Abstract
Purpose
To report a case of malignant fibrous histiocytoma of the lateral canthal area that was diagnosed clinically as a benign epidermal inclusion cyst.
Case summary:
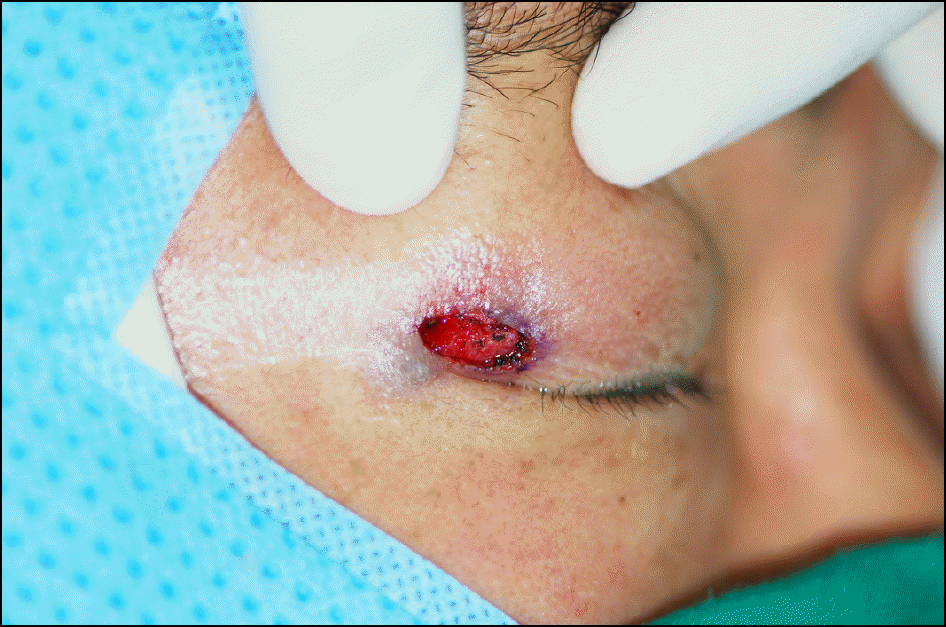
A 49 year-old man presented with a cutaneous mass involving the lateral canthal area. A 0.7-cm cystic lesion was freely movable and non-inflamed. After excisional biopsy, the results of immunohistochemical staining led to a final diagnosis of low-grade malignant fibrous histiocytoma. The specimen from excisional biopsy had margins positive for malignancy; the patient underwent a second procedure for complete resection, and that specimen had tumor-free margins.
Go to : 
References
1. Font RL, Hidayat AA. Fibrous histiocytoma of the orbit. A clinicopathologic study of 150 cases. Hum Pathol. 1982; 13:199–209.
2. Ramzi S, Cotran VK, Tucker Collins. Robbins pathologic basis of disease. 6th ed.Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company;1999.
3. Cole CH, Magee JF, Gianoulis M, Rogers PC. Malignant fibrous histiocytoma in childhood. Cancer. 1993; 71:4077–83.

4. Weiss SW, Enzinger FM. Malignant fibrous histiocytoma: an analysis of 200 cases. Cancer. 1978; 41:2250–66.
5. Weiss SW GJ. Malignant fibrohistiocystic tumours. 4th ed.St. Louis: Mosby;2000.
6. Khong JJ, Chen CS, James CL, et al. Malignant fibrous histiocytoma of the eyelid: differential diagnosis and management. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005; 21:103–8.

7. Kwak JS, Kim KS. A case of intra orbital fibrous histiocytoma. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1974; 15:178–81.
8. Choi WH, Ha IH, Min SG. A case of fibrous histiocytoma in cornea and corneosclerallimbus. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:608–12.
9. Kang SW, Lee ME, Lee WR, et al. A case of malignant fibrous histiocytoma in the conjunctiva. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1989; 30:805–9.
10. Kang TH, Kim SM, Choi WC. A case of fibrous histiocytoma in orbit. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2000; 41:511–6.
11. Kim DH, La TY, Kim MS. A case of fibrous histiocytoma of the corneoscleral limbus treated by lamellar corneoscleral graft. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:1218–22.
12. Belliveau MJ, Brownstein S, Jordan DR, Faraji H. Low-grade, aggressive fibrous histiocytoma of the medial canthus. Can J Ophthalmol. 2008; 43:250.

