Abstract
Purpose
The present study was performed to evaluate the changes in tear film and ocular surface parameters after using sodium hyaluronate (SH) 0.1% alone or in combination with cyclosporine A (CsA) 0.05% in patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy accompanied by dry eye.
Methods
A total of 72 eyes from 36 patients were divided into two groups; 36 eyes of 18 patients were treated with 0.1% SH alone (group 1), and 36 eyes of 18 patients were treated with SH 0.1% and CsA 0.05% (group 2). Tear breakup time (BUT), basal tear secretion test (BST), tear clearance rate (TCR), fluorescein staining (FS) and corneal sensitivity test (CST) were evaluated at pre-treatment and one, three and six months post-treatment. Conjunctival impression cytology was performed and tear CXCL11 (Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand) levels were measured pre-treatment and three months post-treatment.
Results
BUT, BST, TCR, KEP and CST were significantly improved at six months in group 1 (p < 0.05) and at three months in group 2 (p < 0.05). The degree of conjunctival squamous cell metaplasia, goblet cell density and tear CXCL11 levels were significantly changed at three months in group 2 (p < 0.05). However, there were no significant changes in group 1 after 3 months.
Go to : 
References
2. Im WI, Choi SS, Yoo HR, Yoon YS. Correlation between the thyroid associated ophthalmopathy and thyroid function state. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002; 43:431–6.
3. Wiersinga WM, Prummel MF. Grave's ophthalmopathy: a rational approach to treatment. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2002; 13:280–7.

4. Khurana A, Sunder S, Ahluwalia BK, Malhotra KC. Tear film profile in Graves' ophthalmopathy. Acta Ophthalmol. 1992; 70:346–9.

5. Gilbard JP, Farris RL. Ocular surface drying and tear film osmolarity in thyroid eye disease. Acta Ophthalmol. 1983; 61:108–16.

6. Pflugfelder SC, Solomon A, Stern ME. The diagnosis and management of dry eye: a twenty-five-year review. Cornea. 2000; 19:644–9.
7. Nussenblatt RB, Palestine AG. Cyclosporine A: immunology, pharmacology and therapeutic uses. Surv Ophthalmol. 1986; 31:159–69.
8. Hemady R, Tauber J, Foster SC. Immunosuppressive drugs in immune and inflammatory ocular disease. Surv Ophthalmol. 1991; 35:369–85.

9. Jabs DA, Wingard J, Green R, et al. The eye in bone marrow transplantation. Arch Ophthalmol. 1989; 107:1343–8.

10. Bhan AK, Fujikawa LS, Foster CS. T-cell subsets and Langerhans cells in normal and diseased conjunctiva. Am J Ophthalmol. 1982; 94:205–12.

11. Gilbard JP, Rossi SR, Azar DT, Heyda KG. Effect of punctal occlusion by Freeman silicone plug insertion on tear osmolarity in dry eye disorder. CLAO J. 1989; 15:216–8.
12. Lee EH, Jang JW, Lew HM. The changes of tear osmolarity and protein after silicone punctal plug insertion in dry eye. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2001; 42:1509–14.
13. Yen MT, Pflugfelder SC, Feuer WJ. The effect of punctual occlusion on tear production, tear clearance and ocular surface sensation in normal subjects. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001; 131:314–23.
14. Pflugfelder SC, De Paiva CS, Villarreal AL, Stern ME. Effects of sequential artificial tear and cyclosporine A emulsion therapy on conjunctival goblet cell density and transforming growth factor-β2 production. Cornea. 2008; 27:64–9.
15. Wilson SE, Perry HD. Long-term resolution of chronic dry eye symptoms and signs after topical cyclosporine A treatment. Ophthalmology. 2007; 114:76–9.
16. Roberts CW, Carniglia PE, Brazzo BG. Comparison of topical cyclosporine A, punctal occlusion, and a combination for the treatment of dry eye. Cornea. 2007; 26:805–9.
17. Mourits MP, Koornneef L, Wiersinga WM, et al. Clinical criteria for the assessment of disease activity in Graves' ophthalmopathy: a novel approach. Br J Ophthalmol. 1989; 73:639–44.

19. Kaido M, Goto E, Dogru M, Tsubota K. Punctal occlusion for Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Ophthalmology. 2004; 111:895–900.
20. Yoon KC, Jeong IY, Im SK, et al. Therapeutic effect of umbilical cord serum eyedrops for the treatment of dry eye associated with graft-versus-host disease. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2007; 39:231–5.

22. Yoon KC, Heo H, Im SK, et al. Comparison of autologous serum and umbilical cord serum eye drops for dry eye syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007; 144:86–92.

23. Perry HD, Donnenfeld ED. Dry eye diagnosis and management in 2004. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2004; 15:299–304.

