Abstract
Purpose
To compare the visual function among 3 aspheric intraocular lenses (IOLs) after cataract surgery.
Methods
A prospective analysis among 70 eyes of 68 patients who had undergone phacoemulsification and implantation of aspheric IOLs (Acrysof IQ, 30 eyes; Tecnis ZA9003, 20 eyes; Akreos Adapt-AO, 20 eyes) was performed. The best corrected visual acuity (BCVA), refraction, coma, trefoil, spherical aberration, root-mean-square (RMS), contrast sensitivity test, satisfaction and glare was evaluated during the follow-up period of 3 months.
Results
There were no significant differences in BCVA, satisfaction, glare, coma, trefoil, RMS and contrast sensitivity test among the 3 aspheric IOLs. Spherical aberration in Akreos Adapt-AO (0.04±0.05 μ m) was higher compared with Acrysof IQ (0.03±0.04 μ m) and Tecnis ZA9003 (0.11±0.03 μ m)(p<0.01). The predictability of postoperative spherical equivalent in the Akreos Adapt-AO group (−0.57±0.22D) represented a statistically significant myopic refractive error compared with the Acrysof IQ (0.01±0.77D) and the Tecnis ZA9003 (−0.20±0.71D) groups (p=0.04).
Go to : 
References
1. Bellucci R, Morselli S, Piers P. Comparison of wavefront aberrations and optical quality of eyes implanted with five different intraocular lenses. J Refrac Surg. 2004; 20:297–306.

2. Guirao A, Gonzalez C, Redondo M, et al. Average optical perfomance of the human eye as a function of age in a normal population. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1999; 40:203–13.
3. Yoon G, Jeong TM, Cox IG, Williams DR. Vision improvement by correcting higher-order aberrations with phase plates in normal eyes. J Refract Surg. 2004; 20:S523–7.

4. Guirao A, Renondo M, Geraghty E, et al. Corneal optical aberrations and retinal image quality in patients in whom monofocal intraocular lenses were implanted. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002; 120:1143–51.

5. Ricci F, Scuderi G, Missiroli F, et al. Low contrast visual acuity in pseudophakic patients implanted with an anterior surface modified prolate intraocular lens. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2004; 82:718–22.

6. Tzelikis PF, Akaishi L, Trindade FC, Boteon JE. Spherical aberration and contrast sensitivity in eyes implanted with aspheric and spherical intraocular lenses: a comparative study. Am J Ophthalmol. 2008; 145:827–33.

7. Caporossi A, Martone G, Casprini F, Rapisarda L. Prospective randomized study of clinical perfomance of 3 aspheric and 2 spherical intraocular lenses in 250 eyes. J Refract Surg. 2007; 23:639–48.
8. Johansson B, Sundelin S, Wikberg-Matsson A, et al. Visual and optical performance of the Akreos Adapt Advanced Optics and Tecnis Z9000 intraocular lenses: Swedish multicenter study. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:1565–72.
9. Franchini A. Compromise between spherical and chromatic aberration and depth of focus in aspheric intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:497–509.

10. Mester U, Dillinger P, Anterist N. Impact of a modified optic design on visual function: clinical comparative study. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:652–60.

11. Packer M, Fine IH, Hoffman RS. Aspheric intraocular lens selection: the evolution of refractive cataract surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2008; 19:1–4.

12. Piers PA, Weeber HA, Artal P, Norrby S. Theoretical comparison of aberration-correcting customized and aspheric intraocular lenses. J Refract Surg. 2007; 23:374–84.

13. Nin YK, Jansonius NM, Geraphty E, et al. Effect of intraocular lens implantation on visual acuity, contrast sensitivity, and depth of focus. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:2073–81.
14. Pandita D, Raj SM, Vasavada VA, et al. Contrast sensitivity and glare disability after implantation of acrysof IQ natural aspheric intraocular lens: prospective randomized masked clinical trial. J Cataract Refrat Surg. 2007; 33:603–10.
15. Kasper T, Buhren J, Kohnen T. Intraindividual comparison of higher-order aberrations after implantation of aspherical and spherical intraocular lenses as a function of pupil diameter. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:78–84.

16. Bellucci R, Morselli S, Piers P. Comparison of wavefront aberrations and optical quality of eyes implanted with five different intraocular lenses. J Refract Surg. 2004; 20:297–306.

17. Casprini F, Balestrazzi A, Tosi GM, et al. Glare disability and spherical aberration with five foldable intraocular lenses: a prospective randomized study. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2005; 83:20–5.

18. Tzelikis PF, Akaishi L, Trindade FC, Boteon JE. Spherical aberration and contrast sensitivity in eyes implanted with aspheric and spherical intraocular lenses: a comparative study. Am J Ophthalmol. 2008; 145:827–33.

