ. Longstanding adult horizontal strabismus with early childhood onset. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1992; 33:782–7.
13. Wright KW, Spiegel PH. Exotropia. Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus. 2nd ed.New York: Springer;2003. p. 224–31.
14. Rosenbaum AL, Santiago AP. Intermittent Exotropia. Clinical Strabismus Management. Philadelphia: Saunders;1999. p. 163–75.
15. Gregersen E. The polymorphous exo patient. Analysis of 231 successive cases. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh). 1969; 47:579–90.
16. Nusz KJ, Mohney BG, Diehl NN. The course of intermittent exotropia in a population-based cohort. Ophthalmology. 2006; 113:1154–8.

17. Costenbader FD. The physiology and management of divergent strabismus. Allen JH, editor. Strabismic Ophthalmic Symposium I. St Louis: Mosby;1950. p. 353.
18. Biglan AW, Davis JS, Cheng KP, Pettapiece MC. Infantile exotropia. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1996; 33:79–84.

19. von Noorden GK, Campos EC. Examination of the Patient-III. Binocular Vision and Ocular Motility. 6th ed.St Louis: Mosby;2002. p. 211–45.
Go to : 
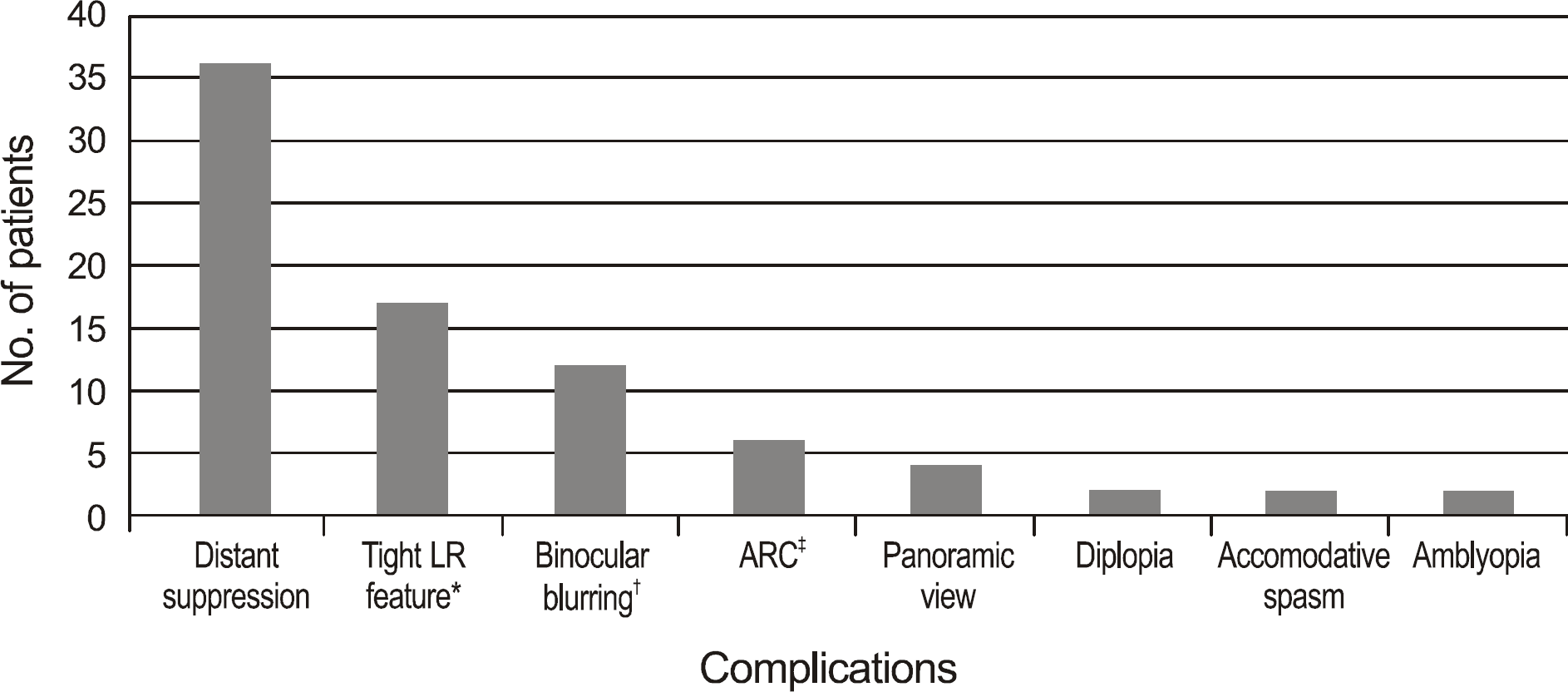 | Figure 3.Motor and sensory complications of longstanding exotropia (duplicative answers possible). * Tight LR feature: mildly reduced adduction may be observed in association with pseudo-overaction of both the superior and inferior oblique muscles, because of the leash effect caused by a tight lateral rectus muscle. † Binocular blurring: 1) each monocular vision was better than 1.0, but binocular vision was worse than 0.8 by Snellen chart. 2) visual acuity was decreased over 2 lines without monocular occlusion. ‡ ARC = abnormal retinal correspondence. |
Table 1.
Demographics of strabismus patients
| Demographics | Total | IXT*: fair fusion at distance | IXT: poor fusion at distance | Constant XT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | 73 | 47 | 17 | 9 |
| Age (mean ± SD, yr) | 29.47 ± 12.13 | 27.57 ± 10.92 | 36.82 ± 12.89 | 25.44 ± 12.28 |
| Age range (yr) | 16–66 | 16–63 | 20–66 | 17–52 |
| Sex (M:F) | 42:31 | 27:20 | 8:9 | 7:2 |
| Stereopsis (mean ± SD, range, sec) | 164.03 ± 597.51 (0–3000) | 44.63 ± 48.21 (0–200) | 568.53 ± 1161.51 (0–3000) | No near stereopsis |
| Poor stereopsis† (patient) | 30 | 11 | 10 | 9 |
| Angle deviation (mean ± SD, PD‡) | 40.68 ± 17.75 | 35.81 ± 15.24 | 46.88 ± 16.21 | 54.44 ± 23.24 |
| Recurrence of XT (patient) | 12 | 6 | 2 | 4 |
Table 2.
Surgical reference table based on the surgical amount that the author usually performed in exotropia surgery
| Deviation (PD*) | Surgical amount (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 6 mm ULR rec.† | | |
| 15 | 7 mm ULR rec. | | |
| 18 | 8.5 mm ULR rec. | | |
| 20 | 10 mm ULR rec. | 5 mm BLR rec.‡ | |
| 25 | | 6 mm BLR rec. | 6 / 4 mm R. & R.§ |
| 30 | | 7 mm BLR rec. | 7.5 / 4 mm R. & R. |
| 35 | | 8 mm BLR rec. | 8 / 4.5 mm R. & R. |
| 40 | | 9 mm BLR rec. | |
| 45 | | 9.5 mm BLR rec. | |
| 50 | | 10 mm BLR rec. | |
| ≥55 | 9 mm BLR rec. + resection of one medial rectus muscle | ||




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download