Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the effect of an injection of bevacizumab into the sub-Tenon’s capsule on ocular surface neovascularization disease including pterygium and corneal neovascularization.
Methods
Twenty-five eyes of 21 patients with pterygium and 19 eyes of 15 patients with corneal neovascularization were given an injection of 5 mg bevacizumab into the sub-Tenon’s capsule. The clinical effects and complications were evaluated by analyzing the changes in anterior segment photo, visual acuity, and intraocular pressure at week one, week two, week four, and every month thereafter.
Results
After injections of bevacizumab, partial remission of corneal neovascularized lesion was observed in five eyes (20%) of the pterygium group, and there were no significant changes in the visual acuity and no complications. In the corneal neovascularization group, corneal neovascularized lesions of 18 eyes (95%: 2 eyes, complete remission 16 eyes, partial remission) improved after injections of the bevacizumab and the scores of extent and severity of corneal neovascularized lesion improved significantly, unlike the pterygium group. The visual acuity of two eyes (11%) improved more than two lines of Yong-Han Jin’s distance visual acuity test and there were no systemic side effects. Localized side effects included four eyes (21%) with punctate epithelial erosions and two eyes (11%) with temporary, elevated intraocular pressure in the corneal neovascularization group. The side effects improved without any additional treatment.
Go to : 
References
1. Folkman J, Ingber D. Inhibition of angiogenesis. Semin Cancer Biol. 1992; 3:89–96.
2. Battegay EJ. Angiogenesis: mechanistic insights, neovascular diseases, and therapeutic prospects. J Mol Med. 1995; 73:333–46.

3. Senger DR, Galli SJ, Dvorak AM, et al. Tumor cells secrete a vascular permeability factor that promotes accumulation of ascites fluid. Science. 1983; 219:983–5.

4. De Vries C, Escobedo JA, Ueno H, et al. The fms-like tyrosine kinase, a receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor. Science. 1992; 255:989–91.
5. Chen J, Liu W, Liu Z, et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors (flt-1) in morbid human corneas and investigation of its clinic importance. Yan Ke Xue Bao. 2002; 18:203–7.
6. Philipp W, Speicher L, Humpel C. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in inflamed and vascularized human corneas. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000; 41:2514–22.
7. Cursiefen C, Rummelt C, Küchle M. Immunohistochemical loca– lization of vascular endothelial growth factor, transforming growth factor alpha, and transforming growth factor beta1 in human corneas with neovascularization. Cornea. 2000; 19:526–33.
8. Lazic R, Gabric N. Intravitreally administered bevacizumab (avastin) in minimally classic and occult choroidal neovascularization secondary to age-related macular degeneration. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2007; 245:68–73.

9. Jorge R, Costa RA, Calucci D, et al. Intravitreal bevacizumab (avastin) for persistent new vessels in diabetic retonopathy (IBEPE study). Retina. 2006; 26:1006–13.
10. Iliev ME, Domig D, Wolf-Schnurrbursch U, et al. Intravitreal bevacizumab (avastin) in the treatment of neovascular glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006; 142:1054–6.

11. Bahar I, Kaiserman I, McAllum P, et al. Subconjunctival bevacizu– mab injection for corneal neovascularization in recurrent pterygium. Curr Eye Res. 2008; 33:23–8.
12. Uy HS, Chan PS, Ang RE. Topical bevacizumab and ocular surface neovascularization in patients with stevens-johnson syndrome. Cornea. 2008; 27:70–3.

13. Awadein A. Subconjunctival bevacizumab for vascularized rejected corneal grafts. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:1991–3.

14. Carrasco MA. Subconjunctival bevacizumab for corneal neovascu– larization in herpetic stromal keratitis. Cornea. 2008; 27:743–5.
15. Bahar I, Kaiserman I, McAllum P, et al. Subconjunctival bevacizu– mab injection for corneal neovascularization. Cornea. 2008; 27:142–7.
16. Lee JW, Park YJ, Kim IT, Lee KW. Clinical results after application of bevacizumab in recurrent pterygium. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:1901–9.

18. Zhang SX, Ma JX. Ocular neovascularization: implication of endogenous angiogenic inhibitors and potential therapy. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2007; 26:1–37.