19. Petternel V, Menapace R, Findl O, et al. Effect of optic edge design and haptic angulation on postoperative intraocular lens position change. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:52–7.

20. Heo H, Kim HG, Yoon KC, Park YG. Comparison of long-term results between one-piece and three-piece acrylate intraocular lens. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:245–52.

21. Ji YS, Lee KH, Park YG, Yoon KC. Clinical results of implantation of hydrophilic acrylic intraocular lenses. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:1065–71.
Go to : 
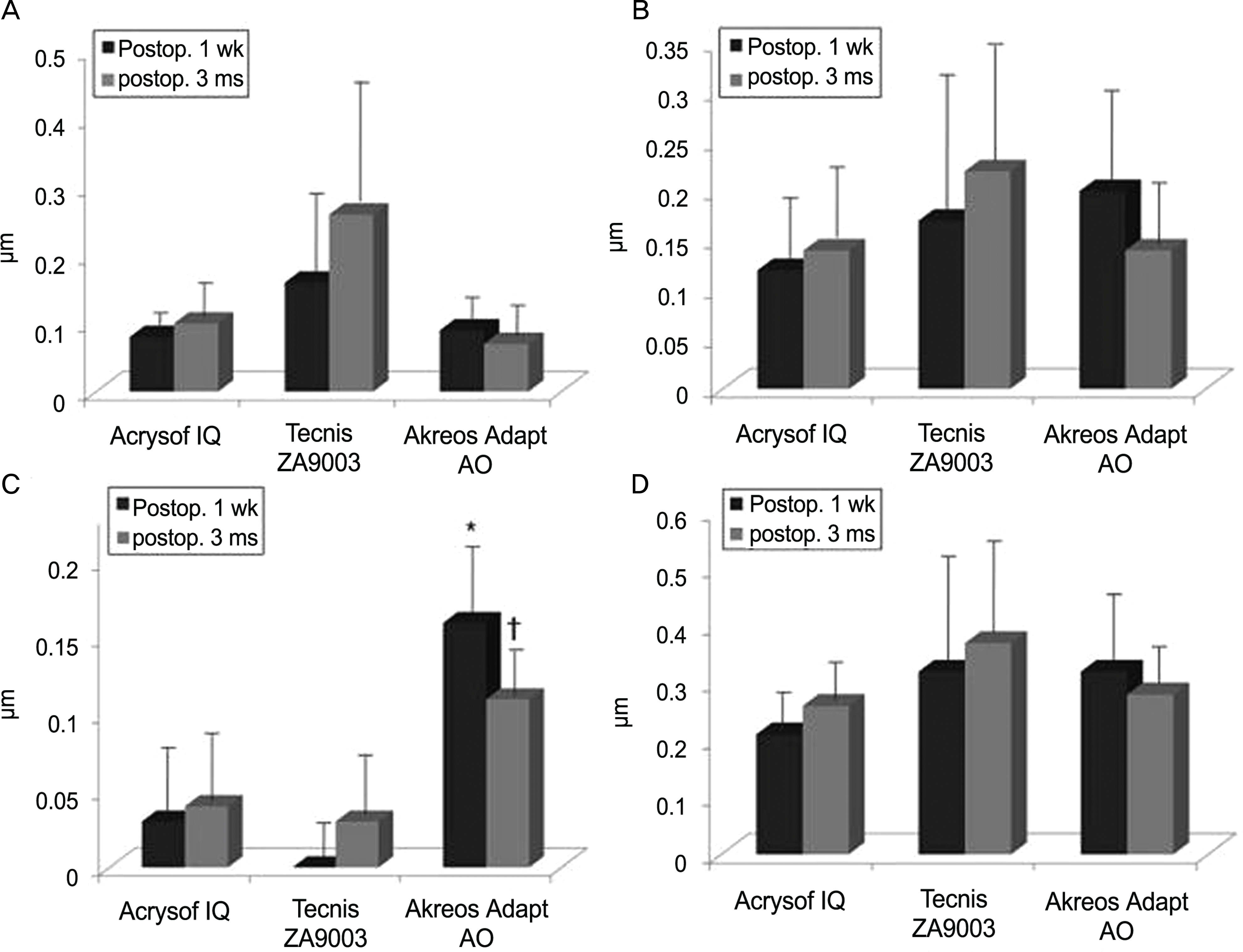 | Figure 1.Comparison of coma (A), trefoil (B) spherical aberration (C) and root-mean-square (RMS) (D) among three aspheric intraocular lenses. Preop.=preoperative; Postop.=postoperative; wk=week; ms=month.* p<0.05 compared with the acrysof IQ and tecnis ZA9003 group at postoperative 1 week; † p<0.05 compared with the acrysof IQ and tecnis ZA9003 group at postoperative 3 months. |
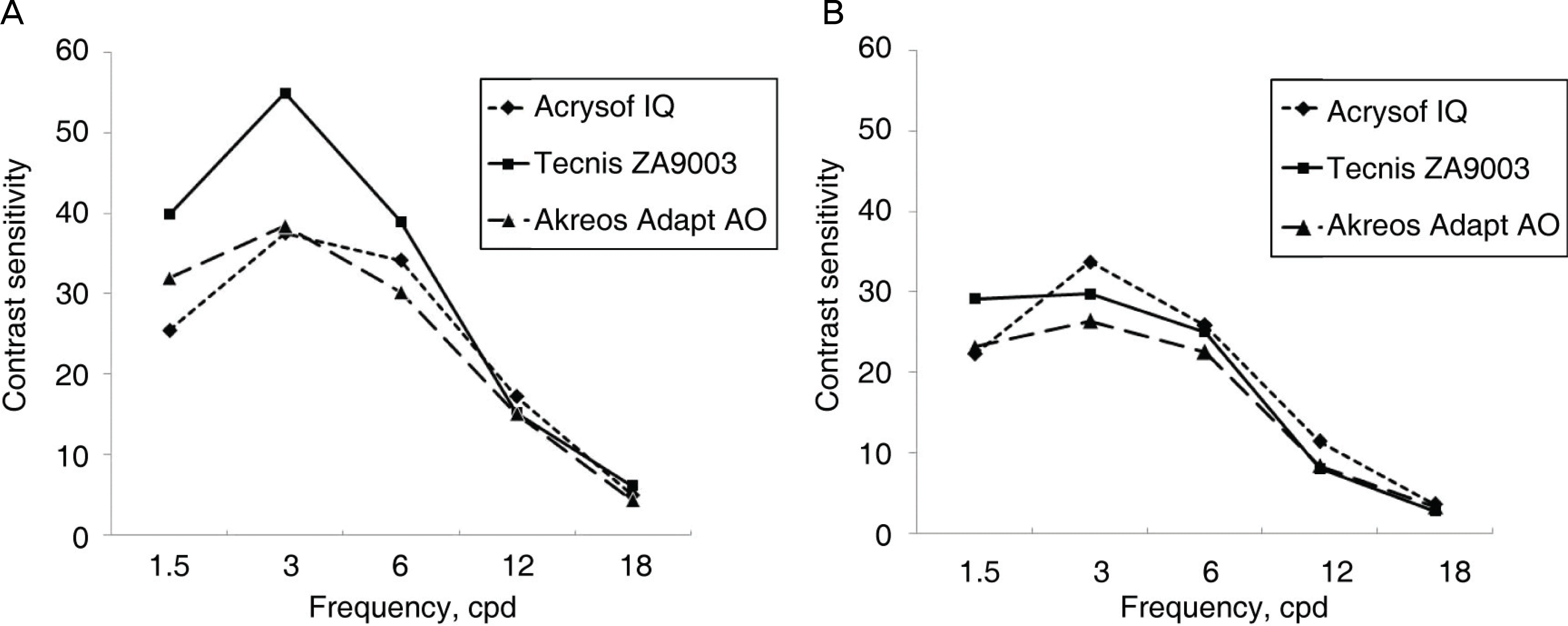 | Figure 2.Comparison of contrast sensitivity test under photopic condition (A) and mesopic condition (B) three months postoperatively. |
