Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the prognosis of vision and the development of amblyopia in primary congenital glaucoma patients.
Methods
The author reviewed 38 eyes of 22 primary congenital glaucoma patients and evaluated variables such as age at time of surgery and at the last visit, preoperative IOP, Cup-to-disc(CD) ratio, corneal diameter, refractive error, axial lengths and IOP, CD ratio and visual acuity at the last visit. According to visual acuity, the patients were divided into 3 groups, good (>0.5), fair (0.1∼0.5), and poor (<0.1). The amblyopia was defined when BCVA was below 0.8 and no evidence of progression of glaucoma. There were 4 types of amblyopia: deprivation, anisometropic, strabismic and organic. The author compared the 3 groups and evaluated factors affecting the vision as well as the prevalence of amblyopia.
Results
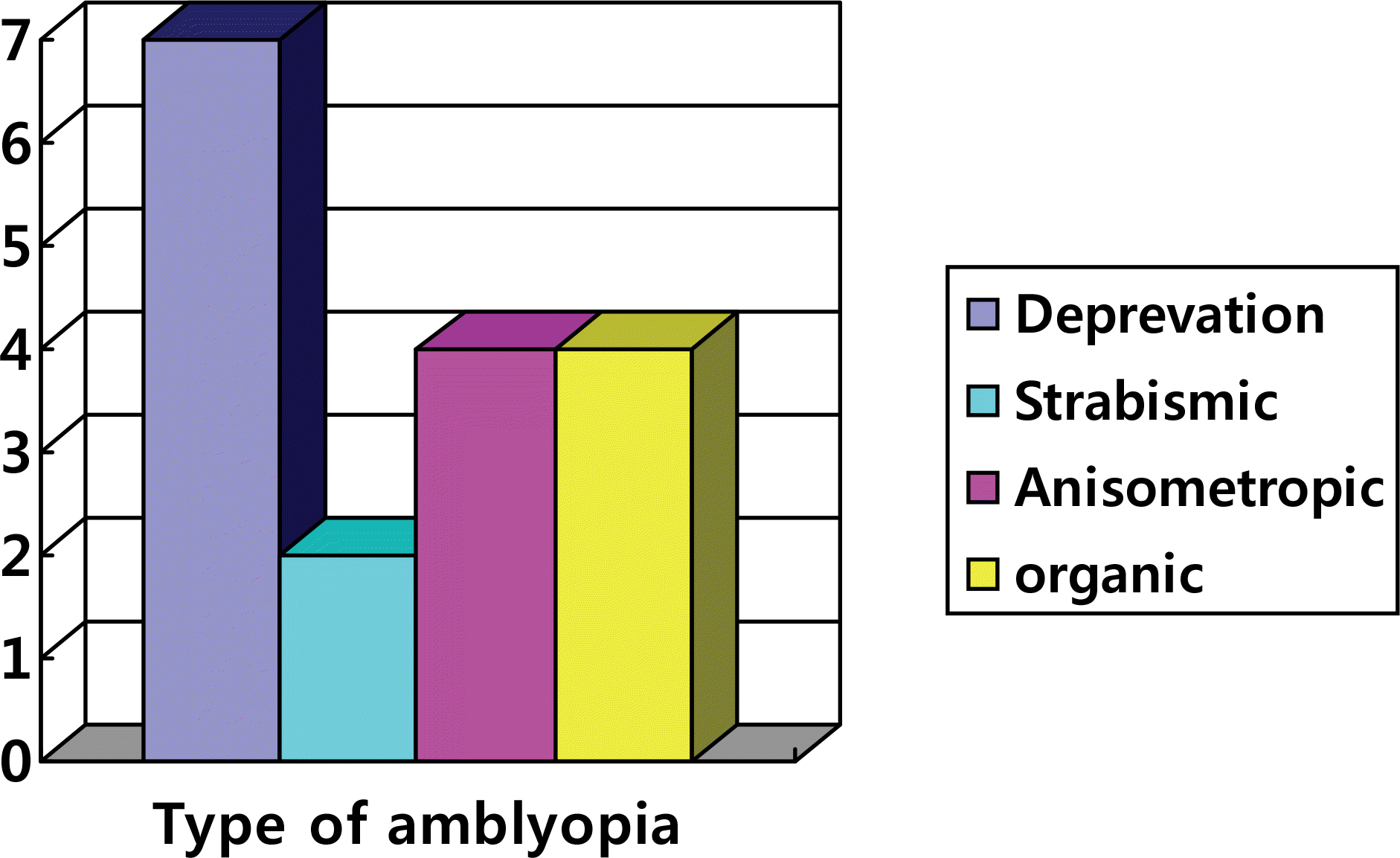
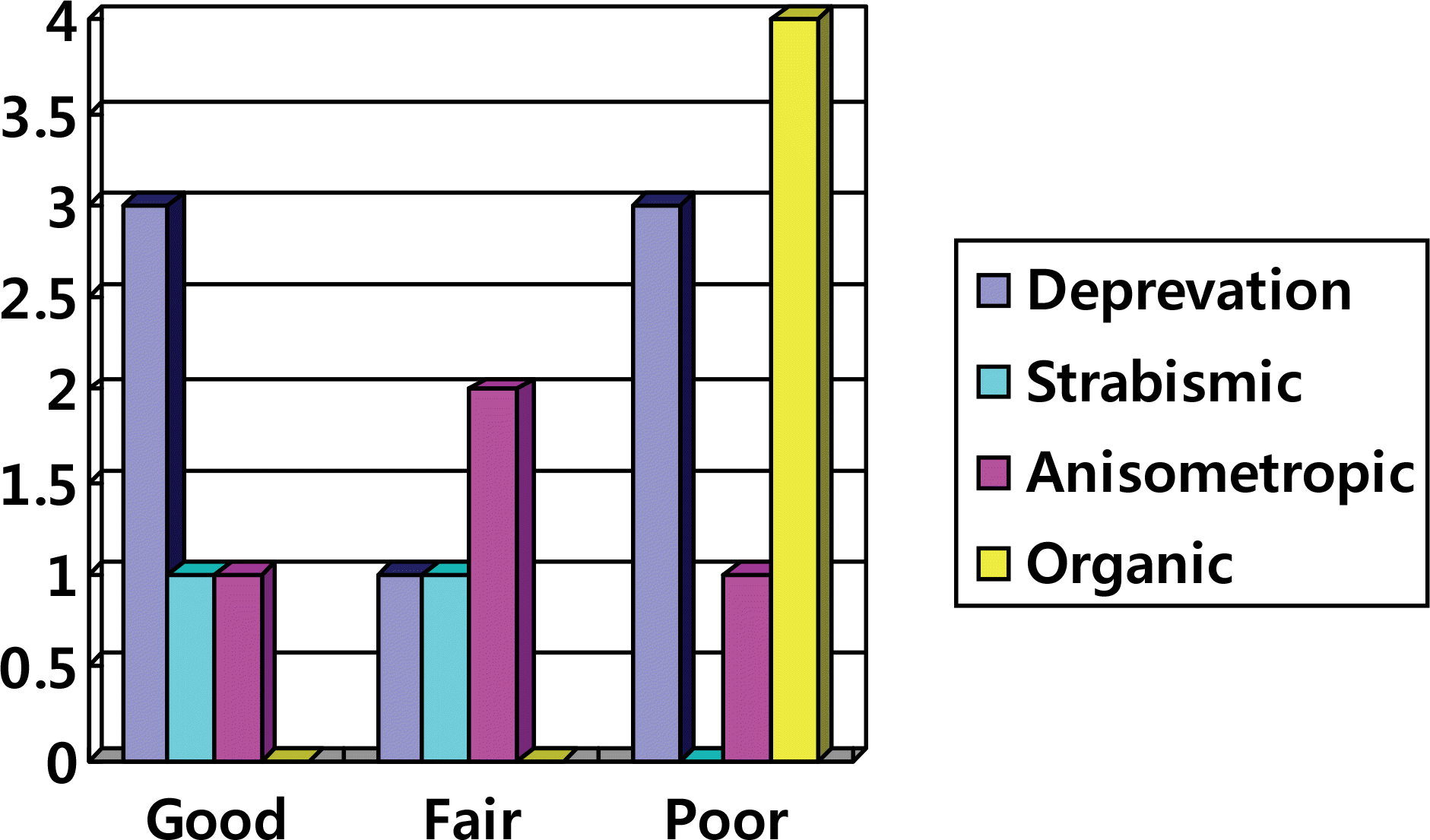
There were 17 eyes in the good group, 4 eyes in the fair group and 17 eyes in the poor group (p<0.05). Amblyopia developed in 17 eyes with 7 eyes showing deprivation amblyopia. Anisometropic and organic amblyopia were each found in 4 eyes, and strabismic amblyopia was found in 2 eyes. The postoperative IOP and CD ratio and preoperative CD ratio were significantly lower in the good group than the other groups (p<0.05).
Go to : 
References
1. Bermejo E, Martinez-Frias ML. Congenital eye malformation: clinical-epidemiological analysis of 1,124,654 consecutive births in spain. Am J Med Genet. 1998; 75:497–504.
2. Richardson KT Jr, Ferguson WJ Jr, Shaffer RN. Long-term functional results in infantile glaucoma. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1967; 71:833–6.
3. Haas J. Principles and problems of therapy in congenital glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol. 1968; 7:140–6.
4. Morgan KS, Black B, Ellis FD, Helveston EM. Treatment of congenital glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1981; 92:799–803.