19. Epstein RJ, Stulting RD, Hendricks RL, Harris DM. Corneal neo-vascularization. Pathogenesis and inhibition. Cornea. 1987; 6:250–7.
20. Shimazaki J, Aiba M, Goto E, et al. Transplantation of human limbal stem epithelium cultivated on amniotic membrane for the treatment of severe ocular surface disorders. Ophthalmology. 2002; 109:1285–90.
21. Solomon A, Espana EM, Tseng SC. Amniotic membrane trans– plantation for reconstruction of the conjunctival fornices. Ophthal– mology. 2003; 110:93–100.
22. Nishida K, Yamato M, Hayashida Y, et al. Corneal reconstruction with tissue-engineered cell sheets composed of autologous oral mucosal epithelium. N Engl J Med. 2004; 351:1170–2.

23. Nakamura T, Inatomi T, Sotozono C, et al. Transplantation of cultivated autologous oral mucosal epithelial cells in patients with severe ocular surface disorders. Br J Ophthalmol. 2004; 88:1280–4.

24. Tseng SC, Di Pascuale MA, Liu DT, et al. Intraoperative mitomycin C and amniotic membrane transplantation for fornix reconstruction in several cicatricial ocular surface diseases. Ophthalmology. 2005; 112:896–903.
25. Hollick EJ, Watson SL, Dart JK, et al. Legeais BioKpro III keratoprosthesis implantation: long–term results in seven patients. Br J Ophthalmol. 2006; 90:1146–51.
26. Inatomi T, Nakamura T, Kojyo M, et al. Ocular surface recon– struction with combination of cultivated autologous oral mucosal epithelial transplantation and penetrating keratoplasty. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006; 142:757–64.
27. Santos MS, Gomes JA, Hofling-Lima AL, et al. Survival analysis of conjunctival limbal graftsand amniotic membrane transplantation in eyes with total limbal stem cell deficiency. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005; 140:223–30.
28. Geerling G, Liu CS, Collin JR, Dart JK. Costs and gains of complex procedures to rehabilitate end stage ocular surface disease. Br J Ophthalmol. 2002; 86:1220–1.

29. Crum R, Szabo S, Folkman J. A new class of steroids inhibits angiogenesis in the presence of heparin or a heparin fragment. Science. 1985; 230:1375–8.

30. Wilhelmus KR, Gee L, Hauck WW, et al. Herpetic Eye Disease Study. A controlled trial of topical corticosteroids for herpes simplex stromal keratitis. Ophthalmology. 1994; 101:1883–95.
31. Cursiefen C, Chen L, Borges LP, et al. VEGF-A stimulates lymphangiogenesis and hemangiogenesis in inflammatory neovascularization via macrophage recruitment. J Clin Invest. 2004; 113:1040–50.

32. Mimura T, Amano S, Usui T, et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor C and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 in corneal lymphangiogenesis. Exp Eye Res. 2001; 72:71–8.

