Abstract
Purpose
To report wavefront analysis of successful treatment of monocular triplopia after cataract extraction.
Case summary
(Case 1) A 59-year-old man visited our clinic for a monocular triplopia in his left eye of five years in duration. The best spectacle-corrected visual acuity (BSCVA) was 1.0 in the left eye, and the patient had a mild cortical cataract. The ocular spherical aberration (0.126 μ m for the 4-mm pupil, 0.351 μ m for the 6-mm pupil) measured by a Hartmann-Shack aberr-ometer increased preoperatively, while the corneal spherical aberration was normal. After cataract surgery, the monocular triplopia disappeared, and the ocular spherical aberration decreased. (Case 2) A 38-year-old man visited our clinic for a monocular trip-lopia in his left eye of a two-year duration. The best spectacle-corrected visual acuity (BSCVA) was 0.3 in the left eye, and the patient had a mild nuclear cataract. The ocular spherical aberration (−0.356 μ m, −1.343 μ m) and trefoil aberration (0.199 μ m, 0.252 μ m) increased preoperatively, while the corneal spherical and trefoil aberrations were normal. After cataract surgery, the monocular triplopia disappeared and the ocular spherical and trefoil aberrations decreased.
Go to : 
References
1. Coffeen P, Guyton DL. Monocular diplopia accompanying ordinary refractive errors. Am J Ophthalmol. 1998; 105:451–9.

2. Bowman KJ, Smith G, Carney LG. Corneal topography and monocular diplopia following near work. Am J Optom Physiol Opt. 1978; 55:818–23.

4. Kuroda T, Fujikado T, Maeda N, et al. Wavefront analysis in eyes with nuclear or cortical cataract. Am J Ophthalmol. 2002; 134:1–9.

5. Fujikado T, Shimojyo H, Hosohata J, et al. Wavefront analysis of eye with monocular diplopia and cortical cataract. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006; 141:1138–40.

6. Kim A, Bessho K, Okawa Y, et al. Wavefront analysis of eyes with cataracts in patients with monocular triplopia. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2006; 26:65–70.
7. Kuroda T, Fujikado T, Maeda N, et al. Wavefront analysis of high-er-order aberrations in patients with cataract. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:438–44.

8. Fujikado T, Kuroda T, Maeda N, et al. Wavefront analysis of an eye with monocular triplopia and nuclear cataract. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004; 137:361–3.

Go to : 
