Abstract
Purpose
To report a case of laser photocoagulation treatment for the patient of Coats' disease accompanying a retinal macrocyst.
Case summary
A three-year-old boy visited the hospital whose chief complaint was visual acuity decrease of his left eye. Fundus examination showed macular scar, foveal hard exudates and inferior retinal cystic lesion in his left eye. Two months later, examination under anesthesia (EUA) and fluorescein angiography (FAG) was performed. The results revealed inferior retinal macrocyst, nasal avascular retina and telangiectasia around the retinal macrocyst. Laser photocoagulation was performed around the retinal macrocyst and at the nasal avascular retina. One year after the laser photocoagulation, retinal macrocyst did not further progress and the retina was stabilized.
References
2. Choi SY, Yu YS. Treatment and clinical results of Coats' disease. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:2190–7.
4. Shields JA, Shields CL, Honavar SG, et al. Classification and management of Coats disease. The 2000 Proctor Lecture. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001; 131:572–83.

6. Shields JA, Shields CL, Honavar S, Demirci H. Coats' disease. Clinical variations and complications of Coats' disease in 150 cases. The 2000 Sanford Gifford Memorial Lecture. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001; 131:561–71.
7. Imre G. Coats' disease. Am J Ophthalmol. 1962; 54:175.
8. Tolentino MJ, McLeod DS, Taomoto M, et al. Pathologic features of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced retinopathy in the nonhuman primate. Am J Ophthalmol. 2002; 133:373–85.

9. Tolentino MJ, Miller JW, Gragoudas ES, et al. Intravitreous injections of vascular endothelial growth factor produce retinal ischemia and microangiopathy in an adult primate. Ophthalmology. 1996; 103:1820–8.

10. Su CY, Chen MT, Wu WS, Wu WC. Concentration of vascular endothelial growth factor in the subretinal fluid of retinal detachment. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2000; 16:463–9.

11. Sun Y, Jain A, Moshfeghi DM. Elevated vascular endothelial growth factor levels in Coats disease: rapid response to pegaptanib sodium. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2007; 245:1387–8.

12. Venkatesh P, Mandal S, Garg S. Management of Coats disease with bevacizumab in 2 patients. Can J Ophthalmol. 2008; 43:245–6.

