Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the clinical courses of children with functional visual loss and to evaluate their psychosocial problems.
Methods
Thirteen children who visited the ophthalmic clinic of Dankook University Hospital because of functional vision loss between August 1, 2005 and January 1, 2009 were examined to establish the cause of lost vision. The results of the child behavior checklist-Korean version (K-CBCL) and the Korean personality inventory for children (KPI-C) were obtained in nine out of the 13 children.
Results
The mean visual acuities at the initial and last visits for nine children in the functional visual loss group were 0.58± 0.28 and 0.89 ± 0.31, respectively. Somatic complaints, social problems and overall behavioral problems were statistically significantly different from those of the control group according to the K-CBCL, and somatic concern was statistically significantly different from that of the control group according to the KPI-C.
Go to : 
References
1. Park JH, Moon NJ. Clinical analysis of 500 low vision patients. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:345–52.
2. Lu Q, Zheng Y, Sun B, et al. A population-based study of visual impairment among pre-school children in Beijing. Am J Ophthalmol. 2009; 147:1075–81.
3. Lai YH, Hsu HT, Wang HZ, et al. The visual status of children ages 3 to 6 years in the vision screening program in Taiwan. J AAPOS. 2009; 13:58–62.

4. Dickmann A, Petroni S, Salerni A, et al. Unilateral amblyopia: An optical coherence tomography study. J AAPOS. 2009; 13:148–50.

5. Villegas RB, Ilsen PF. Functional vision loss: A diagnosis of exclusion. Optometry. 2007; 78:523–33.

6. Baker RS, Schmeisser ET, Epstein AD. Visual system electro-diagnosis in neurologic disease of childhood. Pediatr Neurol. 1995; 12:99–110.

7. Taich A, Crowe S, Kosmorsky GS, Traboulsi EI. Prevalence of psychosocial disturbances in children with nonorganic visual loss. J AAPOS. 2004; 8:457–61.

8. Renner AB, Kellner U, Tillack H, et al. Recording of both VEP and multifocal ERG for evaluation of unexplained visual loss. Doc Ophthalmol. 2005; 111:149–57.

