Abstract
Purposse
To determine the efficacy of using the preferential hyperacuity perimeter (PHP) for the analysis of metamorphopsia following macular-off rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (RRD) surgical repair.
Methods
PHP examination was performed in those who complained of metamorphopsia after successful surgical reattachment of RRD. The subjective symptoms were evaluated based on a scale, ranging from 0 to 10, and were compared with the results of PHP examination. Patients age, duration of retinal detachment, pre and post-operative visual acuity, postoperative presence of subretinal fluid (SRF), surgical methods, presence of epiretinal membrane, and time from operation to PHP test were analyzed to find the correlation with the PHP results.
Results
Of the 19 eyes included in this study, nine eyes were found to have a hyperacuity defect upon PHP examination. In this group, the subjective level of metamorphopsia was significantly worse (p<0.01), the age was significantly higher (p=0.02), and SRF persisted in the macula more frequently at two months postoperatively (p=0.04), as compared to those without the defect. There were no significant differences in the other factors.
References
1. Wang Y, Li SY, Zhu M, Chen SJ, et al. Metamorphopsia after abdominalful retinal detachment surgery: an optical coherence abdominal study. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2005; 83:168–71.
2. Amemiya T, Idia Y, Yoshida H. Subjective and objective ocular disturbance in reattached retina after surgery for retinal abdominal, with special reference to visual acuity and metamorphopsia. Ophthalmologica. 1983; 186:25–30.
3. Framme C, Roider J, Hoerauf H, Laqua H. Complications after external retinal surgery in pseudophakic retinal detachment – are scleral buckling operations still current? Klin Monastbl Augenheilkd. 2000; 216:25–32.
4. Kang JH, Yoon HS. Foveal retinal detachment diagnosed by abdominal coherence tomography after successful retinal detachment surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:1637–41.
5. Ahn JH, Chang MH, Kyung SE. Multifocal electroretinography after reattachment of macula-off retinal detachment. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:479–86.

6. Loewenstein A, Malach R, Goldstein M, et al. Replacing the ams-ler grid: A new method for monitoring patients with age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology. 2003; 110:996–70.
7. Lee SC, Nam WH, Yu SY, Kwak HW. Correlation of OCT and preferential hyperacuity perimeter in exudative age-related abdominal degeneration. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:388–95.
8. Kim ES, Nam WH, Yu SY, et al. Analysis of preferential Hyperacuity perimeter results in maculopathy caused by various retinal disease. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:381–87.
9. Anderson DH, Stern WH, Fisher SK, et al. Retinal detachment in the cat: the pigment epithelial-photoreceptor interface. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1983; 24:906–26.
10. Anderson DH, Stern WH, Fisher SK, et al. The onset of pigment epithelial proliferation after retinal detachment. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1981; 21:10–6.
11. Anderson DH, Guerin CJ, Erickson PA, et al. Morphological abdominal in the reattached retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1986; 27:168–83.
12. Barr CC. The histopathology of successful retina reattachment. Retina. 1990; 10:189–94.
13. Wilson DJ, Green WR. Histopathologic study of the effect of abdominall detachment surgery on 49 eyes obtained post mortem. Am J Ophthalmol. 1987; 103:167–79.
Figure 1.
(A) 54-year-old-man with inferior visual field defect in the left eye for 2 weeks, underwent scleral buckling for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (case No. 7). After the operation, he complained of metamorphopsia. (B) Post-operative 7 months, hyperacuity defects were demonstrated in the preferential hyperacuity perimeter. The location of the hyperacuity defect is corresponded to the boundary of detachment in the macula.
