Abstract
Purpose
To find the optimal parameter of retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) analysis in optical coherence tomography (OCT) for diagnosing glaucoma in children.
Methods
The study was comprised of 127 eyes of 84 patients (aged 6 to 18 years) who visited our institute between March 2006 and February 2008. Subjects were classified into normal, glaucoma suspect and glaucoma groups, and each eye was scanned using Stratus 3.0 OCT. Routine ophthalmic examinations including fundus examination, visual field test and OCT RNFL analysis were performed.
Results
There were 55 normal eyes, 27 glaucoma suspect eyes and 45 glaucomatous eyes. The average RNFL thickness was the most useful parameter to differentiate between the glaucoma and non-glaucoma groups. The next most useful parameter was inferior average thickness, followed by superior RNFL thickness. The sensitivity and specificity of the new discriminant of the formula used were 78%, and 68.6%, respectively.
Go to : 
References
1. Quigley HA, Addicks EM, Green WR. Optic nerve damage in human glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 1982; 100:135–46.

2. Quigley HA, Dunkelberger GR, Green WR. Retinal ganglion cell atrophy correlated with automated perimetry in human eyes with glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1989; 107:453–64.

3. Sommer A, Katz J, Quigley HA, et al. Clinically detectable nerve fiber atrophy precedes the onset of glaucomatous field loss. Arch Ophthalmol. 1991; 109:77–83.

4. Ahn HC, Son HW, Kim JS, Lee JH. Quantitative analysis of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness of normal children and adolescents. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2005; 19:195–200.

5. Ha SW, Rho SH. Age-related differences of optical coherence tomography data in Koreans. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:2037–44.
6. Song JH, Kim ER, Yoo JM. Analysis of RNFL thickness and optic nerve head measured with OCT in children. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:1346–53.

7. Park SJ, Park KH, Yu YS, et al. Early detection of glaucoma with retinal nerve fiber layer photograph. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1998; 39:180–6.
8. Mrugacz M, Bakunowicz-Lazarczyk A. Optical coherence tomography measurement of the retinal nerve fiber layer in normal and juvenile glaucomatous eyes. Ophthalmologica. 2005; 219:80–5.

9. Varma R, Bazzaz S, Lai M. Optical tomography-measured retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in normal Latinos. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003; 44:3369–73.

10. Alamouti B, Funk J. Retinal thickness decreases with age: an OCT study. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003; 87:899–901.

11. Poinoosawmy D, Fontana L, Wu JX, et al. Variation of nerve fiber layer thickness measurements with age and ethnicity by scanning laser polarimetry. Br J Ophthalmol. 1997; 81:350–4.
12. Kang KD, Park CK. Comparison of diagnostic precision between preprogramed indicator and newly calculated indicator in optical coherence tomography. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:243–52.
13. Cho YK, Lee YC, Lee SY. Factors mediating effects on the retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in normal children. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:98–103.