5. Haas JS. End results of treatment. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1955; 59:333–41.
6. Taylor RH, Ainsworth JR, Evans AR, Levin AV. The epidemiology of pediatric glaucoma: the Toronto experience. J AAPOS. 1999; 3:308–15.

7. Barsoum-Homsy M, Chevrette L. Incidence and prognosis of childhood glaucoma: a study of 63 cases. Ophthalmology. 1986; 93:1323–7.
8. Biglan AW, Hiles DA. The visual results following infantile glaucoma surgery. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1979; 16:377–81.

9. O'Reilly J, Lanigan B, O'Keefe M. Long-term visual results following primary trabeculectomy for infantile glaucoma. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2001; 79:472–5.
10. Gollamudi SR, Traboulsi EI, Chamon W, et al. Visual outcome after surgery for Peters' anomaly. Ophthalmic Genet. 1994; 15:31–5.

11. Beck AD. Diagnosis and management of pediatric glaucoma. Ophthalmol Clin North Am. 2001; 14:501–12.

12. Broughton WL, Parks MM. An analysis of treatment of congenital glaucoma by goniotomy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1981; 91:566–72.

13. Morin JD, Merin S, Sheppard RW. Primary congenital glaucoma a survey. Can J Ophthalmol. 1974; 9:17–28.
14. Clothier CM, Rice NS, Dobinson P, Wakefield E. Amblyopia in congenital glaucoma. Trans Ophthalmol Soc U K. 1979; 99:427–31.
15. Robin AL, Quigley HA, Pollack IP, et al. An analysis of visual acuity, visual fields, and disk cupping in childhood glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1979; 88:847–58.

17. Morin JD, Bryars JH. Causes of loss of vision in congenital glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 1980; 98:1575–6.

18. Richardson KT Jr, Ferguson WJ Jr, Shaffer RN. Long-term functional results in infantile glaucoma. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1967; 71:836–7.
19. Wallace DK, Plager DA, Snyder SK, et al. Surgical results of secondary glaucomas in childhood. Ophthalmology. 1998; 105:101–11.