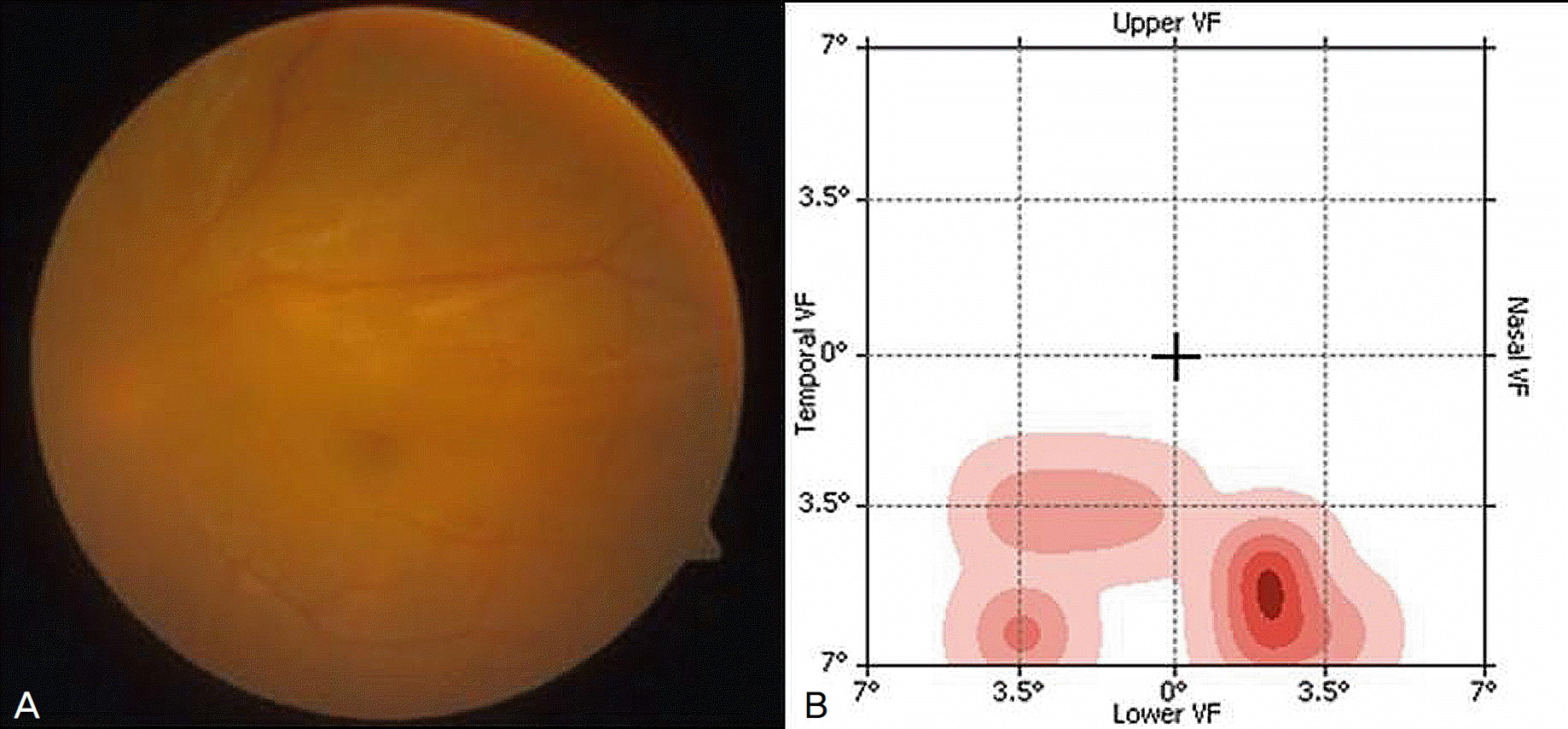
Figure 2.
(A) Normal attached retina. Red Xs represent photoreceptors located in normal position. (B) Total macular ‐off retinal detachment. Green Xs represent photoreceptors displaced position after reattachment. (C) Partial mac-ular‐off retinal detachment. Blue line indicates the boundary of the detachment.
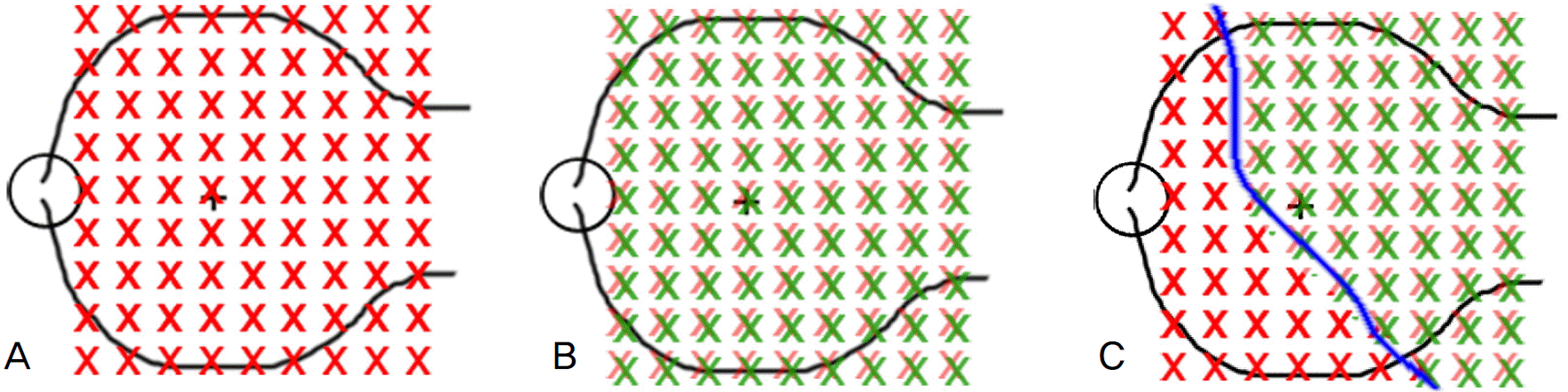
Table 1.
