Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate longitudinal changes in retinal nerve fiber layer thickness (RNFL) and visual field in patients with normal tension glaucoma (NTG).
Methods
Thirty eyes of 30 NTG patients and 30 eyes of 30 normal control subjects were enrolled in the present study. RNFL thickness was measured using optical coherence tomography (OCT), and visual field tests were performed using a Humphrey visual field analyzer at baseline and 23.3 ± 15.3 months later. Changes in RNFL thickness at each clock-hour segment and visual field sensitivities were analyzed. The rates of change in RNFL thickness were also calculated.
Results
Significant differences in RNFL thickness were observed between NTG patients and normal control subjects at the 5, 6, 7 and 12 o'clock positions at baseline (p < 0.001). At follow-up, the RNFL thickness change was not significant for normal control subjects, although it was significant for NTG patients at the 4, 5, 6, 7, 11 and 12 o'clock positions (p < 0.001). Visual field parameters did not change significantly in the normal control subjects or NTG patients. The reduction rates of RNFL thickness were 0.38 μ m/month for the NTG patients and 0.11 μ m/month for the normal control group, displaying a 3.5-fold faster reduction rate for NTG patients.
Conclusions
The NTG group showed greater reductions in RNFL thickness in the upper and lower sectors over time; however, the visual field parameters did not change significantly. The results suggest that progression of glaucoma can be detected in an earlier stage using OCT than can be detected using a visual field test.
Go to : 
References
1. Levene RZ. Low tension glaucoma: a critical review and new material. Surv Ophthalmol. 1980; 24:621–64.

2. Quigley HA, Miller NR, George T. Clinical evaluation of nerve fiber layer atrophy as an indicator of glaucomatous optic nerve damage. Arch Ophthalmol. 1980; 98:1564–71.

3. Gupta N, Weinreb RN. New definitions of glaucoma.Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 1997; 8:38–41.
4. Salmon JF. Predisposing factors for chronic angle-closure glaucoma. Prog Retin Eye Res. 1999; 18:121–32.

5. Quigley HA, Dunkelberger GR, Green WR. Retinal ganglion cell atrophy correlated with automated perimetry in human eyes with glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1989; 107:453–64.

6. Sommer A, Katz J, Quigley HA, et al. Clinically detectable nerve fiber atrophy precedes the onset of glaucomatous field loss. Arch Ophthalmol. 1991; 109:77–83.

7. Sommer A, Miller NR, Pollack I, et al. The nerve fiber layer in the diagnosis of glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 1977; 95:2149–56.

8. Niessen AG, Van Den Berg TJ, Langerhorst CT, Greve EL. Retinal nerve fiber layer assessment by laser polarimetry and standardized photography. Am J Ophthalmol. 1996; 21:484–93.
9. Tuulonen A, Airaksinen PJ, Montaga A, Nieminen H. Screening for glaucoma with a non-mydriatic fundus camera. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh). 1990; 68:445–9.

10. Quigley HA, Katz J, Derick RJ, et al. An evaluation of optic disc and nerve fiber layer examinations in monitoring progression of early glaucoma damage. Ophthalmology. 1992; 99:19–28.

11. Weinreb RN, Shakiba S, Sample PA, et al. Association between quantitative nerve fiber layer measurement and visual field loss in glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1995; 120:732–8.

12. Poinoosawmy D, Tan JC, Bunce C, et al. Longitudinal nerve fiber layer thickness change in normal-pressure glaucoma. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2000; 238:965–9.
13. Tjon-Fo-Sang MJ, Lemij HG. Retinal nerve fiber layer measurements in normal black subjects as determined with scanning laser polarimetry. Ophthalmology. 1998; 105:78–81.

14. Chi T, Ritch R, Stickler D, et al. Racial differences in optic nerve head parameters. Arch Ophthalmol. 1989; 107:836–9.