13. Alvarez-Rivera LG, Abraham-Marin ML, Flores-Orta HJ, et al. Coats' disease treated with bevacizumab. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2008; 83:329–31.
Figure 1.
Fundus photograph of the left eye taken on the day of the first visit. (A) Large retinal cystic lesion at the inferior to the inferotemporal major arcade is observed. (B) Foveal hard exudates and macular scar changes are also observed.
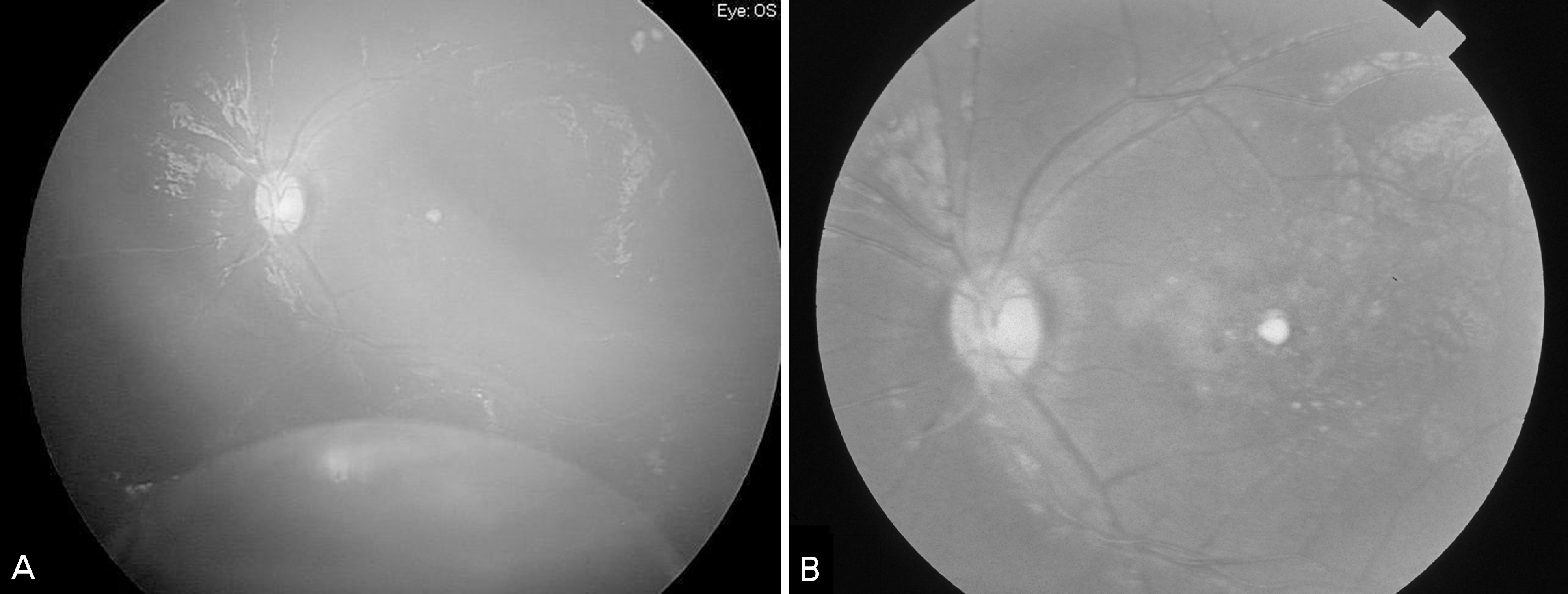
Figure 2.
