Abstract
Purpose
To identify the normal range of factors which can be measured with Ocular Response Analyzer (ORA, Reichert Inc., Depew, NY, USA) in normal Korean, and to analyze factors affecting ORA by measuring intraocular pressure (IOP) of noncontact tonometer (NCT) and central corneal thickness (CCT).
Methods
Three hundred and one normal Korean subjects who did not have specific ophthalmological diseases and surgeries in the past were recruited for this study. Corneal hysteresis (CH), corneal response factor (CRF), corneal-compensated IOP (IOPcc), and Goldmann correlated IOP (IOPg) were measured using ORA. In addition, IOP of NCT and CCT were measured and the results and factors analyzed.
Results
The mean CH measured among normal Korean subjects in this study was 10.70 mmHg. The mean CRF was 10.40 mmHg. CH and CRF were significantly higher in the juvenile group. IOPcc and IOPg as measures of IOP using the ORA had significant correlation with IOP of NCT. In particular, IOPcc appeared to be independent of CCT.
References
1. Dupps WJ Jr. Hysteresis: new mechanospeak for the ophthalmologist. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:1499–501.

2. Luce DA. Determining in vivo biomechanical properties of the cornea with an ocular response analyzer. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:156–62.

3. Touboul D, Roberts C, Kérautret J, et al. Correlations between corneal hysteresis, intraocular pressure, and corneal central pachy-metry. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:616–22.

4. Hager A, Schroeder B, Sadeghi M, et al. The influence of corneal hysteresis and corneal resistance factor on the measurement of intraocular pressure. Ophthalmologe. 2007; 104:484–9.
5. Broman AT, Congdon NG, Bandeen-Roche K, Quigley HA. Influence of corneal structure, corneal responsiveness, and other ocular parameters on tonometric measurement of intraocular pressure. J Glaucoma. 2007; 16:581–8.

6. Lam A, Chen D, Chiu R, Chui WS. Comparison of IOP measure-ments between ORA and GAT in normal Chinese. Optom Vis Sci. 2007; 84:909–14.

7. Kirwan C, O'Keefe M, Lanigan B. Corneal hysteresis and intraocular pressure measurement in children using the Reichert ocular response analyzer. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006; 142:990–2.

