Abstract
Purpose
To report a case of isolated anterior capsule rupture with cataract after blunt ocular trauma.
Case summary
A 38-year-old male complained of decreased visual acuity in the right eye after blunt ocular trauma 5 days earlier. The visual acuity was counting fingers at 30 cm in the right eye, and intraocular pressure, measured using an applanation tonometer, was 25 mm Hg. Slit lamp examination showed a white intumescent cataract with anterior lens capsule rupture and cortical lens material extruding into the anterior chamber. Under local anesthesia, removal of the cataract was approached via a clear corneal incision. After removal of the cataract using irrigation and aspiration, the intact posterior capsule was observed. IOL haptic was implanted in the sulcus, and IOL optic was implanted in the bag. Postoperatively, the BCVA improved in the right eye to 0.8 at 1 month, and the intraocular pressure, by the Goldmann applanation tonometer was 13 mm Hg at that time.
References
1. Lee SI, Song HC. A case of isolated posterior capsule repture and traumatic cataract caused by blunt ocular trauma. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2001; 15:140–4.
2. Rao SK, Parikh S, Padhmanabhan P. Isolated posterior capsule rupture in blunt trauma: pathogenesis and management. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 1998; 29:338–42.

3. Yasukawa T, Kita M, Honda Y. Traumatic cataract with a ruptured posterior capsule from a nonpenetrating ocular injury. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1998; 24:868–9.

4. Saika S, Kin K, Ohmi S, Ohnishi Y. Posterior capsule rupture by blunt ocular trauma. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1997; 23:139–40.

5. Grewal DS, Jain R, Brar GS, Grewal SP. Posterior capsule rupture following closed globe injury: Scheimpflug imaging, pathogenesis, and management. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2008; 18:453–5.

6. Zabriskie NA, Hwang IP, Ramsey JF, Crandall AS. Anterior lens capsule rupture caused by air bag trauma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1997; 123:832–3.

7. Banitt MR, Malta JB, Main SI, Soong HK. Rupture of anterior lens capsule from blunt ocular injury. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:943–5.