9. Vu BL, Easterbrook M, Hovis JK. Detection of color vision defects in chloroquine retinopathy. Ophthalmology. 1999; 106:1799–804.
10. Oh KJ, Lee H. Development of Korean Child Behavior Checklist: a preliminary study. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 1990; 29:452–62.
11. Wirt RD, Lachar D, Klinedenst JK. Multidimensional description of child personality: A manual for the Personality Inventory for Children. Los Angeles: Western Psychological Services;1977.
12. Kim ST, Kim JH, Hwang ST. Development and Standardization of the Korean Personality Inventory for Children. Mental Health Study. 2001; 20:198–212.
13. Pehlivantürk B, Unal F. Conversion disorder in children and adolescents: a 4-year follow-up study. J Psychosom Res. 2002; 52:187–91.
Go to : 
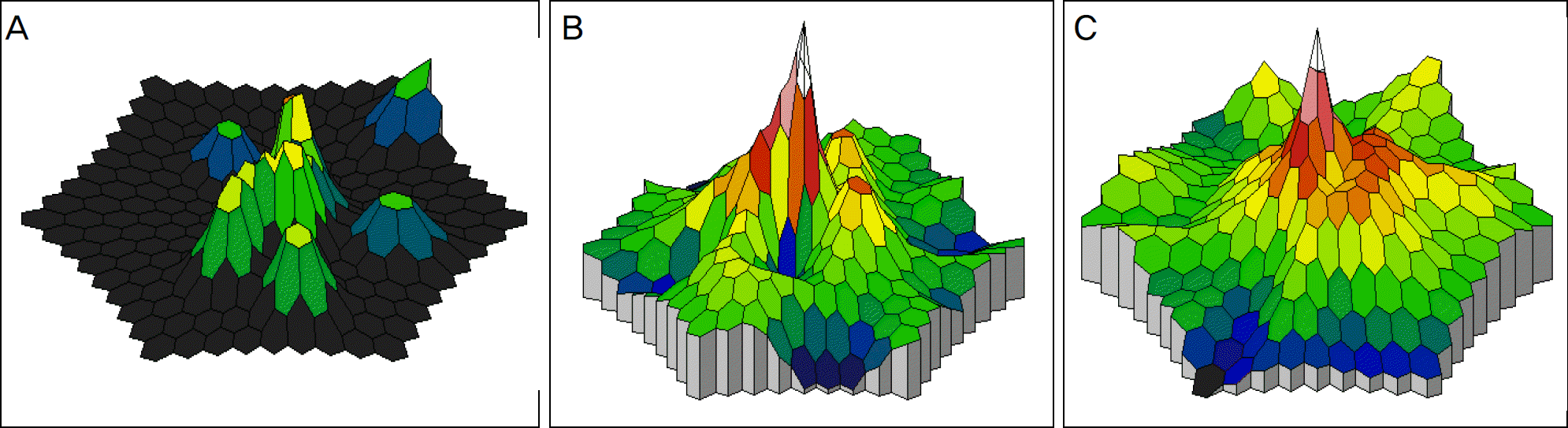 | Figure 1.The results of mfERG were found to be abnormal. The result of A may be due to patient's lack of attention. A=right eye of case 1; B=left eye of case 4; C=left eye of case 5. |
Table 1.
Failing criteria for tests
| Test | Failing criteria |
|---|---|
| Color vision | ≥5 errors on color plates |
| Visual fields | defect or scotoma at any area |
| OCT* | unacceptable foveal contour |
| VEP† | significantly different P100 from averages of |
| control group | |
| mfERG‡ | abnormal figure of P1 amplitude |
Table 2.
Subscales of Korean personality inventory for children and child behavior check list
Table 3.
Demographic characteristics between control group and patient group for KPI-C and K-CBCL
| Rating Scale | Control group (N=160) | Patient group (N=9) | x2 | * p value | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (Mean ± S.D.) (range)† | 10.26 ± 1.48 (7∼12) | 10.4 ± 3.4 (6∼18) | 5.60 | 0.02 | 10.33 ± 2.34 |
| Sex (N, %)‡ | |||||
| Female | 78 (48.8 %) | 7 (77.8 %) | 3.04 | 0.09 | |
| Male | 82 (51.3 %) | 2 (22.2 %) | |||
| These data represent mean ± SD, and range. | |||||
Table 4.
Clinical characteristics and functional findings of the patients
| Case No. Age/Sex | BCVA† R/L |
Color vision |
V/F |
OCT | VEP | mfERG | KCBCL & KPI‐ C | F/U period | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Last | Initial | Last | |||||||
| 1. F/9 | 0.9/1.0 | Fail | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | Fail | normal | 3Y |
| 2. F/11 | 1.0/1.0 | Pass | Pass | Fail | Fail | Pass | Pass | Pass | High scores in | 8M |
| subscale | ||||||||||
| 3. F/8 | 0.07/0.1 | Fail | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | High scores in | 2Y 6M |
| subscale | ||||||||||
| 4. M/13 | 1.0/0.9 | Fail | Pass | Fail | Fail | Pass | Pass | Fail | High scores in | 2Y 9M |
| subscale | ||||||||||
| 5. F/10 | 1.0/1.0 | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | Fail | normal | 2Y |
| 6. M/6 | 1.2/1.2 | Fail | Pass | Fail | Pass | Pass | Fail | Pass | High scores in | 3Y |
| subscale | ||||||||||
| 7. F/9 | 0.9/0.9 | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | Fail | Borderline in | 2Y |