15. Poinoosawmy D, Fontana L, Wu JX, et al. Variation of nerve fiber layer thickness measurements with age and ethnicity by scanning laser polarimetry. Br J Ophthalmol. 1997; 81:350–4.
17. Johnson CA, Cioffi GA, Liebmann JR. The relationship between structural and fucntional alterations in glaucoma: a review. Semin Ophthalmol. 2000; 15:221–3.
18. Tjon-Fo-Sang MJ, de Vries J, Lemij HG. Measurement by nerve fiber layer analyzer of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in normal subjects and patients with ocular hypertension. Am J Ophthalmol. 1996; 122:220–7.
19. Lee WH, Mok KH. Retinal nerve fiber layer measurement by nerve fiber analyzer in normal subjects and patients with glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 1999; 106:1006–8.
20. Choplin NT, Lundy DC, Dreher AW. Differentiating patients with glaucoma from glaucoma suspects and normal subjects by nerve fiber layer assessment with scanning laser polarimetry. Ophthalmology. 1998; 105:2068–76.
21. Tuulonen A, Airaksinen J. Polarimetry of the retinal nerve fiber layer. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 1996; 7:34–8.

22. Lee WH, Mok KH. Nerve fiber layer measurement of the Hong Kong Chinese population by scanning laser polarimetry. Eye. 2000; 14:371–4.
23. Radius RL. Regional specificity in anatomy at the lamina cribrosa. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981; 99:478–80.

24. Quigley HA, Addicks EM. Regional differences in the structure of the lamina cribrosa and their relation to glaucomatous optic nerve damage. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981; 99:137–43.

25. Leung CK, Cheung CY, Weinreb RN, et al. Evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer progression in glaucoma: a study on optical coherence tomography guided progression analysis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010; 51:217–22.

26. Lee EJ, Kim TW, Park KH, et al. Ability of Stratus OCT to detect progressive retinal nerve fiber layer atrophy in glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009; 50:662–8.