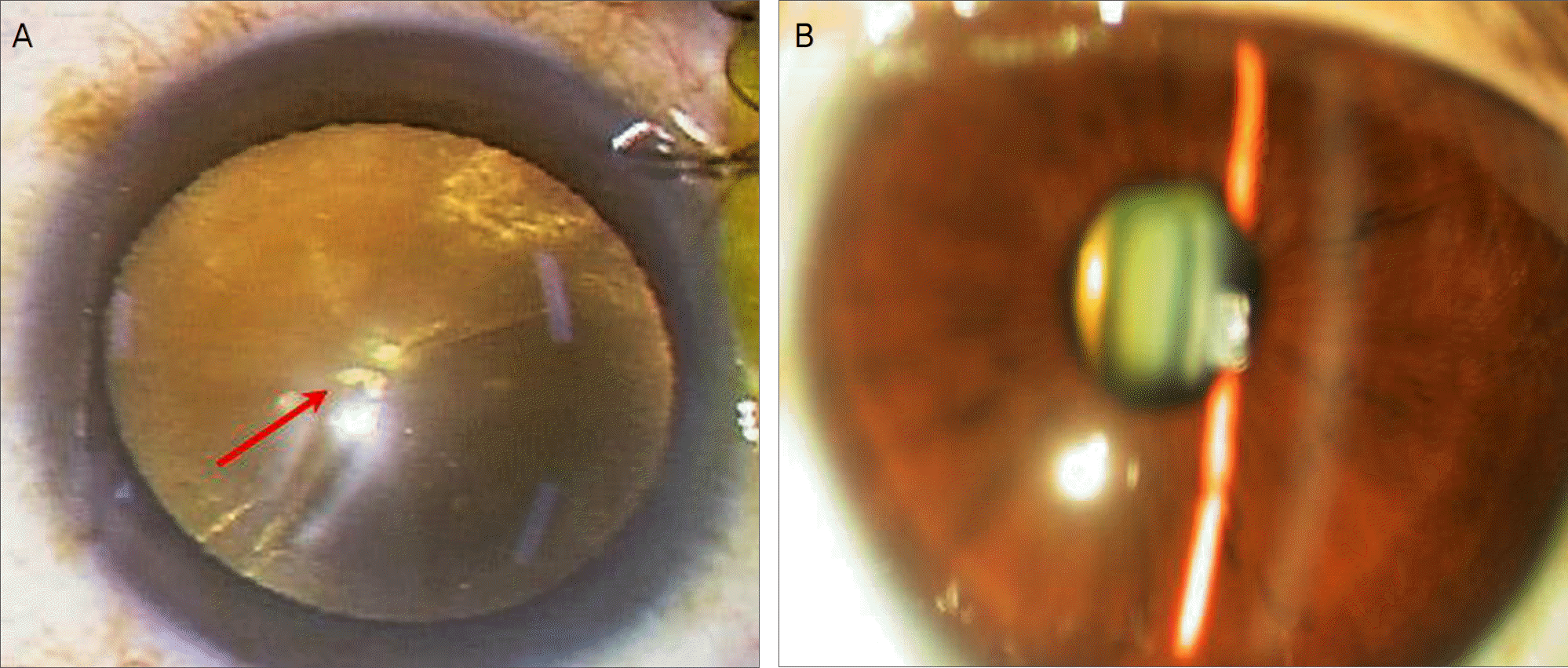 | Figure 1.Preoperative photograph. (Case 1) Intraoperative photograph reveals some cystic vacuoles involving the center of the pupil (red arrow) and mild cortical cataract (A). (Case 2) Slit lamp photograph shows mild nuclear cataract (B). |
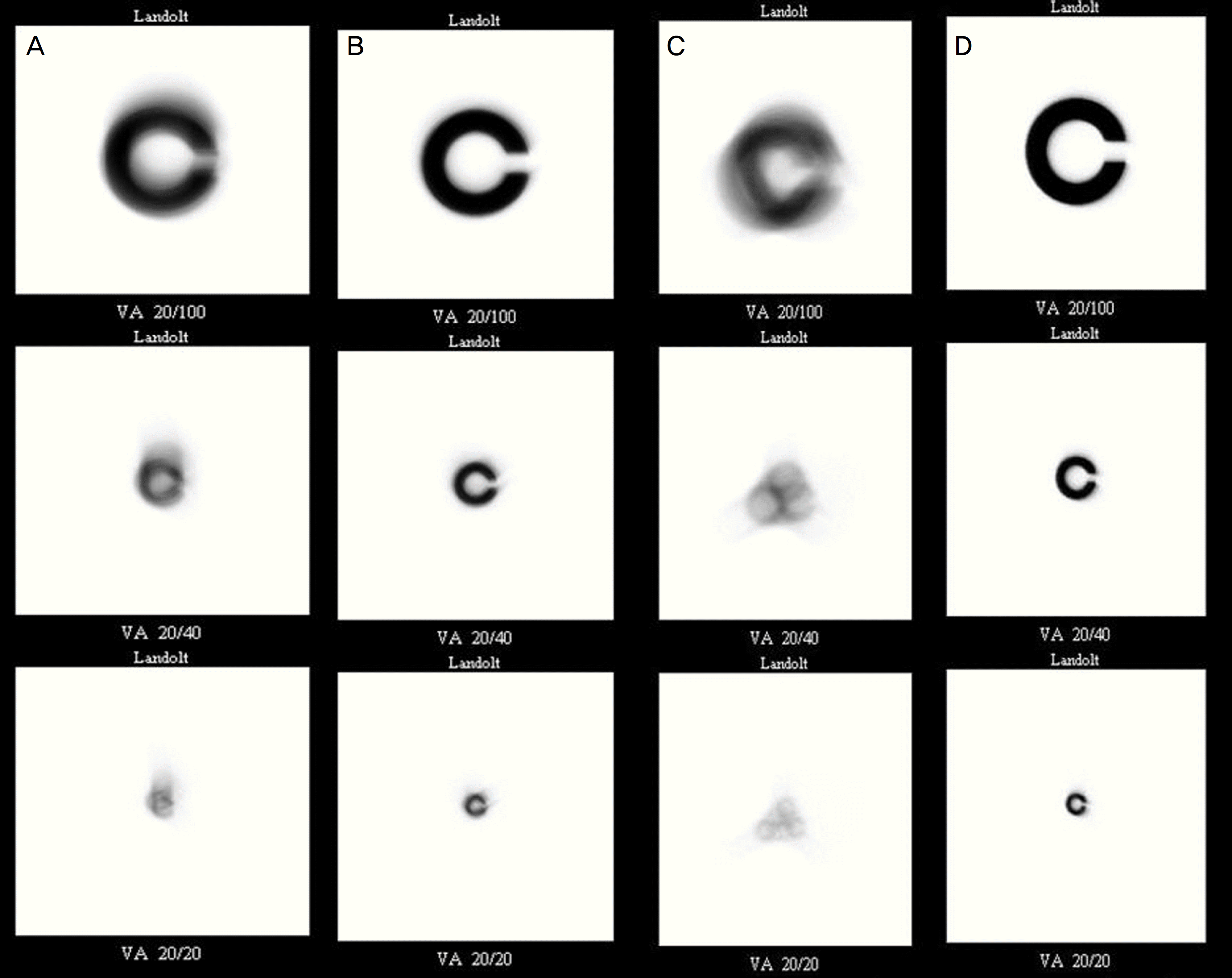 | Figure 2.Simulated image for Landolt C before and after surgery. (Case1) Simulated image for Landolt C shows triple configuration before surgery (A). However, simulated image for Landolt C shows normal pattern after surgery (B). (Case2) Simulated image for Landolt C shows triple configuration before surgery (C). However, simulated image for Landolt C shows normal pattern after surgery (D). |
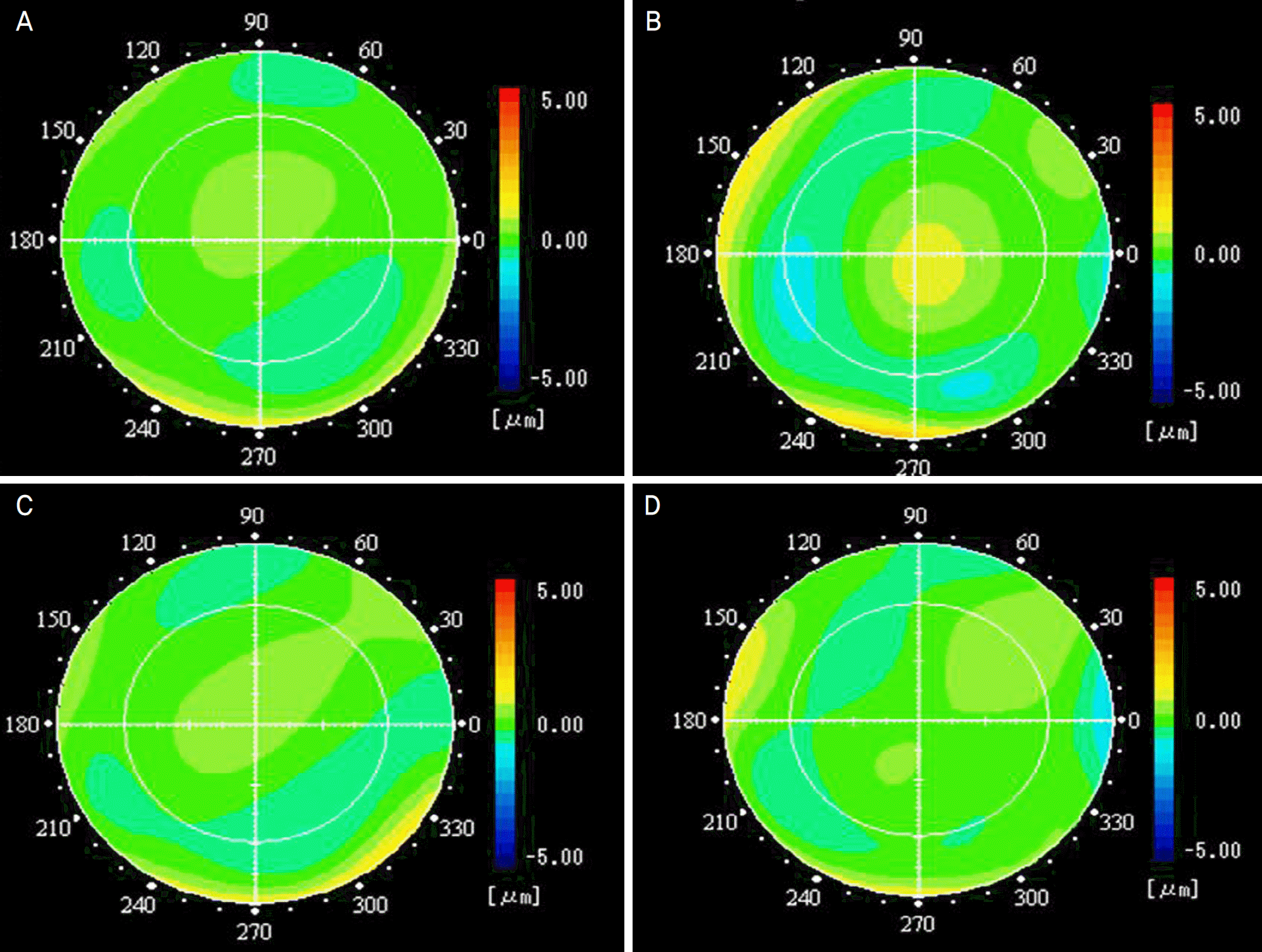 | Figure 3.(Case1) Wavefront analysis of higher-order aberration in the cornea and in oculus before and after surgery. Corneal higher-order aberrations had almost normal pattern before and after surgery (A, C), but ocular higher-order aberrations showed advancement of wavefront (warm color) in the central pupillary area and delay of wavefront (cool color) in peripheral pupillary area before surgery (B) and a normal pattern after surgery (D). |