| subscale | ||||||||||
| 8. F/18 | 1.0/1.0 | Pass | Pass | Fail | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | High scores in | 6M |
| subscale | ||||||||||
| 9. F/9 | 1.0/0.9 | Fail | Fail | Fail | Pass | Pass | Fail | Pass | High scores in | 6M |
| subscale | ||||||||||
| No=number; BCVA=best corrected visual acuity; R=right; L=left; V/F=visual field; OCT, optical coherent tomography; VEP=visual evoked potential; mfERG=multifocal electroretinogram; KCBCL=Child behavior check list-Korean version; K-PIC =Korean Personality Inventory for Children; F/U=Follow up; F=female; M=male; Y=year; M=month; | ||||||||||
Table 5.
Comparisons of Child Behavior Check List, Korean Personality Inventory for Children, between control group and patient grou
| Rating Scale | Control group | Patient group | x2 | * p value | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K‐ CBCL | |||||
| Withdrawn | 53.00 ± 8.05 | 52.33 ± 4.64 | 0.60 | 0.808 | 52.96 ± 7.90 |
| Somatic complaints | 51.40 ± 3.85 | 54.67 ± 7.87 | 5.32 | 0.022 | 51.57 ± 4.19 |
| Anxious/depressed | 51.26 ± 3.38 | 52.00 ± 2.83 | 0.41 | 0.522 | 51.30 ± 3.35 |
| Social problems | 50.79 ± 2.47 | 55.44 ± 5.59 | 25.22 | 0.000 | 51.04 ± 2.89 |
| Thought problems | 51.92 ± 4.38 | 51.11 ± 2.20 | 0.30 | 0.584 | 51.88 ± 4.29 |
| Attention problems | 51.29 ± 3.34 | 52.00 ± 3.12 | 0.38 | 0.536 | 51.33 ± 3.32 |
| Delinquent behavior | 51.75 ± 3.92 | 52.44 ± 6.29 | 0.25 | 0.619 | 51.79 ± 4.06 |
| Aggressive behavior | 51.28 ± 3.49 | 52.89 ± 3.92 | 1.80 | 0.182 | 51.36 ± 3.52 |
| Internalizing problems | 51.23 ± 3.30 | 53.11 ± 4.37 | 2.69 | 0.103 | 51.33 ± 3.37 |
| Externalizing problems | 51.29 ± 3.46 | 53.11 ± 4.62 | 2.27 | 0.134 | 51.39 ± 3.53 |
| Total behavior problems | 51.13 ± 3.28 | 53.44 ± 4.50 | 4.08 | 0.045 | 51.25 ± 3.38 |
| Sex problems | 51.13 ± 3.44 | 50.00 ± 0.00 | 0.97 | 0.327 | 51.07 ± 3.36 |
| Emotional problems | 50.41 ± 1.62 | 50.33 ± 1.00 | 0.02 | 0.894 | 50.40 ± 1.59 |
| K‐ PIC | |||||
| ESR | 53.75 ± 10.47 | 51.78 ± 10.63 | 0.30 | 0.583 | 53.65 ± 10.45 |
| VDL | 44.56 ± 9.89 | 46.89 ± 8.36 | 0.48 | 0.490 | 44.69 ± 9.81 |
| PDL | 44.39 ± 9.92 | 47.89 ± 10.22 | 1.06 | 0.305 | 44.57 ± 9.93 |
| ANX | 45.16 ± 12.13 | 43.44 ± 13.65 | 0.17 | 0.682 | 45.07 ± 12.17 |
| DEP | 44.09 ± 9.75 | 45.67 ± 8.59 | 0.23 | 0.635 | 44.17 ± 9.68 |
| SOM | 44.91 ± 8.96 | 51.33 ± 12.65 | 4.18 | 0.042 | 45.25 ± 9.25 |
| DLQ | 44.53 ± 9.49 | 50.00 ± 9.92 | 2.82 | 0.095 | 44.82 ± 9.57 |
| HPR | 41.24 ± 11.25 | 45.44 ± 8.92 | 1.21 | 0.273 | 41.47 ± 11.15 |
| FAM | 42.11 ± 10.05 | 39.67 ± 6.40 | 0.52 | 0.472 | 41.98 ± 9.90 |
| SOC | 49.26 ± 7.99 | 47.22 ± 4.99 | 0.57 | 0.451 | 49.15 ± 7.86 |
| PSY | 29.09 ± 15.26 | 20.56 ± 2060 | 2.80 | 0.096 | 28.64 ± 14.99 |
| AUT | 36.25 ± 13.26 | 34.22 ± 14.16 | 0.20 | 0.657 | 36.14 ± 13.27 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download