27. Jonas J, Anselm E, Grundler E. Correlation between mean visual field loss and morphometric optic disc variables in the open angle glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1997; 124:488–97.
28. Lee HJ, Choi KR. Longitudinal study of nerve fiber layer thickness change in open angle glaucoma. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002; 43:1656–63.
Go to : 
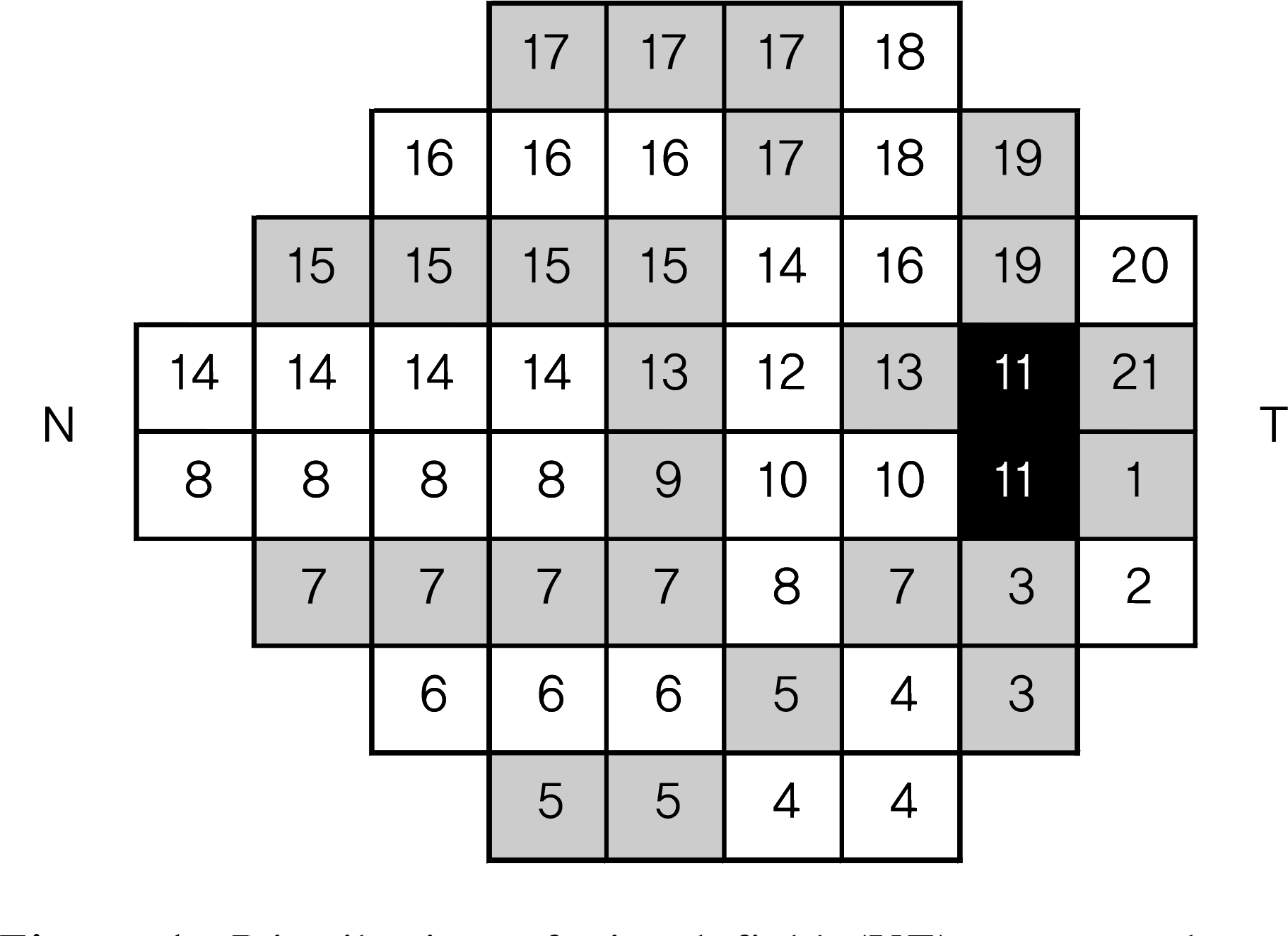 | Figure 1.Distribution of visual field (VF) zones and associated short-wavelength automated perimetry test points relative to temporal (T) and nasal (N) retinal positions. Odd-numbered VF zones are shaded gray. |
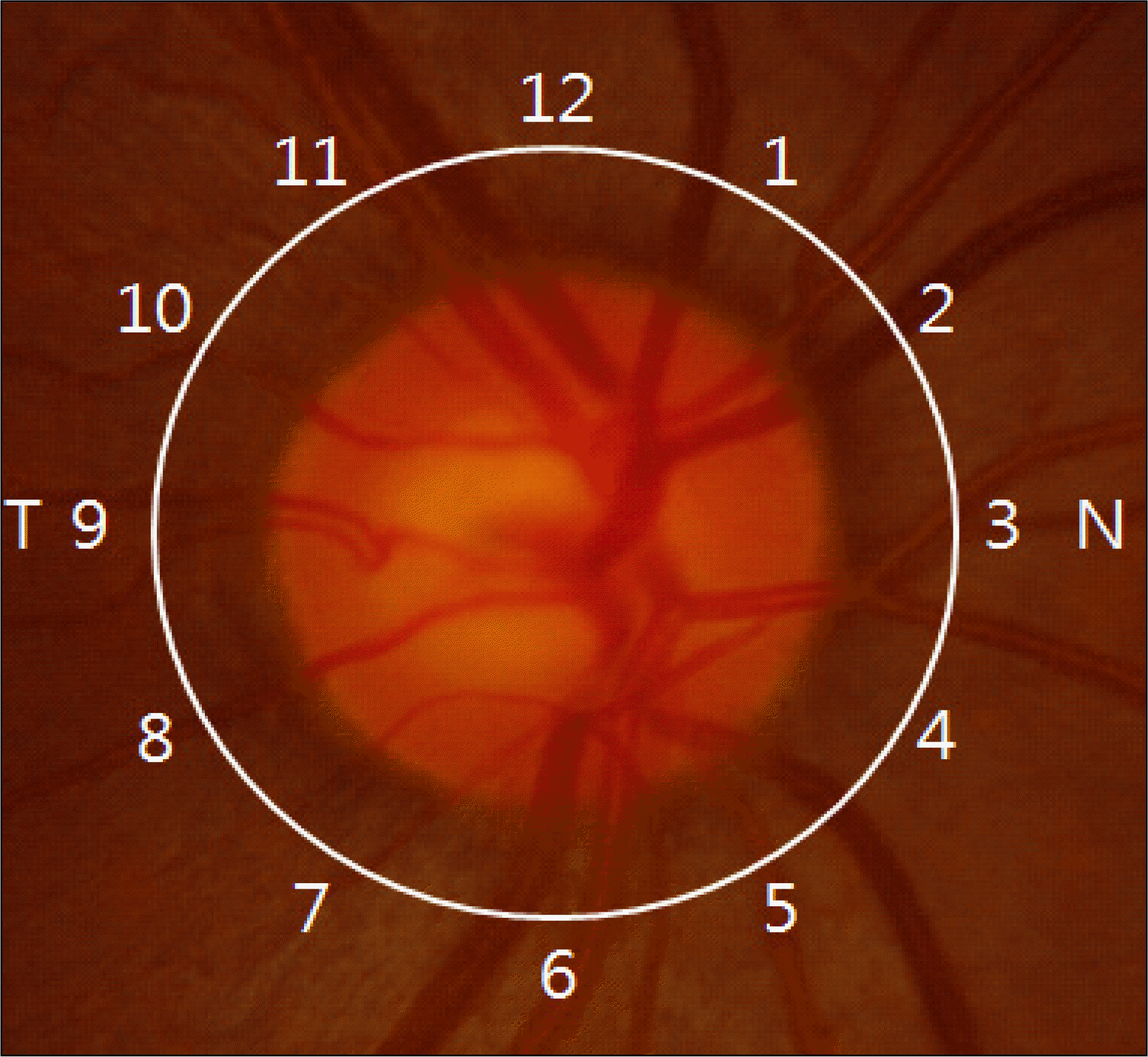 | Figure 2.Optical coherence tomography 30-degree sectors in a clock hour distribution relative to temporal (T) and nasal (N) retinal positions. |
Table 1.
Patient characteristics
| |
Study subjects (n = 60) (mean ± standard deviation) |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Control (n = 30) | NTG* (n = 30) | p value† | |
| Male/Female | 30 (14/16) | 30 (13/17) | 0.332 |
| Age (yr) | 41.4 ± 16.1 | 45.2 ± 12.7 | 0.203 |
| Refractive error (D sph) | −1.211 ± 1.101 | −1.411 ± 2.911 | 0.354 |
| IOP‡ (mmHg) | 13.8 ± 2.3 | 14.1 ± 2.6 | 0.553 |
| Follow up (mon) | 20.74 ± 15.22 | 25.88 ± 15.90 | 0.364 |
| Frequency of OCT§ | 2.83 ± 0.74 | 3.13 ± 0.93 | 0.391 |
| Frequency of VF∏ | 2.93 ± 0.89 | 3.03 ± 0.85 | 0.372 |
| Cup/Disc ratio | 0.28 ± 0.08 | 0.67 ± 0.16 | <0.01 |
| Mean deviation (MD) | −3.13 ± 2.37 | −7.92 ± 6.83 | <0.01 |
| Pattern standard deviation (PSD) | 1.91 ± 0.52 | 6.99 ± 4.85 | <0.01 |
Table 2.