Summary of cases with hyperacuity defect in preferential hyperacuity perimetry
| Case No. | Age |
VA (logMAR) |
Sx. duration (days) | Fovea off | Partial macular detachment | Op. method | SRF* | ERM† fr | Duration om op. to PHP (months) | Metamorphopsia scale | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preop. | Postop. | ||||||||||
| 1 | 55 | 1.00 | 0.30 | 7 | off | + | B‡ | 8 | 8 | ||
| 2 | 71 | 1.10 | 0.52 | 20 | off | + | V§ | + | 5 | 6 | |
| 3 | 49 | 1.69 | 1.00 | 28 | off | B+V | + | + | 7 | 8 | |
| 4 | 73 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 14 | off | + | B | 6 | 9 | ||
| 5 | 62 | 1.00 | 0.15 | 30 | off | V | + | + | 19 | 9 | |
| 6 | 72 | 1.22 | 0.70 | 30 | off | V | + | + | 8 | 8 | |
| 7 | 54 | 0.52 | 0.10 | 14 | + | B | 7 | 6 | |||
| 8 | 57 | 0.70 | 0.30 | 6 | + | B | 15 | 6 | |||
| 9 | 60 | 1.00 | 0.30 | 3 | off | + | B | + | 6 | 6 | |
| Mean | 61.4 | 1.00 | 0.42 | 16.9 | 9.0 | 7.3 | |||||
Table 2.
Summary of cases without hyperacuity defect in preferential hyperacuity perimetry
| Case No. | Age |
VA (logMAR) |
Sx. duration (days) | Fovea off | Partial macular detachment | Op. method | SRF* ERM† | Duration from op. to PHP (months) | Metamorphopsia scale | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preop. | Postop. | |||||||||
| 10 | 42 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 14 | + | B‡ | 16 | 1 | ||
| 11 | 27 | 1.00 | 0.70 | 30 | off | B | 6 | 6 | ||
| 12 | 22 | 1.22 | 1.00 | 14 | off | B | + | 16 | 2 | |
| 13 | 35 | 0.70 | 0.30 | 7 | off | + | B | 15 | 6 | |
| 14 | 58 | 0.40 | 0.20 | 7 | + | V§ | 16 | 2 | ||
| 15 | 71 | 0.30 | 0.05 | 5 | + | V | + | 22 | 2 | |
| 16 | 74 | 0.52 | 0.20 | 14 | off | + | B | 15 | 8 | |
| 17 | 46 | 0.40 | 0 | 14 | + | B | 7 | 2 | ||
| 18 | 28 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 30 | off | + | B | 15 | 1 | |
| 19 | 58 | 1.00 | 0.52 | 7 | off | B | + | 12 | 6 | |
| Mean | 46.1 | 0.65 | 0.35 | 14.2 | 14.0 | 3.6 | ||||
Table 3.
Comparison between groups with and without hyperacuity defect
| PHP (+) group* | PHP (−) group† | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 61.4 | 46.1 | 0.02 |
| VA (logMAR) | |||
| Preop. | 1.00 | 0.65 | 0.06 |
| Postop. | 0.42 | 0.35 | 0.50 |
| Symptom duration (days) | 16.9 | 14.2 | 0.72 |
| Fovea-off | 7 | 6 | 0.28 |
| Buckle (No.) | 5 | 8 | 0.29 |
| Vitrectomy (No.) | 3 | 2 | 0.29 |
| ERM‡ (No.) | 3 | 2 | 0.33 |
| SRF§ (No.) | 5 | 1 | 0.04 |
| Duration from op to PHP (months) | 9.0 | 13.8 | 0.05 |
| Metamorphopsia scale | |||
| Median | 8 | 2 | <0.01 |
| Minimum | 6 | 1 | – |
| Maximum | 9 | 8 | – |
Table 4.
Sum mmary of cases with par tial macular retinal detachment in hyperacuity defect group
| Case | Location of detachment | Fovea-off | Boundary of detachment | Location of |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | In the macula | Fovea-off | In the macula | hyperacuity defect |
| 1 | Inferior | off | ST*, SN† | ST |
| 2 | Temporal | off | SN. IN‡, IT§ | SN |
| 4 | Temporal | off | SN, IN | SN |
| 7 | Superior | ST, SN | ST, SN | |
| 8 | Superior | ST, SN | ST | |
| 9 | Inferior | off | ST, SN | ST, SN, IN |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download