20. Yang LL, Lambert SR. Peters'anomaly. A synopsis of surgical management and visual outcome. Ophthalmol Clin North Am. 2001; 14:467–77.
21. Kushner BJ. Successful treatment of functional amblyopia associated with juvenile glaucoma. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1988; 226:150–3.

23. Mandal AK, Gothwal VK, Bagga H, et al. Outcome of surgery on infants younger than 1 month with congenital glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 2003; 110:1909–15.

24. Mandal AK, Bhatia PG, Bhaskar A, Nutheti R. Long-term surgical and visual outcomes in Indian children with developmental glaucoma operated on within 6 months of birth. Ophthalmology. 2004; 111:283–90.

25. Kargi SH, Koc F, Biglan AW, Davis JS. Visual acuity in children with glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 2006; 113:229–38.

26. Jaafar MS, Kazi GA. Normal intraocular pressure in children: a comparative study of the Perkins applanation tonometer and the pneumatonometer. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1993; 30:284–7.

27. Pensiero S, Da Pozzo S, Perissutti P, et al. Normal intraocular pressure in children. J Pediatric Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1992; 29:79–84.

28. Von Noorden GK, Campos EC. Binocular Vision and Ocular Motility. 6th ed.St. Louis: Mosby;2002. p. 246.
Go to : 
Table 1.
Comparison of patients profiles between three groups based upon visual acuity
| | Poor | Fair | Good | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (M:F) | 11:6 | 1:3 | 10:7 | 0.349* |
| Eyes (OD:OS) | 10:7 | 2:2 | 7:10 | 0.589* |
| Type of surgery | | | | 1.000* |
| Trabeculotomy | 12 | 3 | 11 | |
| Trabeculectomy | 4 | 1 | 5 | |
| Both | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Number of surgery | 1.41±0.71 | 1.80±1.78 | 1.72±0.82 | 0.549† |
| Age at surgery (mon) | 31.5±45.5 | 3.3±2.2 | 30.4±40.2 | 0.448† |
| Follow-up (mon) | 88.6±83.8 | 105.0±85.21 | 124.2±67.7 | 0.411† |
| Age at last visit (yr) | 9.7±8.5 | 9.0±7.1 | 12.5±5.9 | 0.462† |
| Total (n) | 17 | 4 | 17 | |
Table 2.
Comparison of intraocular pressure and CD ratio between three groups
| | Poor | Fair | Good | p-value* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preop IOP† (mmHg) | 32.34±11.47 | 29.75±7.59 | 29.53±11.61 | 0.770 |
| Postop IOP (mmHg) | 20.13±11.42 | 15.25±4.50 | 12.71±3.06 | 0.039 |
| Preop CD‡ | 0.81±0.20 | 0.63±0.15 | 0.62±0.22 | 0.035 |
| Postop CD | 0.85±0.23 | 0.35±0.07 | 0.53±0.25 | 0.002 |
| Axial length (mm) | 24.83±3.98 | 20.73±1.15 | 24.81±3.17 | 0.308 |
| Corneal diameter (mm) | 12.93±1.45 | 12.12±0.85 | 13.01±0.51 | 0.351 |
Table 3.
Comparison of intraocular pressure and CD ratio between 2 groups
| | Good | Others | p-value* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preop IOP† (mmHg) | 29.53±11.61 | 31.76±10.72 | 0.542 |
| Postop IOP (mmHg) | 12.71±3.06 | 19.11±10.44 | 0.018 |
| Preop CD‡ | 0.62±0.22 | 0.78±0.20 | 0.026 |
| Postop CD | 0.53±0.25 | 0.79±0.28 | 0.017 |
| Axial lengths (mm) | 24.81±3.17 | 23.80±3.88 | 0.564 |
| Corneal diameter (mm) | 13.01±0.51 | 12.76±1.37 | 0.484 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download