Baseline retinal nerve fiber layer thickness (μ m) of control and NTG
| Clock hour position (o'clock) |
Mean ± standard deviation (μ m) |
p value† | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control group | NTG* group | ||
| 1 | 105.50 ± 40.51 | 100.20 ± 24.65 | 0.596 |
| 2 | 75.79 ± 24.06 | 79.90 ± 15.13 | 0.561 |
| 3 | 52.14 ± 12.84 | 58.13 ± 10.37 | 0.134 |
| 4 | 61.86 ± 20.19 | 62.93 ± 11.10 | 0.853 |
| 5 | 95.57 ± 23.19 | 80.40 ± 20.12 | 0.041 |
| 6 | 128.79 ± 36.50 | 95.83 ± 28.95 | 0.050 |
| 7 | 123.93 ± 28.47 | 97.77 ± 36.74 | 0.013 |
| 8 | 66.93 ± 21.32 | 65.07 ± 20.44 | 0.786 |
| 9 | 54.64 ± 12.08 | 56.33 ± 12.13 | 0.668 |
| 10 | 74.21 ± 26.07 | 75.20 ± 14.70 | 0.896 |
| 11 | 118.36 ± 27.95 | 103.47 ± 23.12 | 0.090 |
| 12 | 122.57 ± 23.08 | 100.83 ± 29.61 | 0.011 |
| Total | 90.11 ± 17.11 | 81.34 ± 16.26 | 0.116 |
Table 3.
Baseline visual field parameter of control and NTG
| Visual field zone |
Mean ± standard deviation |
p value† | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control group | NTG* group | ||
| 1 | −1.29 ± 2.23 | −1.80 ± 3.63 | 0.629 |
| 2 | −1.21 ± 1.31 | −3.83 ± 6.20 | 0.034 |
| 3 | −1.46 ± 0.77 | −3.52 ± 6.76 | 0.111 |
| 4 | −1.45 ± 0.82 | −4.44 ± 6.70 | 0.022 |
| 5 | −2.29 ± 1.16 | −5.08 ± 6.05 | 0.021 |
| 6 | −1.83 ± 0.84 | −4.61 ± 6.23 | 0.023 |
| 7 | −1.82 ± 0.94 | −5.71 ± 8.98 | 0.026 |
| 8 | −1.97 ± 1.33 | −7.27 ± 8.97 | 0.003 |
| 9 | −1.29 ± 1.64 | −4.73 ± 9.40 | 0.060 |
| 10 | −1.00 ± 0.96 | −1.47 ± 3.72 | 0.648 |
| 11 | 0 | 0 | |
| 12 | −1.07 ± 0.92 | −3.80 ± 7.92 | 0.208 |
| 13 | −1.79 ± 1.48 | −4.33 ± 8.60 | 0.125 |
| 14 | −2.16 ± 1.32 | −7.30 ± 8.21 | 0.002 |
| 15 | −1.88 ± 0.73 | −6.68 ± 8.31 | 0.004 |
