Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the change in hyperdeviation according to position change in patients with vertical strabismus.
Methods
The authors measured the hyperdeviation in 32 patients with vertical strabismus at 6 m, 2 m, and 33 cm in the seated position and at 2 m and 33 cm in the supine position using the alternate prism cover test.
Results
The mean amount of hyperdeviation in the seated position was 6.31±6.27 PD at 6 m, 6.31±6.27 PD at 2 m, and 3.69±6.65 PD at 33 cm. The mean hyperdeviation in the supine position was 6.09±6.37 PD at 2 m and 3.55±6.36 PD at 33 cm. There was no significant difference in hyperdeviation according to the change of position at the same measuring distance. No significant difference between the hyperdeviation at 6 m in the seated position and 2 m in the supine position was found (P>0.05).
References
1. von Noorden GK, Campos EC. Binocular vision and ocular motility: Theory and management of strabismus. 6th ed.St. Louis: Mosby;2002. p. 591–3.
2. Jeon YH, Kim SY. The change of exodeviation in the seated and supine position. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:264–8.
3. Becker R, Krizizok TH, Wassill H. Use of preoperative assessment of positionally induced cyclotorsion: a video-oculographic study. Br J Ophthalmol. 2004; 88:417–21.

4. Gordes RS, Vaseghi S, Pansell T, et al. Influence of the body position to cyclorotation in healthy probands. Ophthalmologe. 2002; 99:142.
5. Swami AU, Steinert RF, Osborne WE, White AA. Rotational malposition during laser in situ keratomileusis. Am J Ophthalmol. 2002; 133:561–2.

6. Cho HH, Sohn MA. The ocular cyclotorsion induced by the positional change. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:2911–7.
7. Jwa WB, Hong SJ, Lee JH, Lee JM. Evaluation of the ocular cyclotorsion during laser in situ keratomileusis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:2099–104.
8. Jun JY, Hun D, Chang HR. Position-induced cyclotorsion under monocular fixation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:111–6.
Figure 2.
The distribution of hyperdeviation angle at 6 m in the seated position in 32 patients with vertical strabismus.* PD=prism diopters.
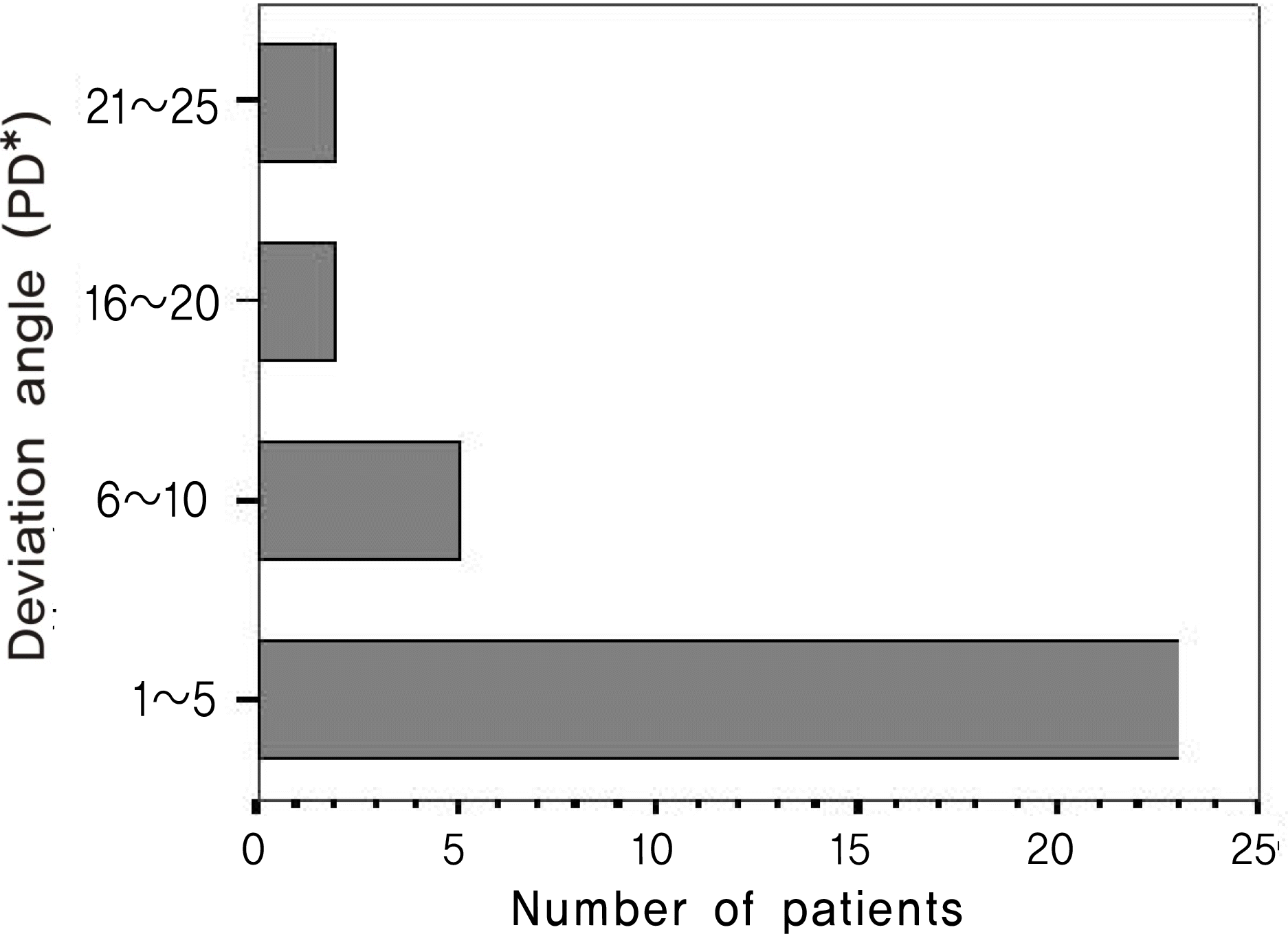
Figure 3.
