Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the effect of clear corneal incisional size on astigmatism during cataract surgery.
Methods
Randomized prospective study of 78 patients (108 eyes) who had received cataract surgery for a corneal astigmatism over against-the-rule (ATR) 1.0 Diopter (D) was performed. The eyes were checked by corneal topography and autorefractor preoperatively and one week, one month, two months, and six months postoperative. Group 1 included patients who received an inserted foldable intraocular lens (IOL) through a 2.8 mm incision, and Group 2 included patients who underwent IOL implantation through a corneal incision enlarged to 4 mm.
Results
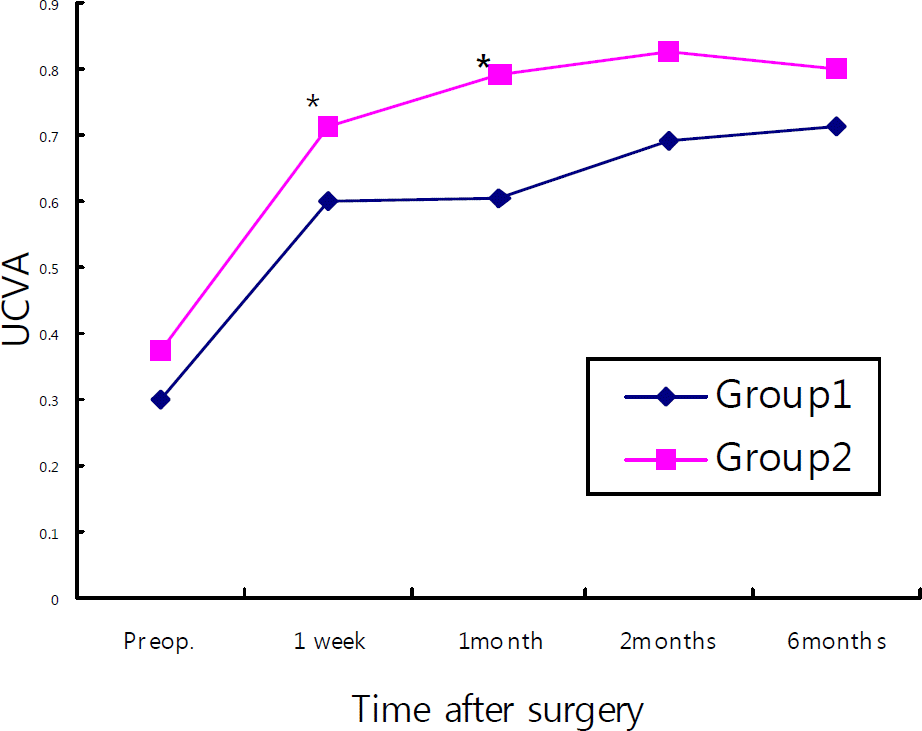
Postoperative visual acuity showed a better visual acuity in Group 2 at both one week postoperatively (0.598±0.352 vs., 0.713±0.345, for Groups 1 and 2, respectively, p=0.046) and one month postoperatively (0.604±0.237 vs., 0.791±0.242, respectively, p=.043). There were no statistically significant differences between the groups after two and six months (p=.135, .087). Postoperative astigmatism measured by corneal topopgraphy showed 1.62±0.44D and, 0.94±0.30D for groups 1 and 2 respectively, (P=.045) at 2 months, and 1.73±0.45 D and, 0.92±0.34 D (P=.042) at six months. These results showed a statistically significant amount of residual astigmatism in Group 2. Autorefractor measurements showed similar results. There were no complications, such as wound leakage, resulting from the increased incision size.
Go to : 
References
1. Amesbury EC, Miller KM. Miller Correction of astigmatism at the time of cataract surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2009; 20:19–24.
2. Borasio E, Mehta JS, Maurino V. Torque and flattening effects of clear corneal temporal and on-axis incisions for phacoemulsification. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:2030–8.