| 16 | −1.79 ± 0.81 | −7.43 ± 8.80 | 0.002 |
| 17 | −1.73 ± 1.20 | −7.06 ± 7.23 | <0.001 |
| 18 | −1.50 ± 2.34 | −7.38 ± 8.06 | 0.001 |
| 19 | −1.29 ± 1.33 | −5.78 ± 7.49 | 0.003 |
| 20 | −0.93 ± 1.44 | −3.37 ± 5.35 | 0.026 |
| 21 | −0.64 ± 1.78 | −2.97 ± 5.35 | 0.122 |
| MD‡ | −2.81± 1.87 | −7.93 ± 6.83 | 0.001 |
| PSD§ | 1.92 ± 0.52 | 6.99 ± 4.85 | <0.001 |
Table 4.
Changes in retinal nerve fiber layer thickness (μ m) for control and NTG (mean ± standard deviation)
| Clock hour position (o'clock) |
Control (20.74 ± 15.22 months follow up) |
NTG* (25.88 ± 15.90 months follow up) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Follow up | p value† | Baseline | Follow up | p value† | |
| 1 | 105.50 ± 24.65 | 107.93 ± 22.64 | 0.414 | 100.20 ± 40.51 | 95.30 ± 40.20 | 0.225 |
| 2 | 75.79 ± 15.13 | 79.64 ± 12.53 | 0.223 | 79.90 ± 24.06 | 74.97 ± 25.92 | 0.079 |
| 3 | 52.14 ± 10.37 | 54.79 ± 11.46 | 0.498 | 58.13 ± 12.84 | 52.53 ± 17.07 | 0.069 |
| 4 | 61.86 ± 11.10 | 61.57 ±10.63 | 0.941 | 62.93 ± 20.19 | 56.37 ± 18.79 | 0.021 |
| 5 | 95.57 ± 20.12 | 96.79 ± 18.66 | 0.730 | 80.40 ± 23.19 | 69.83 ± 23.52 | 0.019 |
| 6 | 128.79 ± 28.95 | 132.29 ± 25.20 | 0.242 | 95.83 ± 36.50 | 84.63 ± 33.88 | 0.008 |
| 7 | 123.93 ± 36.74 | 119.86 ± 31.10 | 0.285 | 97.77 ± 28.47 | 86.30 ± 24.73 | 0.001 |
| 8 | 66.93 ± 20.44 | 63.50 ± 20.95 | 0.122 | 65.07 ± 21.32 | 63.53 ± 22.27 | 0.402 |
| 9 | 54.64 ± 12.13 | 52.57 ± 12.25 | 0.348 | 56.33 ± 12.08 | 55.03 ± 13.44 | 0.604 |
| 10 | 74.21 ± 14.70 | 72.29 ± 13.24 | 0.377 | 75.20 ± 26.07 | 74.10 ± 26.30 | 0.510 |
| 11 | 118.36 ± 23.12 | 110.93 ± 24.55 | 0.198 | 103.47 ± 27.95 | 97.20 ± 32.47 | 0.011 |