8. Moreno-Montañés J, Maldonado MJ, García N, et al. Reproducibility and clinical relevance of the ocular response analyzer in nono-perated eyes: corneal biomechanical and tonometric implications. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008; 49:968–74.
Figure 1.
The difference between the “inward” applanation and the “outward” applanation is called corneal hysteresis (CH).
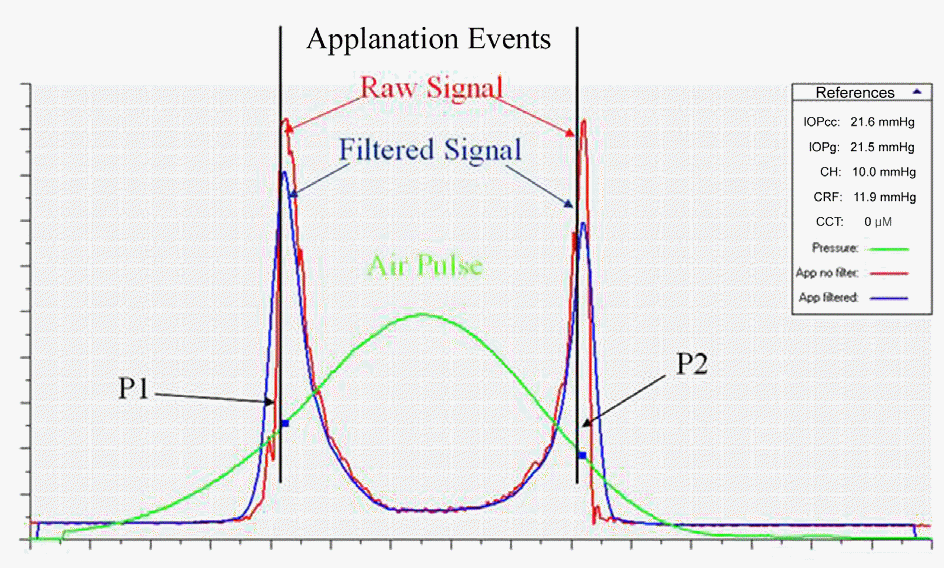
Figure 3.
Histogram of corneal compensated IOP measured by Ocular Response Analyzer (IOPcc) and non contact tonometer (NCT) for normal eyes.
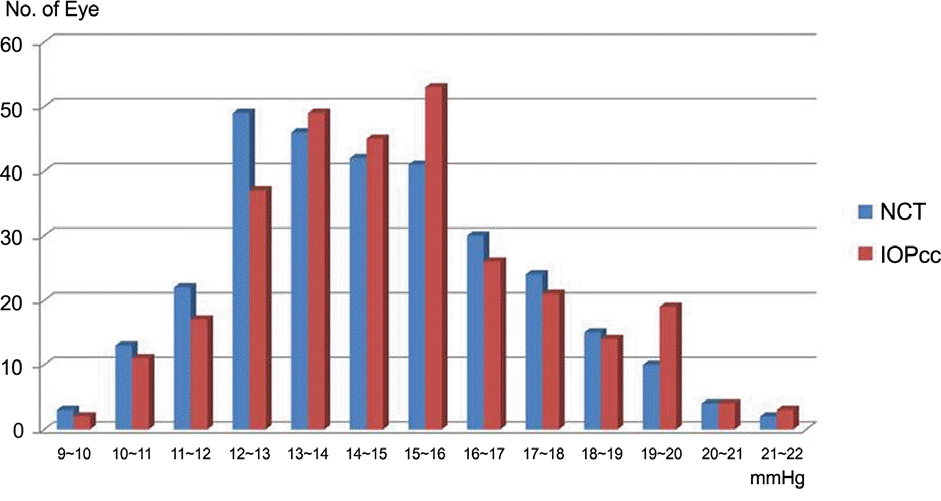
Figure 4.
Statistical correlations between parameters (Pearson correlation test). The yellow squares indicate significance with a high level of correlation, r≥±0.7. The blue squares indicate significance with a moderate correlation, r≥±0.4. The gray squares indicate statically not significance with correlation, p>0.05.(CH=corneal hysteresis; CRF=corneal resistance factor; IOPcc=corneal compensated IOP; IOPg=Goldmann-correlated IOP; CCT=central corneal thickness; NCT=non contact tonometer)
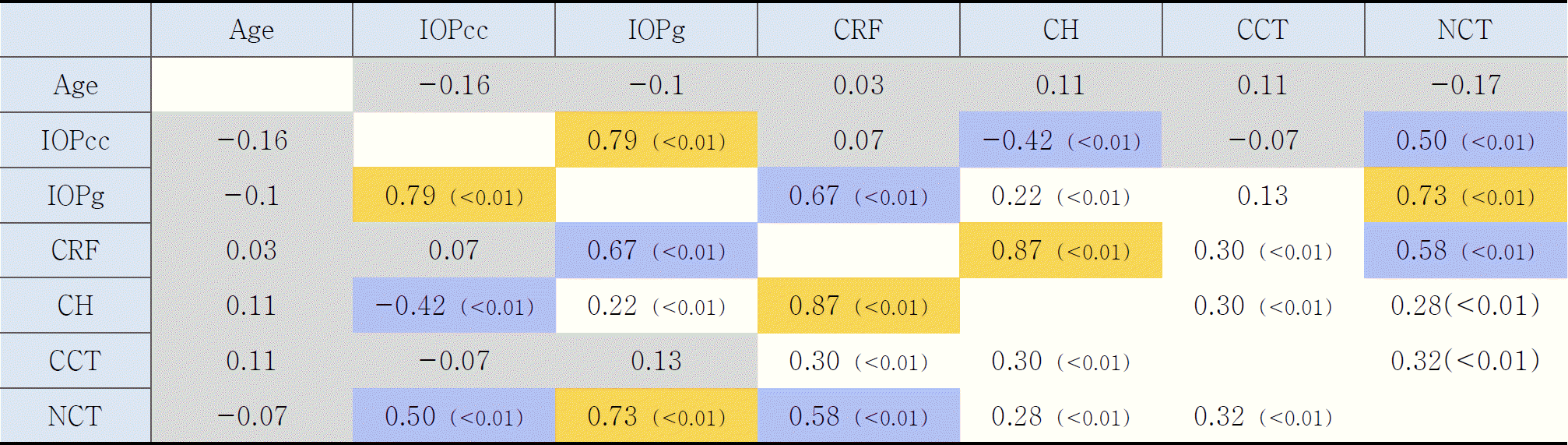
Table 1.
Ocular response analyzer parameter range of Korean normal subjects
| Parameter | N. of Eye | Ave± St dev (mmHg) | Range (mmHg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CH* | 301 | 10.70±1.45 | 7.5∼15.8 |
| CRF† | 301 | 10.40±1.61 | 6.5∼15.9 |
| IOPcc‡ | 301 | 14.90±2.50 | 9.2∼21.7 |
| IOPg§ | 301 | 14.61±2.70 | 8.3∼21.7 |
| NCTП | 301 | 14.27±2.47 | 9.0∼21.0 |
| CCT# | 301 | 542.88±34.13 μm | 470∼658 μm |
Table 2.
Ocular response analyzer parameter of Korean normal subjects comparing to juveniles and adults (paired t-test)
| Juvenile (≤19 years) | Adult(≥20 years) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CH* | 11.06 mmHg | 10.62 mmHg | <0.05 |
| CRF† | 11.06 mmHg | 10.25 mmHg | <0.01 |
| IOPcc‡ | 15.52 mmHg | 14.76 mmHg | <0.05 |
| IOPg§ | 15.78 mmHg | 14.35 mmHg | <0.01 |
| NCTП | 15.44 mmHg | 14.00 mmHg | <0.01 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download