Go to : 
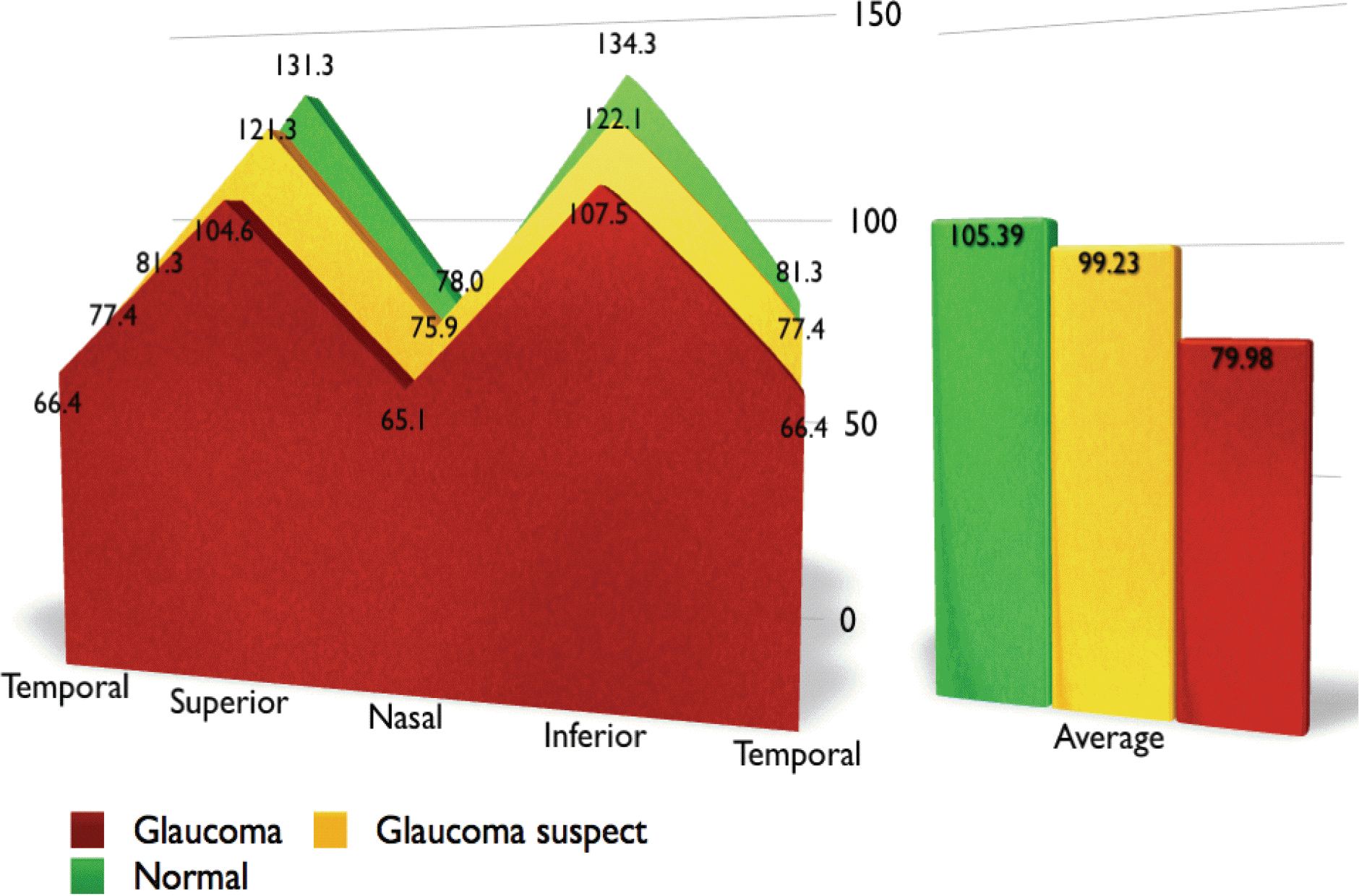 | Figure 1.Comparison of mean value between normal, glaucoma suspect and glaucomatous eye using optical coherence tomography retinal nerve fiber layer analysis. |
Table 1.
Characteristics and average retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in each group (N=127)
| | Normal | Glaucoma suspect | Glaucoma | p-value* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number (eye) | 55 | 27 | 45 | |
| Gender (Male/Female) | 26/29 | 15/12 | 24/21 | |
| Visual Acuity | 0.43±0.28 | 0.40±0.25 | 0.34±0.30 | <0.001 |
| Refraction error (D) | −2.49±1.92 | −2.7±2.71 | −2.4±2.62 | 0.23 |
| Age (year± SD) | 13.1±3.1 | 14.3±4.5 | 13.7±4.1 | 0.17 |
Table 2.
Comparison of mean value between normal, glaucoma suspect and glaucomatous eye using optical coherence tomography retinal nerve fiber layer analysis and optic nerve head ophthalmoscopic examination
| | | Normal | Glaucoma suspect | Glaucoma | p-value* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OCT RNFL analysis | Superior | 131.26±14.09 | 121.3±35.7 | 104.59±38.72 | 0.002 |
| | Nasal | 78.0±15.2 | 75.92±18.64 | 65.09±25.53 | 0.072 |
| | Inferior | 134.34±12.91 | 122.07±33.18 | 107.45±46.53 | 0.004 |
| | Temporal | 81.31±17.2 | 77.38±38.84 | 66.409±23.2 | 0.064 |
| | Average | 105.39±9.22 | 99.23±28.31 | 79.98±28.85 | <0.001 |
| Ophthalmoscopic | Cup/Disk Horizontal Ratio | 0.41±0.15 | 0.50±0.19 | 0.68±0.21 | <0.001 |