| 12 | 122.57 ± 29.61 | 119.21 ± 27.02 | 0.417 | 100.83 ± 23.08 | 90.30 ± 24.34 | 0.001 |
| Total | 90.11 ± 16.26 | 89.27 ± 14.42 | 0.697 | 81.34 ± 17.11 | 75.10 ± 16.09 | <0.001 |
Table 5.
Changes in visual fields parameters (db) for control and NTG (mean ± standard deviation)
| Zone (o'clock) |
Control (20.74 ± 15.22 months follow-up) |
NTG* (25.88 ± 15.90 months follow-up) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Follow-up | p value† | Baseline | Follow up | p value† | |
| 1 | −1.29 ± 2.23 | −4.21 ± 7.86 | 0.128 | −1.80 ± 3.63 | −1.77 ± 2.56 | 0.965 |
| 2 | −1.21 ± 1.31 | −2.29 ± 2.16 | 0.037 | −3.83 ± 6.20 | −2.70 ± 4.50 | 0.145 |
| 3 | −1.46 ± 0.77 | −1.61 ± 1.48 | 0.755 | −3.52 ± 6.76 | −3.48 ± 4.70 | 0.958 |
| 4 | −1.45 ± 0.82 | −2.60 ± 1.90 | 0.028 | −4.44 ± 6.70 | −4.62 ± 7.02 | 0.773 |
| 5 | −2.29 ± 1.16 | −3.12 ± 1.77 | 0.072 | −5.08 ± 6.05 | −6.37 ± 7.41 | 0.034 |
| 6 | −1.83 ± 0.84 | −1.64 ± 1.48 | 0.657 | −4.61 ± 6.23 | −5.94 ± 8.06 | 0.068 |
| 7 | −1.82 ± 0.94 | −1.73 ± 1.20 | 0.797 | −5.71 ± 8.98 | −6373 ± 9.37 | 0.207 |
| 8 | −1.97 ± 1.33 | −1.69 ± 0.89 | 0.411 | −7.27 ± 8.97 | −7.47 ± 8.92 | 0.733 |
| 9 | −1.29 ± 1.64 | −1.50 ± 1.91 | 0.711 | −4.73 ± 9.40 | −6.27 ± 10.13 | 0.327 |
| 10 | −1.00 ± 0.96 | −1.39 ± 1.76 | 0.518 | −1.47 ± 3.72 | −2.17 ± 3.43 | 0.099 |
| 11 | 0 | 0 | | 0 | 0 | |
| 12 | −1.07 ± 0.92 | −2.29 ± 1.64 | 0.023 | −3.80 ± 7.92 | −4.67 ± 7.95 | 0.271 |
| 13 | −1.79 ± 1.48 | −2.00 ± 1.30 | 0.690 | −4.33 ± 8.60 | −5.03 ± 7.68 | 0.430 |
| 14 | −2.16 ± 1.32 | −2.29 ± 1.77 | 0.815 | −7.30 ± 8.21 | −7.61 ± 7.69 | 0.675 |