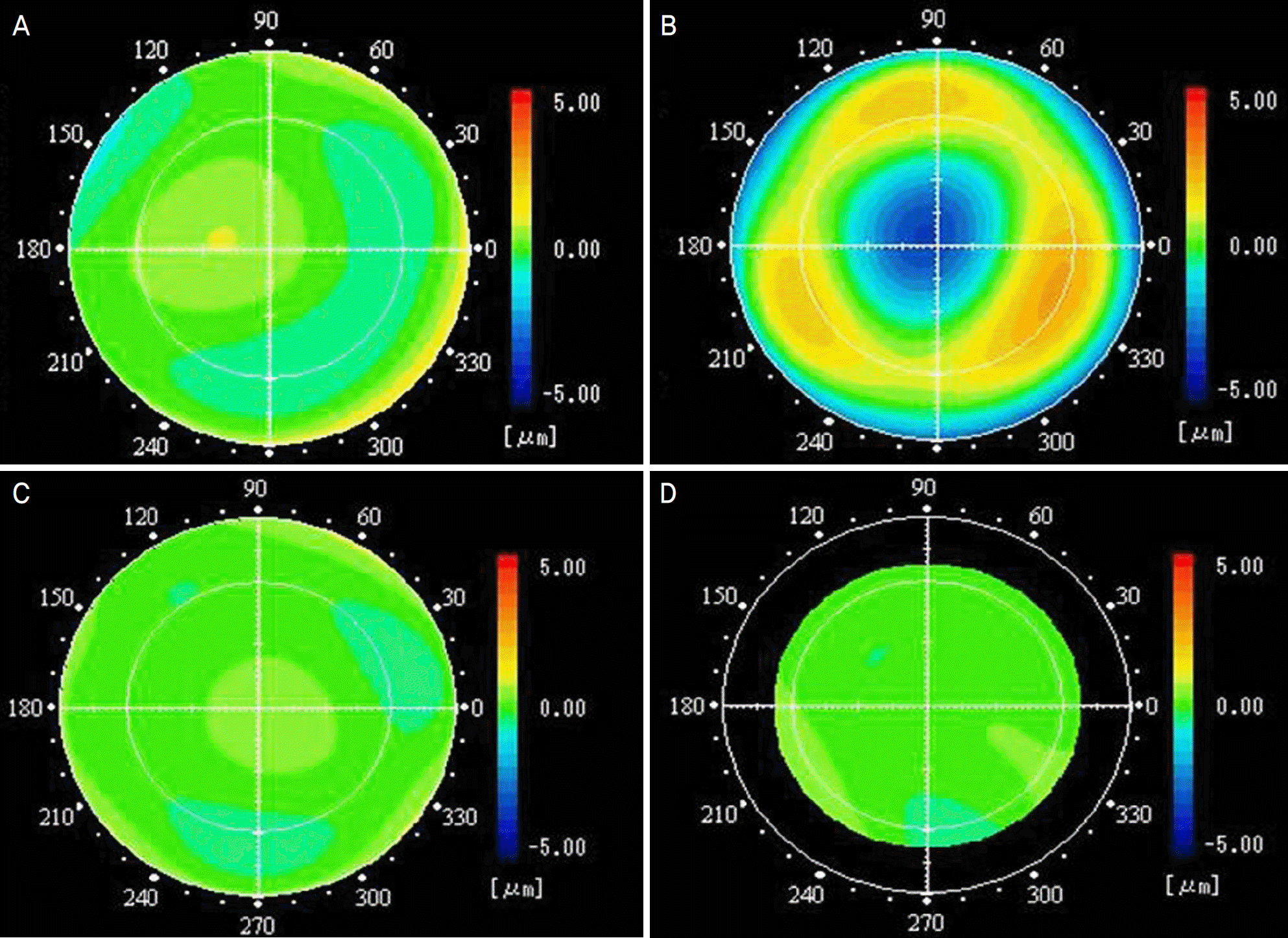 | Figure 4.(Case 2) Wavefront analysis of higher-order aberration in the cornea and in oculus before and after surgery. Corneal higher-order aberrations had almost normal pattern before and after surgery (A, C), but ocular higher-order aberrations showed a delay of wavefront (cool color) in the central pupillary area and trefoil pattern in the peripheral area before surgery (B) and a normal pattern after surgery (D). |
Table 1.
Comparison of ocular and corneal higher-order aberrations in (Case 1) before and after cataract surgery (Vector Zernike analysis up to 4 th order for 4 mm pupil diameter and 6th order for 6 mm pupils
| Pupil diameter (mm) | Mean HO A* (µm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-op. | Post-op. | |||
| Ocular aberration | Total HOA | 4.0 | 0.179 | 0.124 |
| Coma | 4.0 | 0.094 | 0.055 | |
| Trefoil | 4.0 | 0.053 | 0.029 | |
| SA | 4.0 | 0.126 | −0.024 | |
| Corneal aberration | Total HOA | 4.0 | 0.089 | 0.103 |
| Coma | 4.0 | 0.068 | 0.077 | |
| Trefoil | 4.0 | 0.028 | 0.048 | |
| SA† | 4.0 | 0.049 | 0.041 | |
| Ocular aberration | Total HOA | 6.0 | 0.507 | 0.355 |
| Coma | 6.0 | 0.229 | 0.177 | |
| Trefoil | 6.0 | 0.200 | 0.194 | |