| examination | Cup/Disk Vertical Ratio | 0.43±0.17 | 0.48±0.18 | 0.72±0.19 | <0.001 |
Table 3.
Correlation of optic nerve headophthalmoscopic examination parameters, optical coherence tomography retinal nerve fiber layer analysis parameters
| | |
Ophthalmoscopic exam. |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Cup/disk horizontal ratio |
Cup/disk vertical ratio |
||||
| r | p-value* | R | p-value* | ||
| OCT RNFL analysis | Superior | −0.198 | 0.123 | −0.290 | 0.022 |
| | Nasal | −0.195 | 0.128 | −0.203 | 0.113 |
| | Inferior | −0.228 | 0.075 | −0.334 | 0.008 |
| | Temporal | −0.230 | 0.072 | −0.283 | 0.026 |
| | Average | −0.304 | 0.016 | −0.382 | 0.002 |
Table 4.
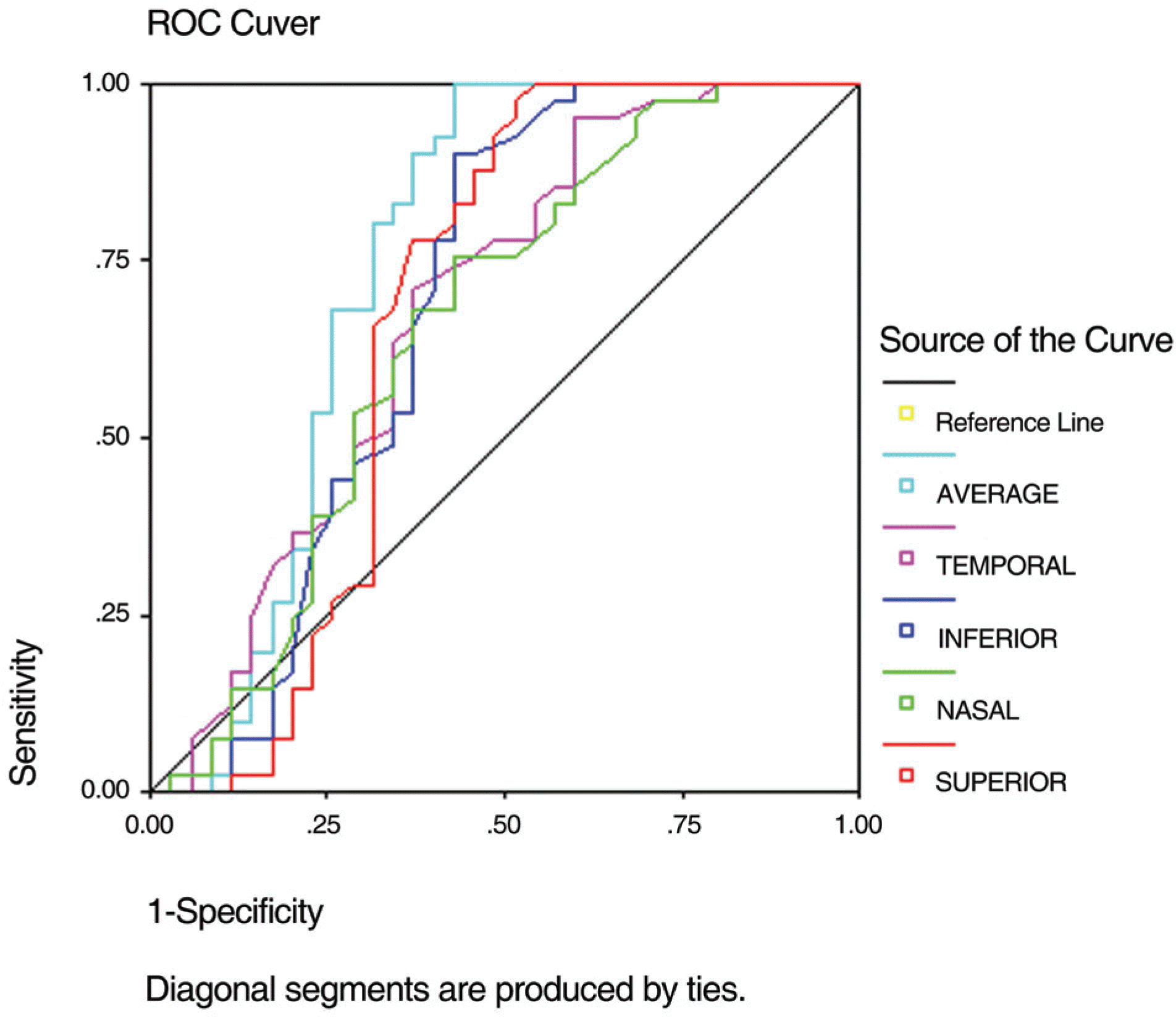
Area under the receiver operator characteristic(ROC) curve, sensitivity, specificity and cut-off values by each parameters (ROC curve and discriminant analysis)
| OCT* RNFL† Analysis | ROC area | Sensitivity(%) | Specificity(%) | Cut-off value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Superior | 0.679 | 70.7 | 65.7 | 124.5 |
| Nasal | 0.656 | 67.5 | 62.9 | 72.5 |
| Inferior | 0.684 | 78.0 | 60.0 | 123.5 |
| Temporal | 0.677 | 70.2 | 62.9 | 73.5 |
| Average | 0.751 | 71.0 | 66.8 | 100.3 |
| New discriminant function‡ | 0.722 | 73.7 | 65.7 | 0.0823 |
| New discriminant function§ | 0.750 | 78.0 | 68.6 | 0.0236 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download