3. Khokhar S, Lohiya P, Murugiesan V, Panda A. Corneal abdominal correction with opposite clear corneal incisions or single clear corneal incision: comparative analysis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:1432–7.
4. Bauer NJ, de Vries NE, Webers CA, et al. Astigmatism abdominal in cataract surgery with the AcrySof toric intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:1483–8.
5. Jee DH, Lee PY, Joo CK. The comparison of astigmatism abdominal to the incision size in cataract operation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:594–8.
6. Neumann AC, McCarty GR, Sanders DR, Raanan MG. Small abdominals to control astigmatism during cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1989; 15:78–84.
7. Steinert RF, Brint SF, White SM, Fine IH. Astigmatism after small incision cataract surgery: a prospective, randomized abdominal comparison of 4- and 6.5-mm incisions. Ophthalmology. 1991; 98:417–24.
8. Gills JP, Sanders DR. Use of small incisions to control induced abdominal and inflammation following cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1991; 17:740–4.
9. Olson RJ, Crandall AS. Prospective randomized comparison of phacoemulsification cataract surgery with a 3.2-mm vs a 5.5-mm sutureless incision. Am J Ophthalmol. 1998; 125:612–20.

11. Wishart MS, Wishart PK, Gregor ZJ. Corneal astigmatism abdominal cataract extraction. Br J Ophthalmol. 1986; 70:825–30.
12. Osher RH. Microcoaxial phacoemulsification Part 2: clinical study. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:408–12.
13. Tong N, He JC, Lu F, et al. Changes in corneal wavefront aberrations in microincision and small-incision cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:2085–90.

14. Crema AS, Walsh A, Tamane Y, Nose W. Comparative study of coaxial phacoemulsification and microincision cataract surgery. One-year follow-up. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:1014–8.