33. Singh D, Singh K. Transciliary filtration using the fugo blade TM. Ann Ophthalmol. 2002; 34:183–7.
Go to : 
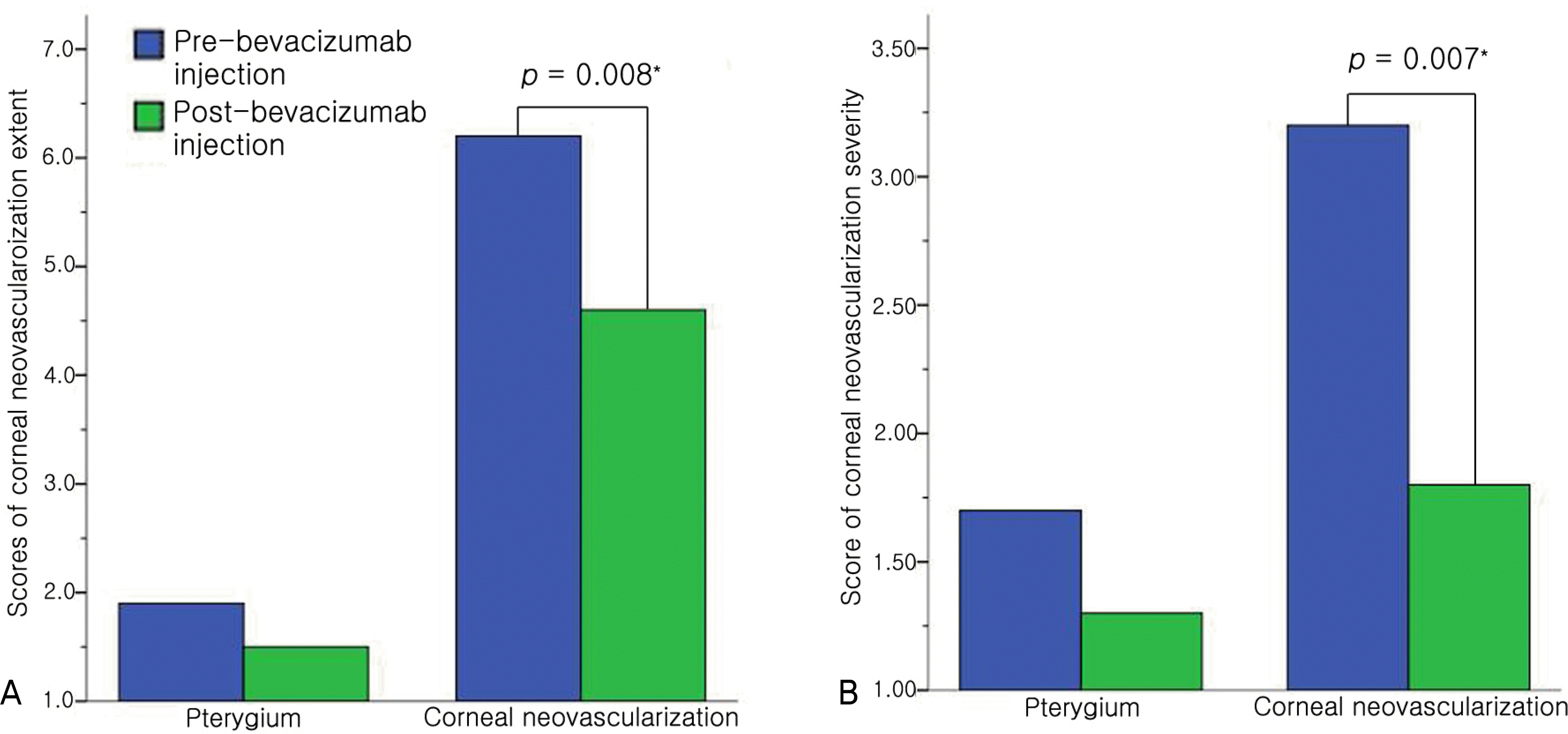 | Figure 1.Comparison of the changes in the average scores of corneal neovascularizaion before and after sub-Tenon’s capsule injections of bevacizumab. (A) There was a significant decrease of the score of corneal neovascularization extent in the corneal neovascularization group. (B) There was a significant decrease of the score of corneal neovascularization severity in the corneal neovascularization group.*
p<0.05, Wilcoxon signed ranks test. |
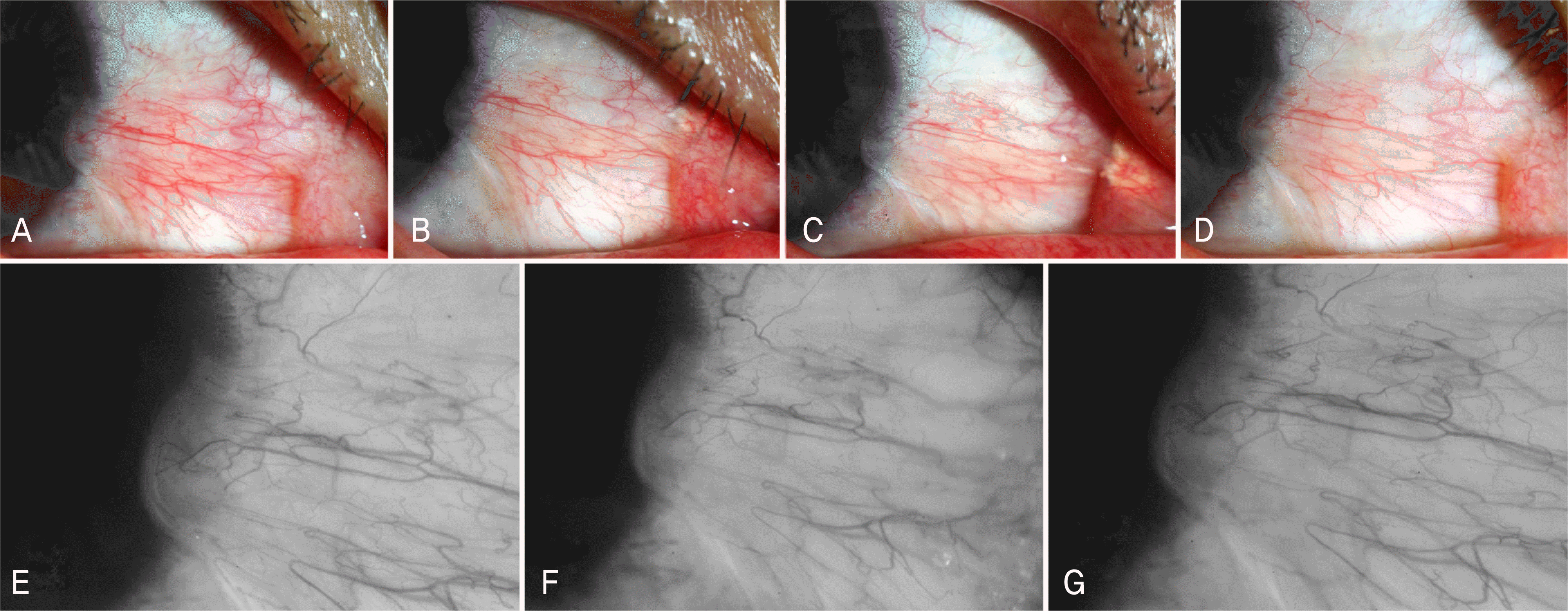 | Figure 2.Thirty-eight-year-old man with a history of pterygium over 10 years. Color photographs of his right eye before bevacizumab injection (A), 2 weeks after the first injection (B), 1 month after the second injection (C), 2 months after the third injection (D). Conjunctival injection was subsided slightly but magnified photographs of pterygium head showed unchanged lesion of corneal neovascularizaion (extent 1, severity 1.5) at before bevacizumab injection (E), 1 month after the second injection (F), 2 months after the third injection (G). p<0.05, Wilcoxon signed ranks test. |
