Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the clinical usefulness of the 10-prism-diopter (PD) fixation test in the diagnosis of amblyopia.
Methods
The study comprised 132 children (42 normal, 90 amblyopes) who underwent the 10-PD fixation test and stereoacuity test. The sensitivity, specificity, false-positive and false-negative rates of the 10-PD fixation test were analyzed according to the clinical diagnosis.
Results
The 10-PD fixation test sensitivity was 86%, the specificity was 61%, the false-positive rate was 17% and the false-negative rate was 24%. Data showed agreement between the 10-PD fixation test and the stereoacuity test (γ=0.737, p=0.000). The results in the 10-PD base-down test and base-out test also showed agreement (γ=0.779, p=0.000).
References
1. von Noorden GK. Amblyopia: a multidisciplinary approach. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1985; 26:1704–16.
5. Wirght KW, Edelman P, Walonker F, Yiu S. Reliability of fixation preference testing in diagnosing amblyopia. Arch Ophthalmol. 1986; 104:549–53.
6. Lee SJ, Park SH, Shin HH. Stereopsis in child amblyopes. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1995; 36:1598–604.
7. Emin CS, Mehmet CM, Sansal G, et al. The reliability of grading the fixation preference test for the assessment of interocular visual acuity differences in patients with strabismus. J AAPOS. 2005; 9:468–74.
8. Wirght KW, Frances W, Paula E. 10-Diopter fixation test for amblyopia. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981; 99:1242–6.
9. Parks MM. The monofixation syndrome. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1969; 67:609–57.
Figure 1.
Responses to 10-PD base-out test. We regarded A and B as positive response that means equal fixation preference, C and D as negative response or suppression. (A) Non fixating eye (right eye) makes convergence and left eye maintain fixation while also converging. (B) Both eyes make version movement to the opposite side on which the prism was placed, followed by a convergence to the fixation target. (C) Version movement of both eyes, with no convergence. (D) No movement of either eye.
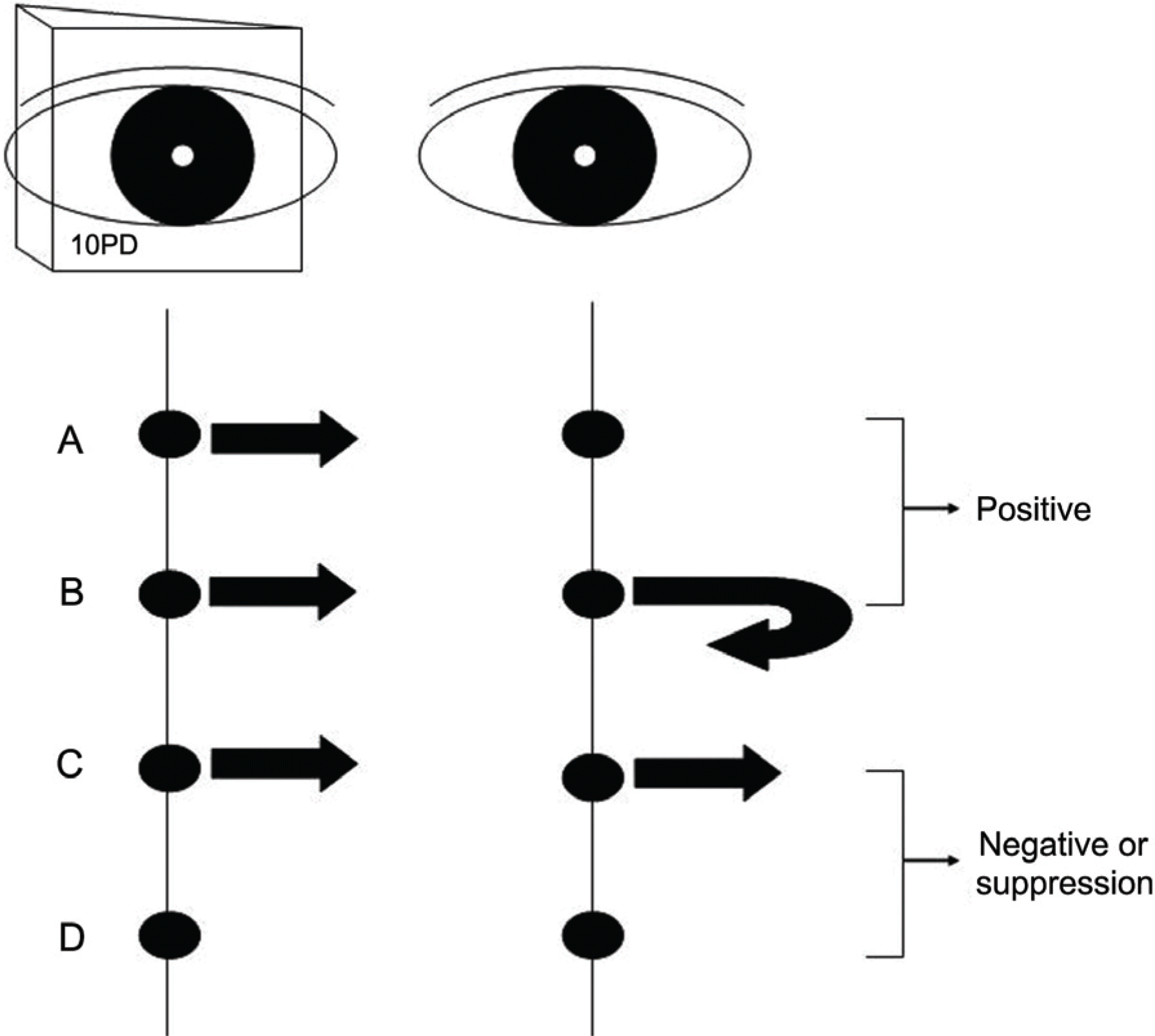
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of patients
|
Amblyopia group |
Normal group | p* | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| strabismic amblyopia | anisometric amblyopia | |||
| Age at time of test performed (years) | 7.2±1.5 | 7.6±1.8 | 6.4±2.4 | 0.305 |
| Visual acuity of amblyopic eye | 0.48±0.16 | 0.44±0.19 | - | 0.125 |
| Total | 90 | 42 | - | |
Table 2.
Definitions of sensitivity, specificity, false-positive, and false-negative rates in the diagnosis of amblyopia
| Clinical Test | t Amblyopia | Normal | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amblyopia | A | B | A+B |
| Normal | C | D | C+D |
| Total | A+C | B+D | A+B+C+D |
Table 3.
The results of 10-prism-diopter fixation test
| Clinical 10-PD test* | Amblyopia | Normal | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amblyopia | Strabismic amblyopia | 32 | 4 | 36 |
| Anisometropic amblyopia | 50 | 4 | 54 | |
| Normal | 17 | 25 | 42 | |
| Total | 99 | 33 | 132 | |
Table 4.
The results of stereopsis
| Clinical Stereopsis | Amblyopia | Normal | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amblyopia | 77 | 13 | 90 |
| Normal | 9 | 33 | 42 |
| Total | 86 | 46 | 132 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download