13. Dzubow LM. Mohs surgery report: spindle cell fibrohistiocytic tumors: classification and pathophysiology. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1988; 14:490–5.

14. Morris SR, deSousa JL, Barrett AW, Malhotra R. Benign fibrous histiocytoma of the eyelid mimicking keratoacanthoma. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007; 23:73–5.

15. Belal A, Kandil A, Allam A, et al. Malignant fibrous histiocytoma: a retrospective study of 109 cases. Am J Clin Oncol. 2002; 25:16–22.
16. Stojadinovic A, Leung DH, Hoos A, et al. Analysis of the prognostic significance of microscopic margins in 2,084 localized primary adult soft tissue sarcomas. Ann Surg. 2002; 235:424–34.

17. Matsumoto S, Ahmed AR, Kawaguchi N, et al. Results of surgery for malignant fibrous histiocytomas of soft tissue. Int J Clin Oncol. 2003; 8:104–9.

Go to : 
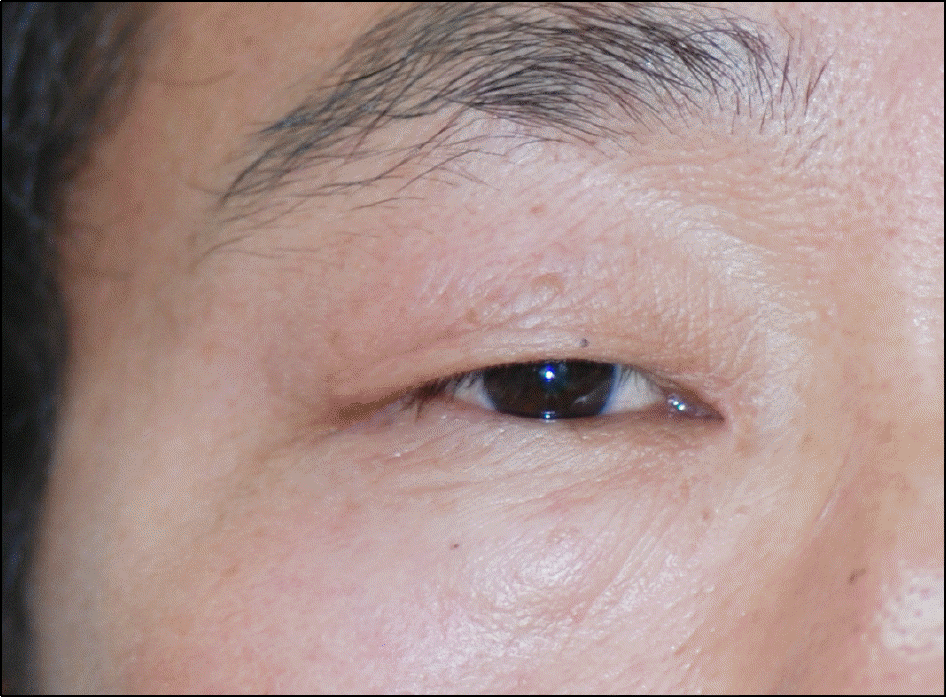
 | Figure 1.Clinical appearance of the right lateral canthal lesion at initial presentation shows a cystic and pedunculated nodule. |
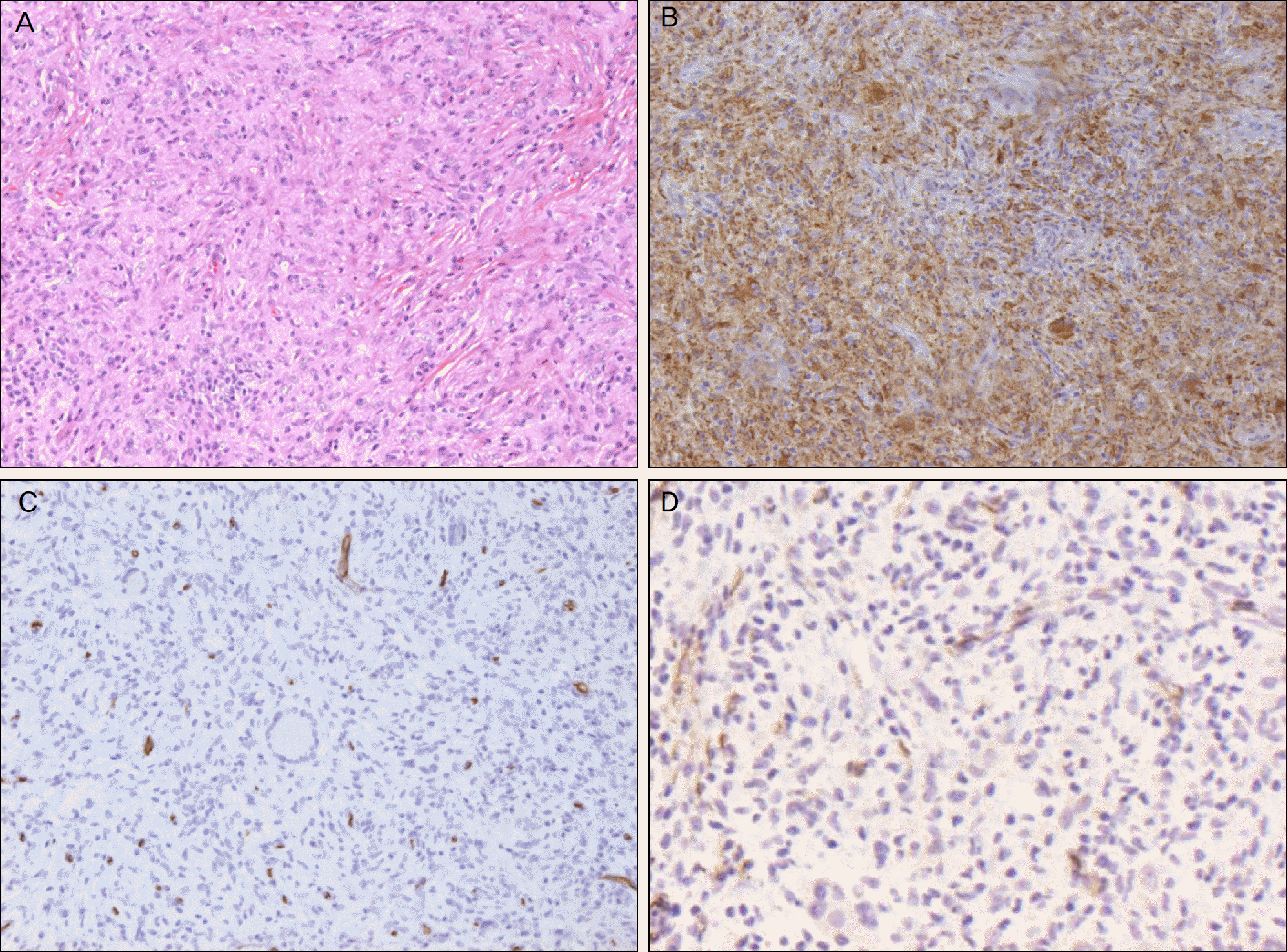 | Figure. 2.Hematoxylin and eosin staining of the excised lesion shows storiform pattern of fibroblasts characteristic of fibrous histiocytoma (A) (H&E stain, ×200). The results of immunohistochemical staining is positive for CD68 (B) (CD68, ×200) and negative for CD34 (C) and smooth muscle actin (D) (CD34, SMA ×200). |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download