Comparison of hyperdeviation angle (Mean± SD) at 6 m and 2 m in the seated position in 32 patients with vertical strabismus (p>0.05, paired t-test).* PD=prism diopters.
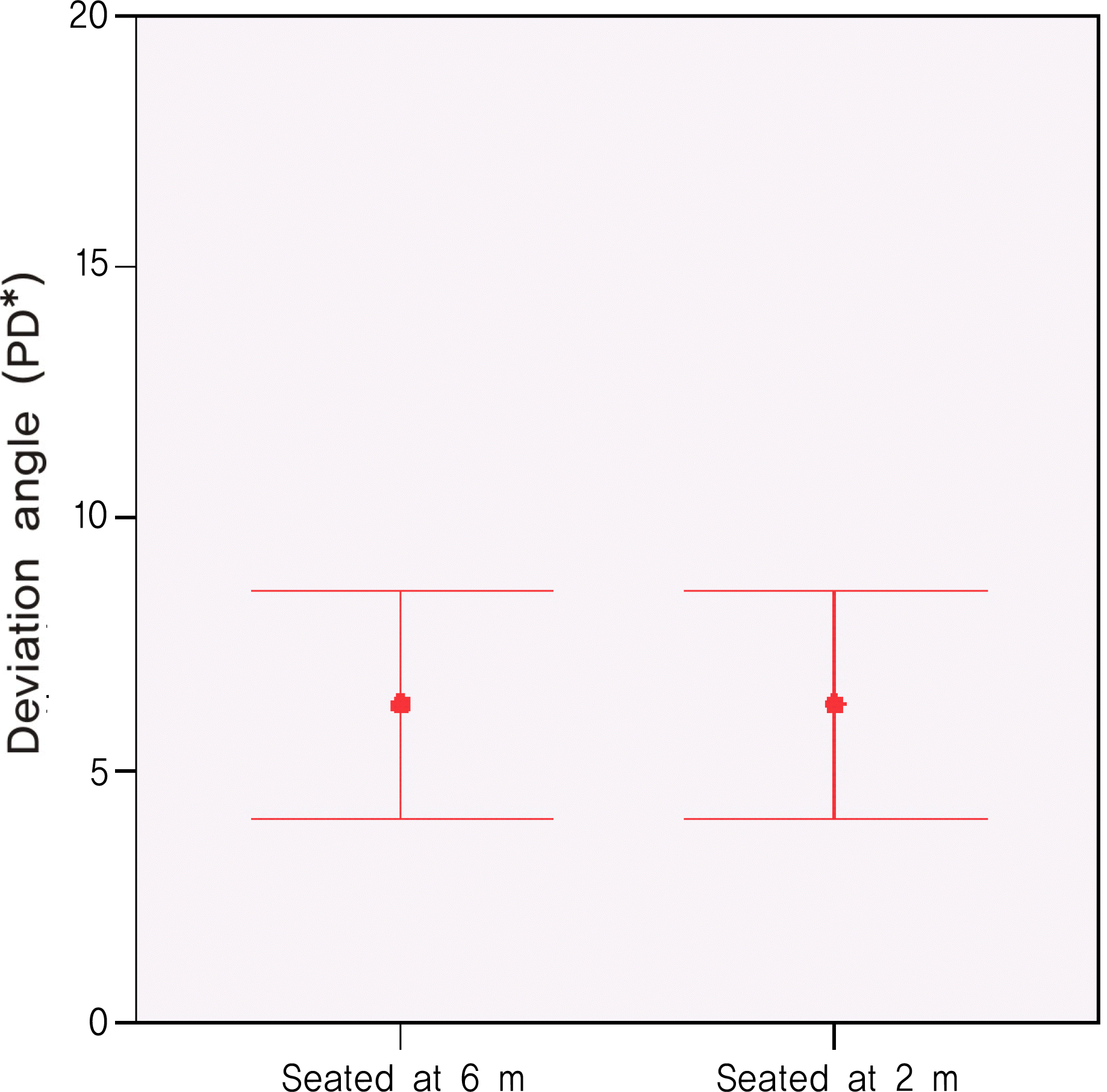
Figure 4.