8. Campanella PC, Aminlari A, DeMaio R. Traumatic Cataract and Wiegers Ligamnet. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 1997; 28:422–3.
9. Kim SA, Han SY, Kim TH, et al. A case of posterior capsule rupture after blunt trauma in child. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:1512–6.
10. Kim KS, Ahn Y. A case of isolated posterior capsular rupture caused by blunt trauma. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:1431–4.
Figure 1.
Preoperative and intraoperative photographs. (A) Slit lamp photograph of the right eye shows the triangular shape of the anterior lens capsule rupture and white intumescent cataract (the arrows show the edge of an anterior capsule rupture). The cortical lens material extrudes into the anterior chamber. (B) Scheimflug image of Pentacam shows anterior capsule rupture with intumescent cataract and intact posterior capsule. The central anterior chamber depth is 1 mm. (C) After removal of lens cortex, intact posterior capsule is seen (arrow). (D) Specular microscopy shows normal range of endothelial cell count and pleomorphism index.
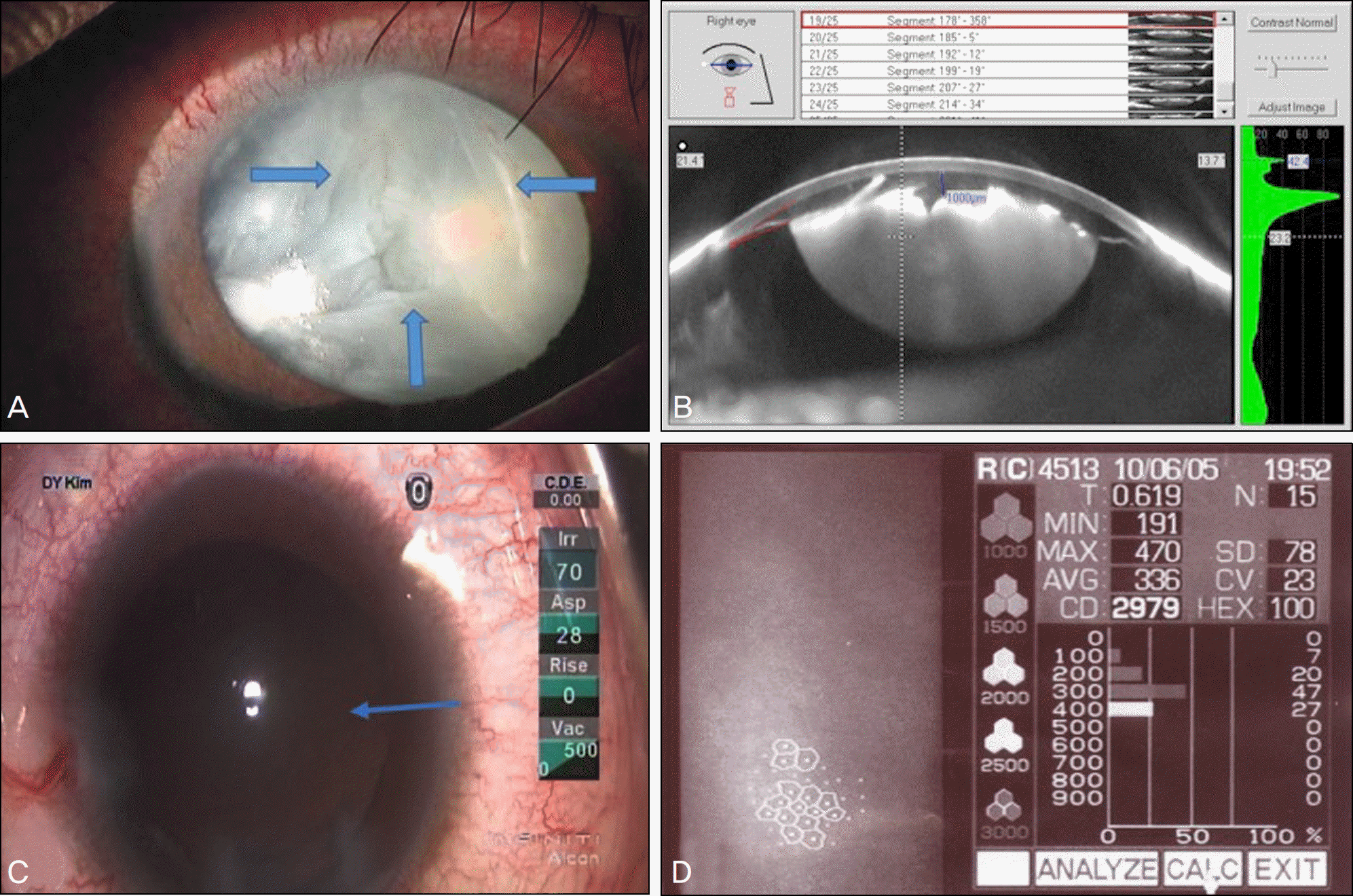
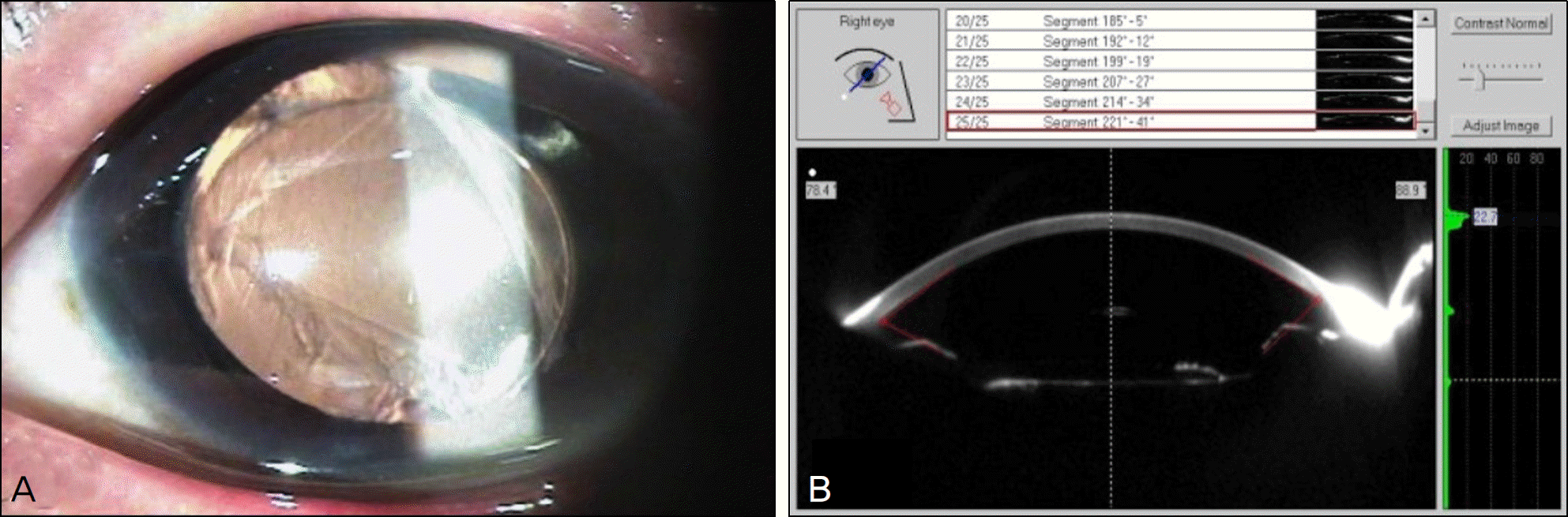
Figure 2.
Postperative photographs 1 month after surgery. (A) The slit lamp photograph shows a well positioned IOL (haptic is located in the sulcus and optic is located in the bag). The triangular shape of anterior capsule rupture is seen. (B) Scheimpflug image shows that IOL optic is well located in the bag. And the central anterior chamber depth is normal.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download