24. O'Brien PD, Collum LM. Dry eye: Diagnosis and current treatment strategies. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2004; 4:314–9.
25. Small DS, Acheampong A, Reis B, et al. Blood concentrations of cyclosporin during long term treatment with cyclosporin ophthalmic emulsion in patients with moderate to severe dry eye disease. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2002; 18:411–8.
26. Laibovitz RA, Solch S, Andriano K, et al. Pilot trial of cyclosporine 1% ophthalmic ointment in the treatment of keratoconjunctivitis sicca. Cornea. 1993; 12:315–23.

27. Raphael M, Bellefqih S, Piette JCH, et al. Conjunctival biopsy in Sjögren's syndrome: correlations between histological and immunohistochemical features. Histopathology. 1988; 13:191–202.

28. Kunert KS, Tisdale AS, Stern ME, et al. Analysis of topical cyclosporine A treatment of patients with dry eye syndrome. Arch Ophthalmol. 2000; 118:1489–96.
29. Turner K, Pflugfelder SC, Ji Z, et al. Interleukin-6 levels in the conjunctival epithelium of patients with dry eye disease treated with cyclosporine A ophthalmic emulsion. Cornea. 2000; 19:492–6.
30. Stevenson D, Tauber J, Reis BL. Efficacy and safety of cyclosporin A ophthalmic emulsion in the treatment of moderate-to-severe dry eye disease: a dose-ranging, randomized trial. The Cyclosporin A Phase 2 Study Group. Ophthalmology. 2000; 107:967–74.
31. Moon JW, Lee HJ, Shin KC, et al. Short term effects of topical cyclosporine A and viscoelastic on the ocular surfaces in patients with dry eye. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2007; 21:189–194.
32. Altiparmak UE, Acar DE, Ozer PA, et al. Topical cyclosporine A for the dry eye findings of thyroid orbitopathy patients. Eye (Lond). 2009 Oct 16. [Epub ahead of print].