Comparison of hyperdeviation angle (Mean± SD) at 6 m in the seated position and at 2 m in the supine position in 32 patients with vertical strabismus(p>0.05, paired t-test). * PD=Prism diopters.
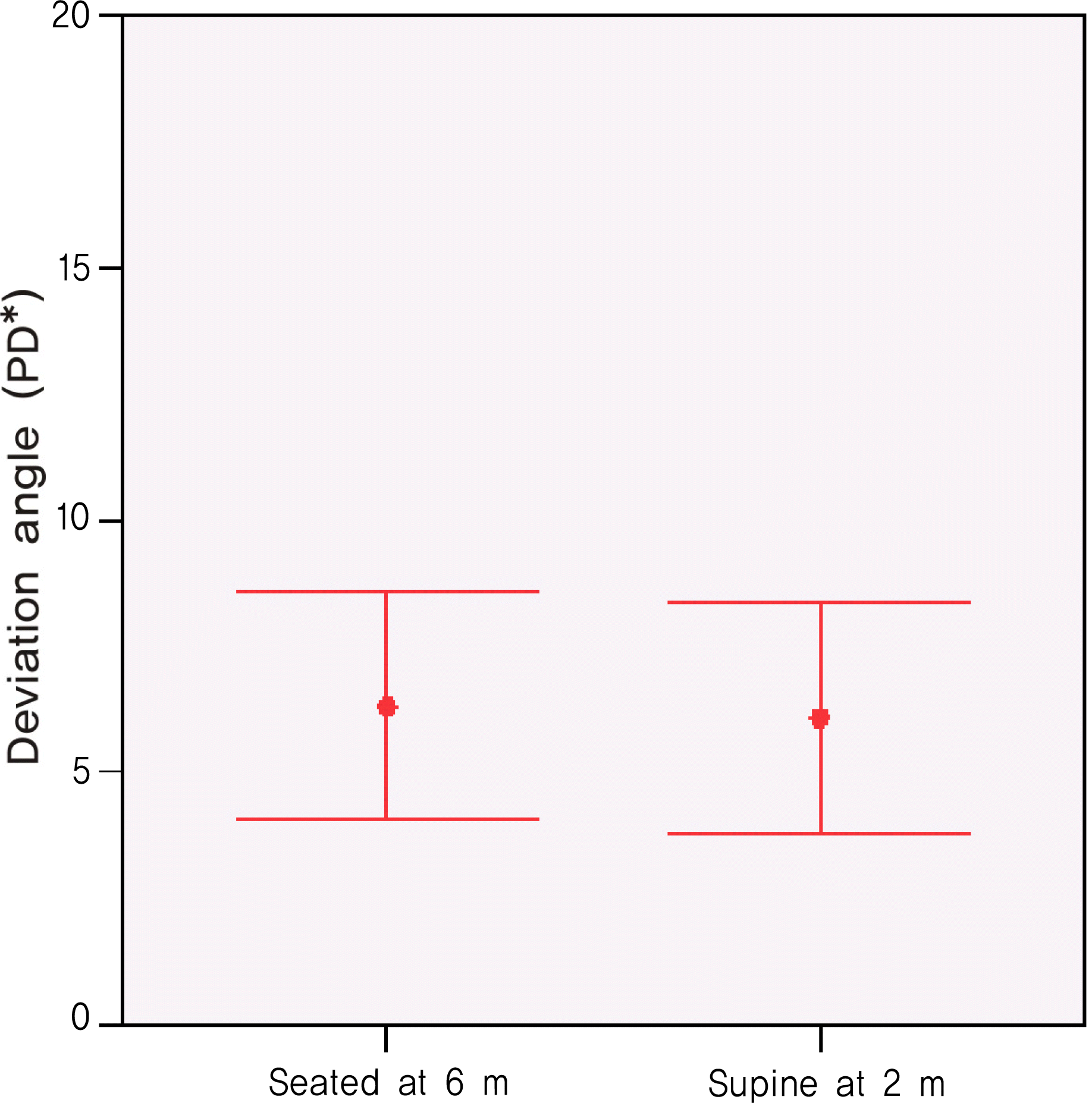
Table 1.