| 15 | −1.88 ± 0.73 | −2.00 ± 1.42 | 0.705 | −6.68 ± 8.31 | −6.30 ± 7.46 | 0.700 |
| 16 | −1.79 ± 0.81 | −1.66 ± 1.32 | 0.751 | −7.43 ± 8.80 | −7.07 ± 7.92 | 0.674 |
| 17 | −1.73 ± 1.20 | −2.36 ± 3.03 | 0.373 | −7.06 ± 7.23 | −8.34 ± 6.84 | 0.213 |
| 18 | −1.50 ± 2.34 | −1.82 ± 2.18 | 0.644 | −7.38 ± 8.06 | −6.88 ± 6.81 | 0.658 |
| 19 | −1.29 ± 1.33 | −1.64 ± 1.75 | 0.502 | −5.78 ± 7.49 | −6.15 ± 6.57 | 0.706 |
| 20 | −0.93 ± 1.44 | −2.00 ± 4.66 | 0.289 | −3.37 ± 5.35 | −4.93 ± 6.58 | 0.126 |
| 21 | −0.64 ± 1.78 | −1.71 ± 2.05 | 0.073 | −2.97 ± 5.35 | −2.47 ± 3.50 | 0.554 |
| MD‡ | −2.81± 1.87 | −3.20 ± 2.76 | 0.902 | −7.93 ± 6.83 | −9.04 ± 7.46 | 0.055 |
| PSD§ | 1.92 ± 0.52 | 2.76 ± 1.90 | 0.064 | 6.99 ± 4.85 | 7.52 ± 4.74 | 0.272 |
Table 6.
Rate of changes in retinal nerve fiber layer thickness parameters (μ m/month) for control and NTG (mean ± standard deviation)
| Clock hour position (o'clock) | Control (20.74 ± 15.22 months follow-up) | (25.88 ± 15.90 months follow-up NTG* | ) p value† |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −0.10 ± 0.75 | −0.46 ± 0.11 | 0.01 |
| 2 | −0.09 ± 0.65 | −0.37 ± 0.10 | 0.02 |
| 3 | −0.08 ± 0.58 | −0.26 ± 0.09 | <0.01 |
| 4 | −0.09 ± 0.73 | −0.27 ± 0.08 | 0.33 |
| 5 | −0.09 ± 0.83 | −0.37 ± 0.14 | 0.60 |
| 6 | −0.11 ± 0.64 | −0.45 ± 0.18 | 0.01 |
| 7 | −0.11 ± 0.75 | −0.49 ± 0.22 | 0.01 |
| 8 | −0.11 ± 0.45 | −0.31 ± 0.09 | 0.07 |
| 9 | −0.09 ± 0.36 | −0.26 ± 0.05 | 0.07 |
| 10 | −0.08 ± 0.46 | −0.37 ± 0.11 | <0.01 |
| 11 | −0.12 ± 0.80 | −0.48 ± 0.17 | 0.03 |
| 12 | −0.13 ± 0.87 | −0.46 ± 0.10 | 0.02 |
| Total | −0.11 ± 0.35 | −0.38 ± 0.06 | <0.01 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download