| SA | 6.0 | 0.351 | 0.083 | |
| Corneal aberration | Total HOA | 6.0 | 0.381 | 0.414 |
| Coma | 6.0 | 0.195 | 0.204 | |
| Trefoil | 6.0 | 0.120 | 0.129 | |
| SA | 6.0 | 0.284 | 0.263 | |
Table 2.
Comparison of ocular and corneal higher-order aberrations in Case 2 before and after cataract surgery (Vector Zernike analysis up to 4 th order for 4-mm pupil diameter and 6 th order for 6-mm pupils)
| Pupil diameter (mm) | Mean HO A* (µm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-op. | Post-op. | |||
| Ocular aberration | Total HOA | 4.0 | 0.425 | 0.076 |
| Coma | 4.0 | 0.012 | 0.053 | |
| Trefoil | 4.0 | 0.199 | 0.048 | |
| SA | 4.0 | −0.356 | 0.019 | |
| Corneal aberration | Total HOA | 4.0 | 0.081 | 0.058 |
| Coma | 4.0 | 0.076 | 0.027 | |
| Trefoil | 4.0 | 0.012 | 0.027 | |
| SA† | 4.0 | 0.02 | 0.041 | |
| Ocular aberration | Total HOA | 6.0 | 1.407 | 0.318 |
| Coma | 6.0 | 0.097 | 0.045 | |
| Trefoil | 6.0 | 0.252 | 0.153 | |
| SA | 6.0 | −1.343 | −0.068 | |
| Corneal aberration | Total HOA | 6.0 | 0.263 | 0.285 |
| Coma | 6.0 | 0.204 | 0.018 | |
| Trefoil | 6.0 | 0.066 | 0.106 | |
| SA | 6.0 | 0.123 | 0.239 | |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download