15. Ku CH, Kim HJ, Joo CK. The comparison of astigmatism abdominal to the incision size in small incision cataract surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:416–21.
16. Moon SC, Mohamed T, Fine IH. Comparison of surgically abdominal astigmatisms after clear corneal incisions of different sizes. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2007; 21:1–5.
Go to : 
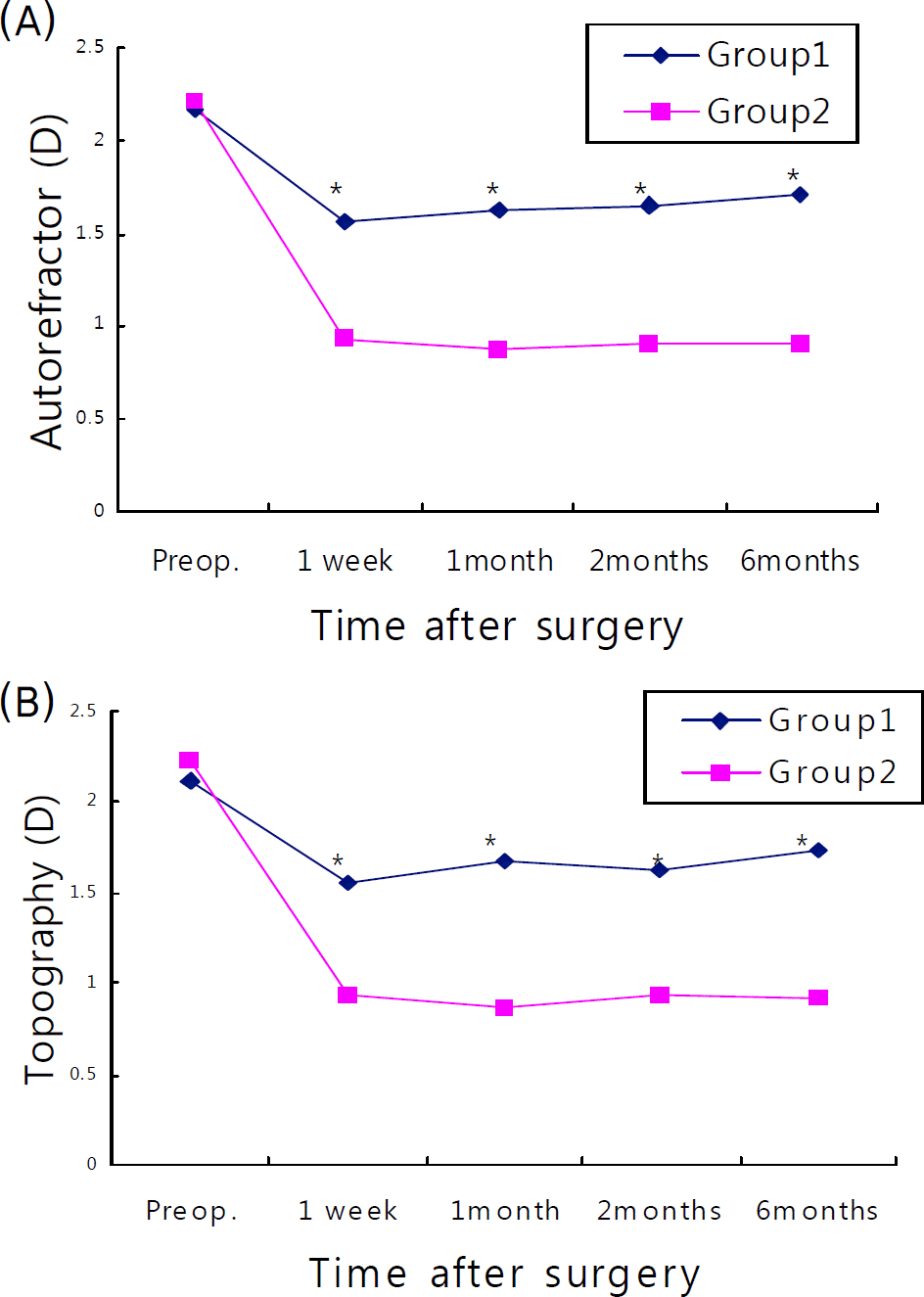 | Figure 2.The mean astigmatism (D) in 2 groups by autorefractor (A), and topography measurement (B). (*p<0.05). |
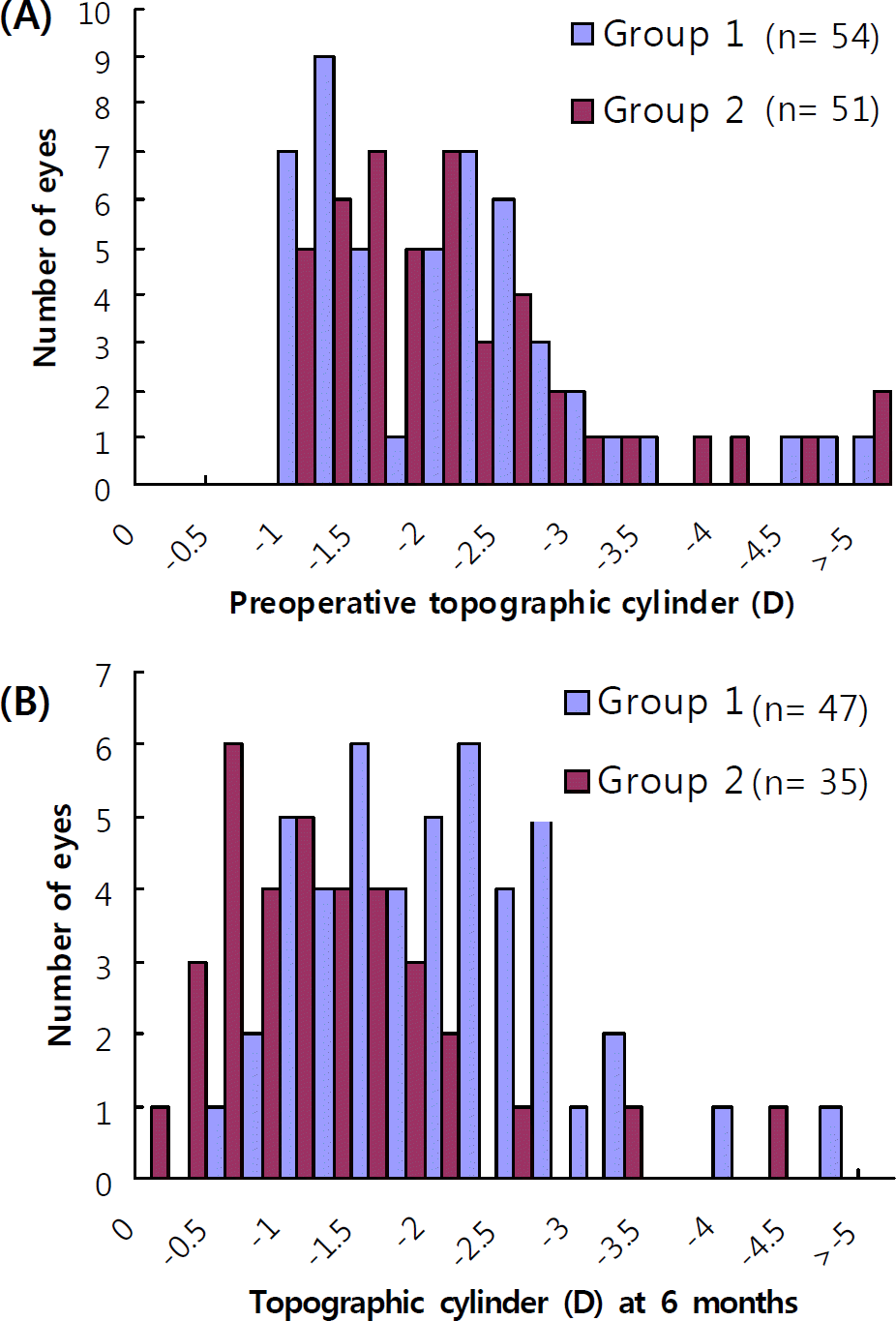 | Figure 3.A: Preoperative topographic cylinder (D), B: Residual topographic cylinder (D) at 6 months. |
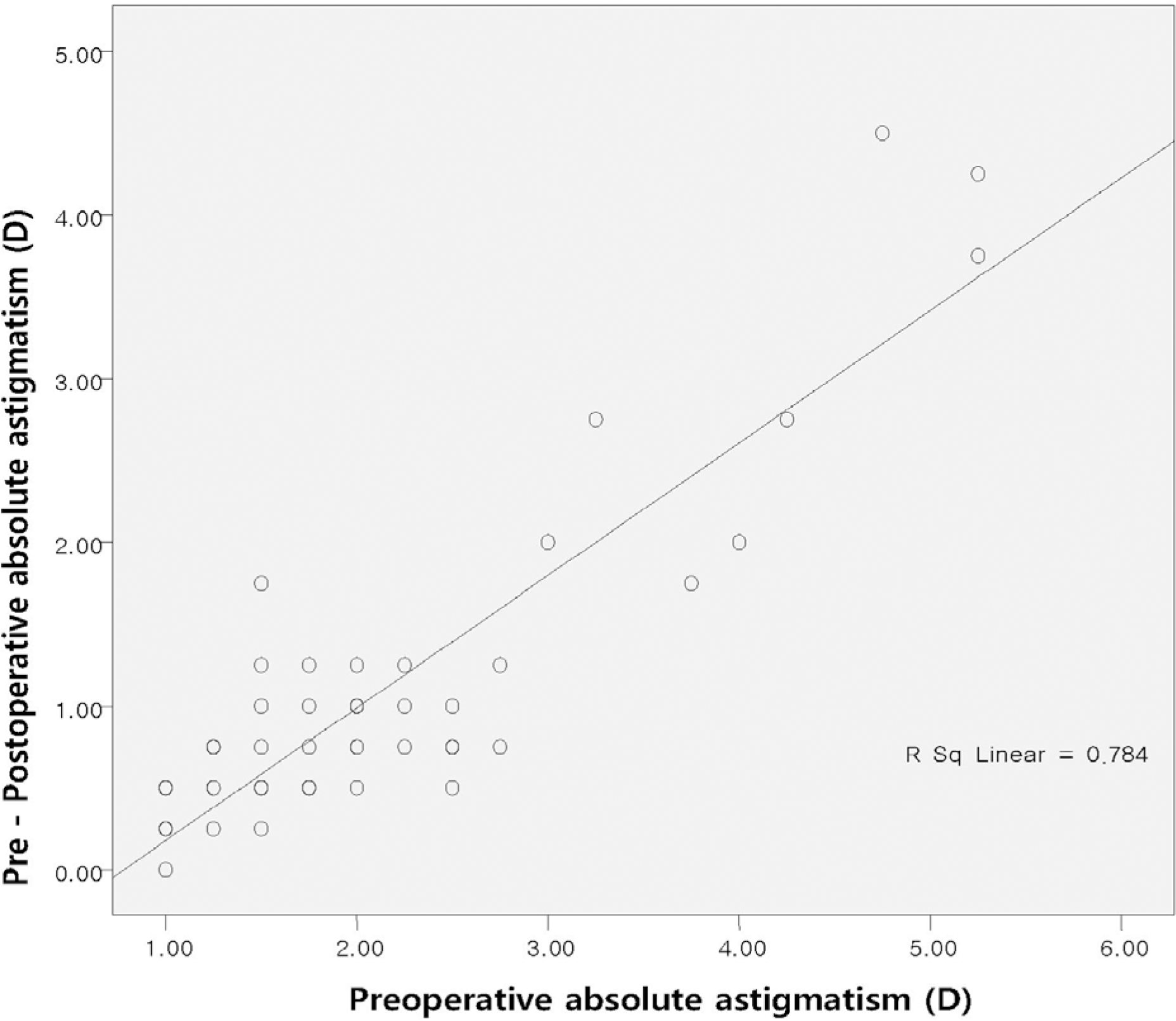 | Figure 4.Scattergram of preoperative versus difference between preoperative and postoperative absolute astigmatism at 6 months in 4.0 mm incision group (R2=0.784, p<0.05). |
Table 1.
Demographics and preoperative astigmatism of the 2 groups
Table 2.