Table 1.!
Characteristics of patients in aspheric intraocular lens groups
Table 2.
Changes of the preoperative and postoperative uncorrected visual acuity (UCVA), best-corrected visua acuity (BCVA) and spherical equivalent among three aspheric intraocular lenses
| Variables | Acrysof IQ SN60WF | Tecnis Z9003 | Akreos Adapt-AO | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UCVA (logMAR) | | | | |
| Preop. | 1.26±0.24 | 1.36±0.17 | 1.47±0.14 | 0.62 |
| Postop. 3 ms | 0.25±0.31 | 0.33±0.37 | 0.45±0.42 | 0.81 |
| BCVA (logMAR) | | | | |
| Preop.† | 1.06±0.60 | 1.16±0.68 | 1.38±0.81 | 0.58 |
| Postop.‡ 3 ms§ | 0.22±0.31 | 0.28±0.39 | 0.42±1.09 | 0.71 |
| Spherical equivalent (D)* | | | | |
| Preop. | −1.47±4.96 | −1.69±2.57 | −1.36±2.12 | 0.47 |
| Postop. 3 ms | −0.47±1.10 | −0.63±0.48 | −0.64±1.19 | 0.57 |
Table 3.
Changes of the postoperative anterior chamber depth and the distance between posterior surface of iris and anterior surface of intraocular lens (IOL)
Table 4.
Characteristics of the three aspheric intraocular lenses




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download