 | Figure 3.Fifty-one-year-old woman with a month history of herpes zoster keratoconjunctivitis. Before bevacizumab injection, (A) Left eye showed some of small, round stromal opacities(arrow heads) (extent 1). (B) Slight limbal elevation with injection of conjunctiva (arrow) was noted. (C) Magnified photograph of superior cornea showed severity 1. Two weeks after the first injection, (D) stromal opacities, (E) limbal elevated lesion, and conjunctival injection disappeared. (F) Corneal neovascularized lesion disappeared completely (extent 0 and severity 0) until 6 months. p<0.05, Wilcoxon signed ranks test. |
 | Figure 4.Sixty-three-year-old man with one-month history of herpes stromal keratitis. Before bevacizumab injection (A) Left eye showed corneal neovascularization at the inferior portion (extent 2). (B, C) Magnified photograph of inferior cornea showed severity 2. (D, E, F) Two weeks after the first injection, inferior corneal neovascularized lesion disappeared completely (extent 0 and severity 0) until 6 months. p<0.05, Wilcoxon signed ranks test. |
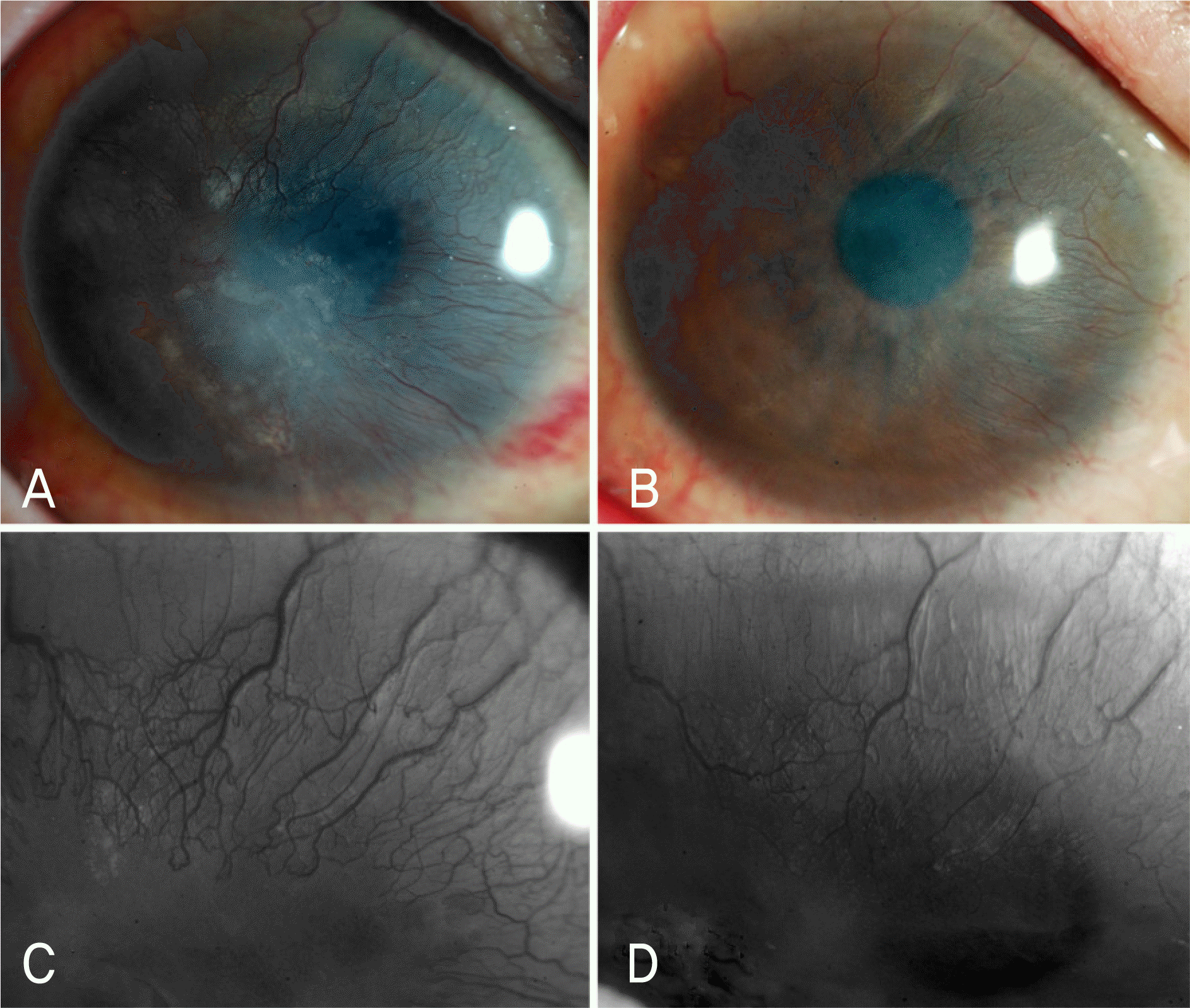 | Figure 5.Twenty-five-year-old woman with one-year history of ocular surface disease caused by Stevens-Johnson syndrome. (A) Right eye showed epithelial and stromal opacification at the central cornea with total peripheral corneal neovascularization (extent 12) before bevacizumab injection. (B) One month after the fifth injection, it showed marked reduction of corneal opacification, with significant disappearance of blood vessels (extent 6.5). (C) Magnified photograph of superior cornea before bevacizumab injection showed severity 4 and (D) 1 month after the fifth injection showed severity 3. Her best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) was 20/500 before bevacizumab injection, and eventually it improved to 20/100. p<0.05, Wilcoxon signed ranks test. |
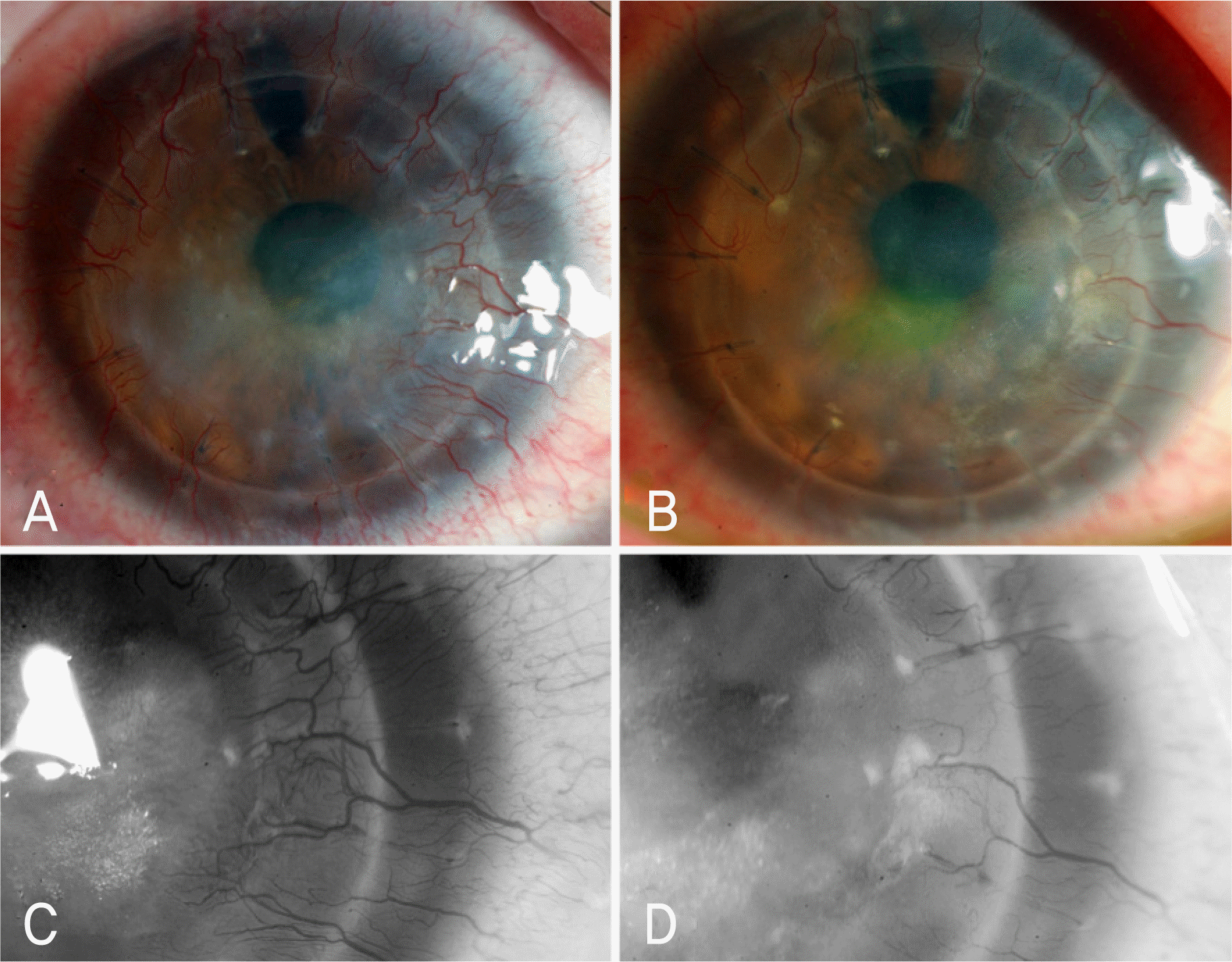 | Figure 6.Forty-five-year-old woman with 3-month history of ocular surface disease caused by rejected corneal graft. (A) Photograph of right eye showed central stromal opacity with nearly total peripheral corneal neovascularization (extent 11) before bevacizumab injection.