Mean hyperdeviation angle of 32 patients with vertical strabismus measured at different distances in the seated and supine position (Mean± SD)
| Measuring distance | Seated position | Supine position | p-value† |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 m | 6.31±6.27 PD* | ||
| 2 m | 6.31±6.27 PD* | 6.09±6.37 PD* | >0.05 |
| 33 cm | 3.69±6.65 PD* | 3.55±6.36 PD* | >0.05 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


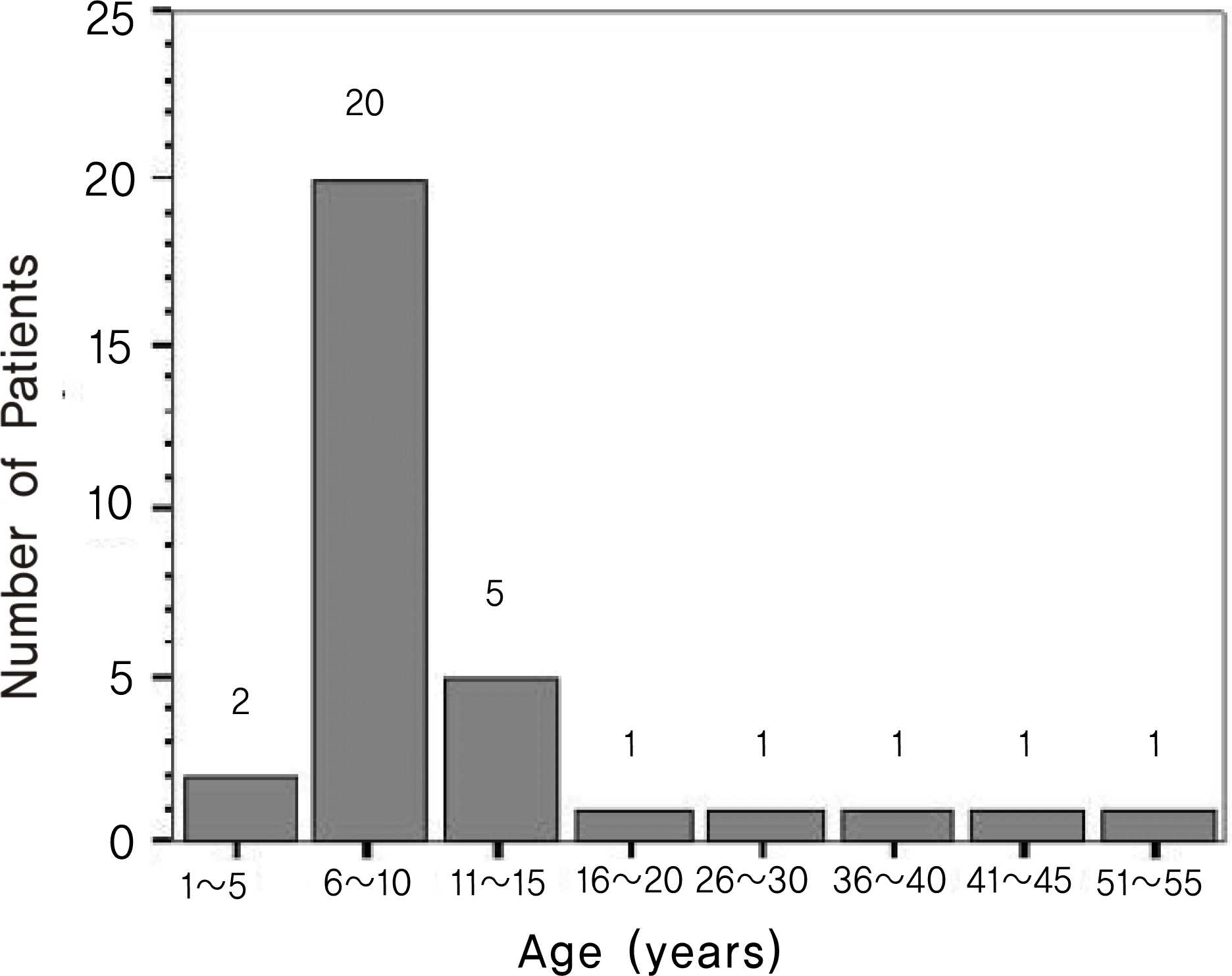
 XML Download
XML Download