Ultrasonography of the left eye taken on the day of the first visit. Cystic lesion and intracystic hypoechoic signals are observed.
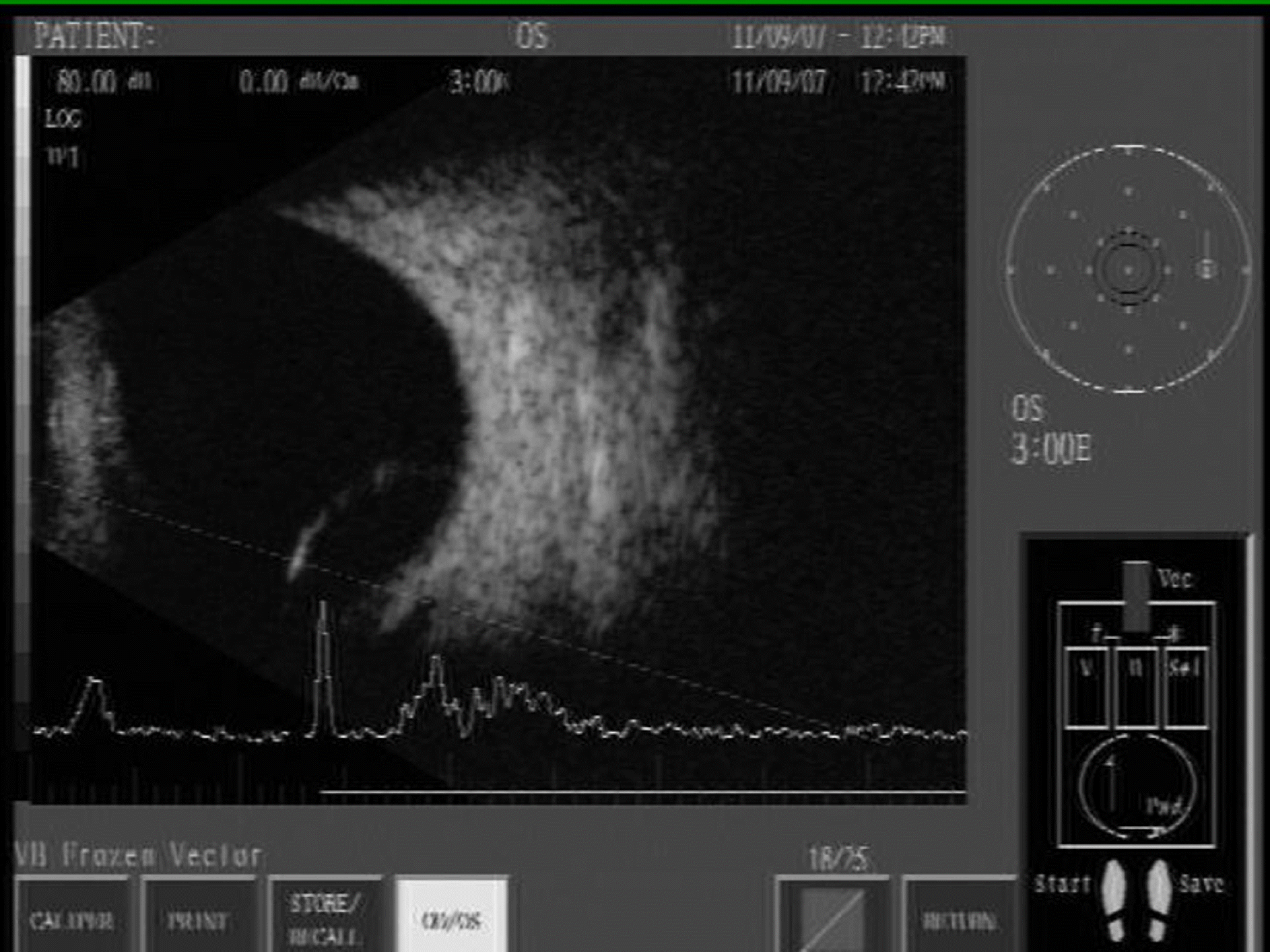
Figure 3.
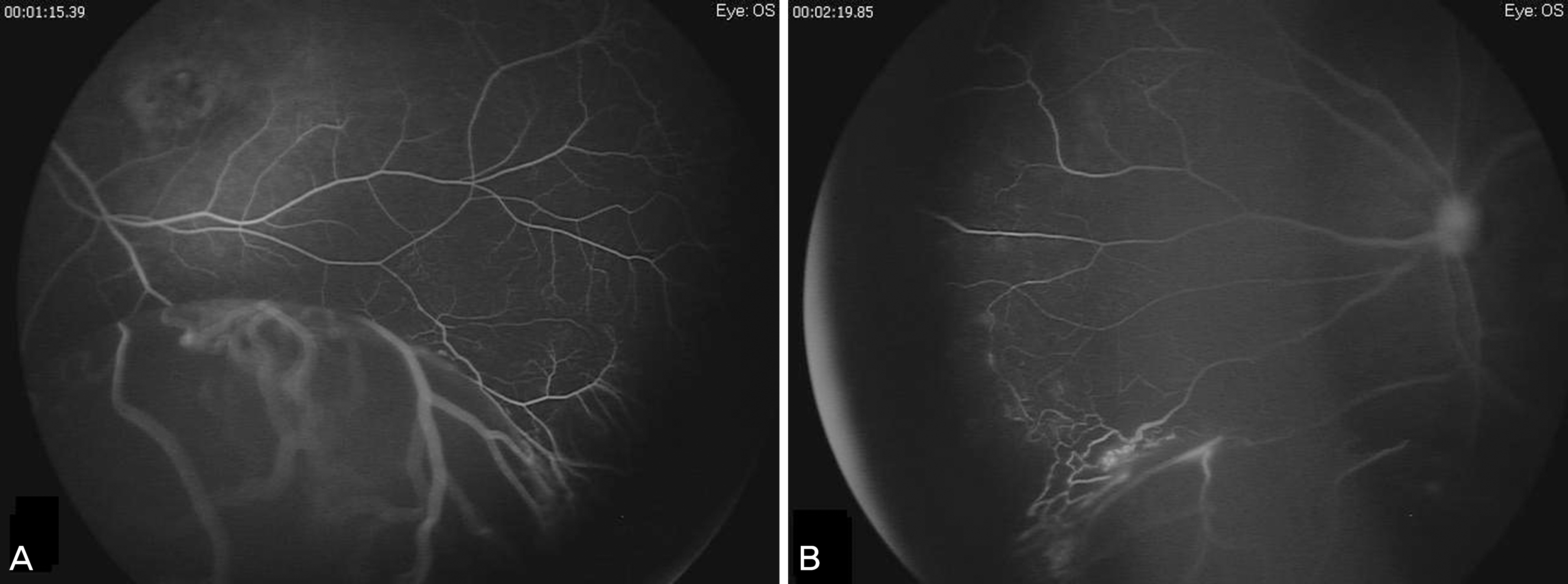
Fluorescein angiogram before the laser photocoagulation during the examination under anesthesia shows retinal macrocyst (A), telangiectatic vessel around the macrocyst and nasal avascular area (B).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download