(B) One month after the fifth injection, it showed marked reduction of central corneal opacity with significant disappearance of blood vessels (extent 6). (C) Magnified photograph of nasal cornea before bevacizumab injection showed severity 3.5 and (D) 1 month after the fifth injection showed severity 3. Her best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) was 20/100 before bevacizumab injection, and eventually it improved to 20/50. p<0.05, Wilcoxon signed ranks test. |
Table 1.
Distribution of corneal neovascularization group
Table 2.
Baseline characteristics and outcomes of bevacizumab injections to subtenoncapsule for pterygium and corneal neovascularization (Mean± Standard Deviation)
| Pterygium | Corneal neovascularization | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of patients (eyes) | 21 (25) | 15 (19) |
| Male : Female (eyes) | 9 (10) : 12 (15) | 10 (12) : 5 (7) |
| Age (years) | 53±12.1 | 46.6±17.5 |
| Mean number of injections (Mean days of interval) | 1.6 (15.7) | 3.8 (14.2) |
| Mean duration of follow-up (months) | 3.6±1.3 | 4.2±1.5 |
| Regression of lesions (eyes) | CR*: 0 (0%) | CR*: 2 (11%) |
| PR†: 5 (20%) | PR†: 16 (84%) | |
| Change of visual acuity (eyes) | none | 2 (11%)‡ |
| Side effects (eyes) | none | 6 (32%)§ |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download