33. Oh HJ, You IC, Yoon KC. Changes of tear parameters after using cyclosporine A in dry eye with thyroid ophthalmopathy. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:630–6.
34. McInnis KA, Britain A, Lausch RN, Oakes JE. Human corneal epithelial cells synthesize ELR(−)alpha-chemokines in response to proinflammatory mediators. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2007; 15:295–302.
Go to : 
 | Figure 1.Impression cytologic findings (PAS, ×400) (A,B). Specimen before (A) and 3 months after (B) treatment of topical 0.1% sodium hyaluronate. (A) Loss of goblet cell and large, polygonal epithelial cells with a nucleocytoplasmic ratio of 1:4 or 1:5 (squamous metaplasia grade 2) is visible. (B) Goblet cell density and microscopic findings did not changed after 3 months of treatment. (C, D) Specimen before (C) and 3 months after (D) treatment of topical 0.1% sodium hyaluronate and 0.05% cyclosporine A. (C) Loss of goblet cell and large, polygonal epithelial cells with a nucleocytoplasmic ratio of 1:4 or 1:5 (squamous metaplasia grade 2) were visible. (D) Increased periodic acid-Schiff positive goblet cells and round epithelial cells with a nucleocytoplasmic ratio of 1:3 (squamous metaplasia grade 1) are shown after 3 months of treatment. |
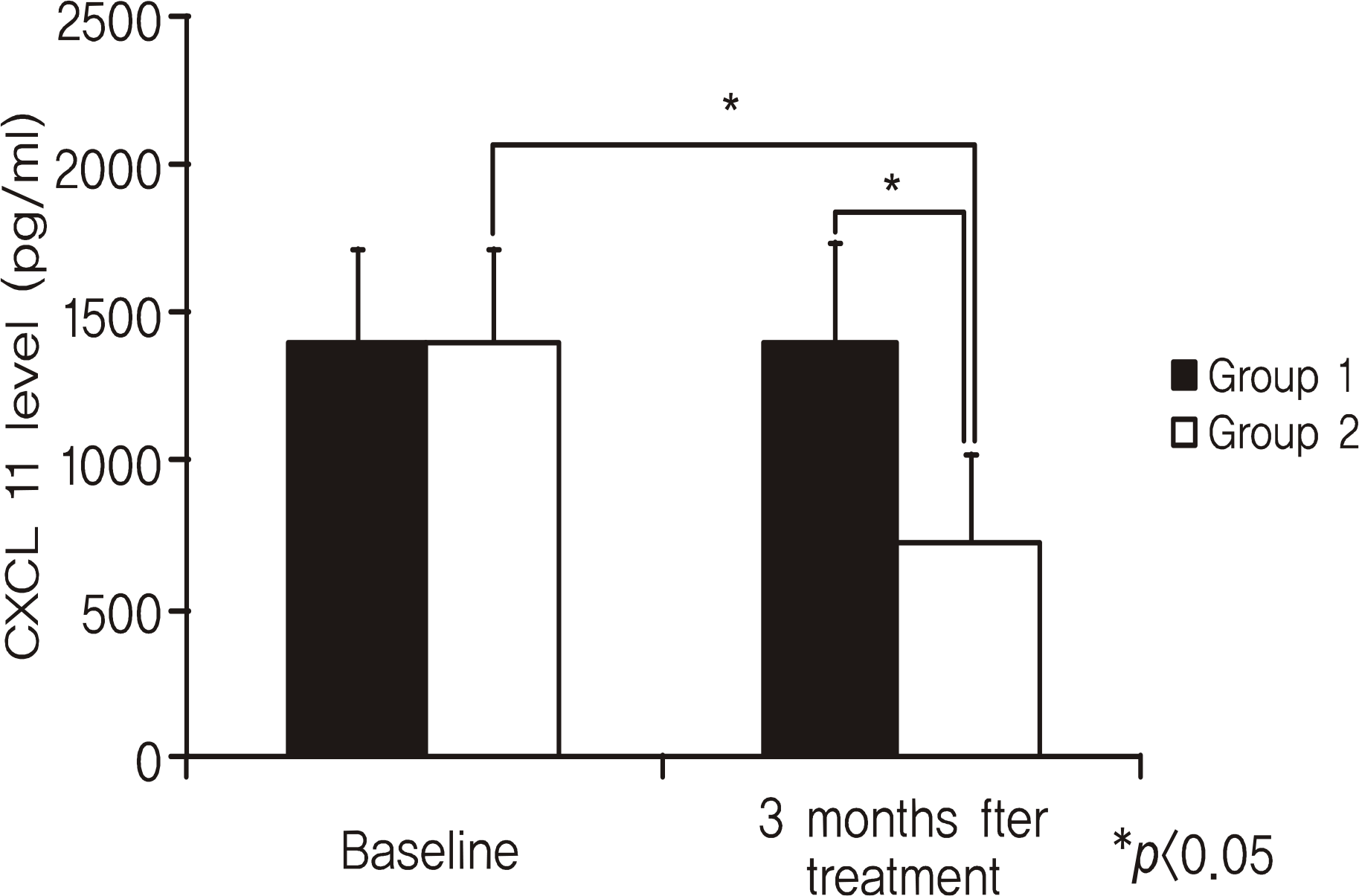 | Figure 2.Comparison of tear CXCL11 levels between before and 3 months after treatment with topical 0.1% sodium hyaluronate alone (Group 1) or topical 0.1% sodium hyaluronate and 0.05% cyclosporine A (Group 2). |
Table 1.
Changes in tear film and ocular surface parameters before and after treatment with topical 0.1% sodium hyaluronate alone (Group 1) or topical 0.1% sodium hyaluronate and 0.05% cyclosporine A (Group 2)
| | | Baseline | 1 month after treatment | 3 months after treatment | 6 months after treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tear break up time (sec) | Group 1 | 3.94 ± 1.24 | 3.81 ± 1.19 | 3.78 ± 1.17 | 6.17 ± 2.91* |
| Group 2 | 4.19 ± 1.26 | 4.19 ± 1.28 | 5.89 ± 2.88*† | 7.58 ± 2.60*† | |
| Basal tear secretion (mm) | Group 1 | 4.61 ± 2.09 | 5.03 ± 2.44 | 4.28 ± 2.24 | 8.14 ± 2.59* |
| Group 2 | 4.83 ± 2.30 | 4.47 ± 1.93 | 7.78 ± 2.50*† | 9.28 ± 2.08*† | |
| Tear clearance rate ((log2)-1) | Group 1 | 2.75 ± 0.73 | 2.56 ± 0.69 | 2.39 ± 0.49 | 5.78 ± 0.93* |
| Group 2 | 2.83 ± 2.44 | 2.78 ± 0.72 | 5.28 ± 1.16*† | 5.44 ± 0.84* | |
| Fluorescein staining score | Group 1 | 2.75 ± 0.73 | 2.72 ± 0.74 | 2.75 ± 0.73 | 1.56 ± 0.69* |
| Group 2 | 2.44 ± 1.16 | 2.44 ± 1.18 | 1.39 ± 0.93*† | 1.33 ± 0.86* | |
| Corneal sensitivity (mm) | Group 1 | 54.36 ± 4.13 | 55.56 ± 4.30 | 55.75 ± 3.05 | 58.33 ± 2.39* |
| Group 2 | 54.86 ± 4.22 | 55.28 ± 4.30 | 57.92 ± 2.50*† | 58.06 ± 2.47* |
Table 2.
Changes in impression cytologic findings before and 3 months after treatment in the both groups
| | | Baseline | 3 months after teatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | Conjunctival squamous cell metaplasia (grade) | 2.22 ± 0.88 | 2.00 ± 0.84 |
| Goblet cell density (cell/mm2) | 132.89 ± 60.00 | 127.39 ± 51.91 | |
| Group 2 | Conjunctival squamous cell metaplasia (grade) | 2.33 ± 0.84 | 0.89 ± 0.76*† |
| Goblet cell density (cell/mm2) | 134.56 ± 57.19 | 199.06 ± 39.68*† |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download