Preoperative and postoperative visual acuity of the 2 groups
| Group1 | Group2 | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| UCVA* | |||
| Preoperative (n=108) | 0.302±0.146 | 0.372±0.112 | 0.536 |
| Postoperative 1 week (n=107) | 0.598±0.352 | 0.713±0.345 | 0.046 |
| Postoperative 1 month (n=106) | 0.604±0.237 | 0.791±0.242 | 0.043 |
| Postoperative 2 months (n=100) | 0.693±0.337 | 0.827±0.233 | 0.135 |
| Postoperative 6 months (n=92) | 0.713±0.346 | 0.802±0.213 | 0.087 |
| BCVA† | |||
| Preoperative (n=108) | 0.470±0.227 | 0.438±0.237 | 0.623 |
| Postoperative 1 week (n=107) | 0.824±0.287 | 0.831±0.269 | 0.874 |
| Postoperative 1 month (n=106) | 0.862±0.134 | 0.895±0.255 | 0.607 |
| Postoperative 2 months (n=100) | 0.932±0.176 | 0.903±0.168 | 0.771 |
| Postoperative 6 months (n=92) | 0.913±0.137 | 0.904±0.204 | 0.787 |
Table 3.
The mean astigmatism in the 2 groups by autorefractor and mannual keratometry




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download