Abstract
Purpose
To investigate ocular complications that occur after orbital preservation surgery for paranasal malignancies and to identify the early clinical features of ophthalmic manifestations in paranasal malignancy patients.
Methods
We reviewed the clinical charts of patients following ophthalmic consultation after orbital preservation surgery for paranasal malignancies. We also investigated the early clinical features of ophthalmic manifestations in patients with paranasal malignancies.
Results
In our study, 54 patients had paranasal malignancies. Among them, 41 had undergone orbital preservation surgery, and 19 patients sought an ophthalmology consultation. There were seven patients who presented with eye symptoms caused by paranasal malignancies before the diagnosis. Paranasal malignancies included squamouscell carcinoma (13 cases), adenocarcinoma (3 cases), plasmocytoma (1 case), malignant schwannoma (1 case), and undifferentiated carcinoma (1 case). The locations of the origin of the tumor included the maxillary sinus (16 cases) and the ethmoid sinus (3 cases). The most common eye symptoms after orbital preservation surgery were enophthalmos, lid retraction, tearing, strabismus, inflammation, dry eyes, and cataracts, in order of frequency. Patients who visited the ophthalmic clinic due to paranasal malignancies had eye symptoms such as proptosis, nonspecific ocular pain, strabismus, tearing, eyelid swelling, and relative afferent pupillary defects, in order of frequency.
Conclusions
Ocular complications were more common if the paranasal malignancy had invaded the orbital bone. However, many of the patients with disease invasion of the periosteum had no nasal or ocular symptoms upon presentation. Therefore, these patients should be managed carefully since symptoms may initially be vague and nonspecific.
References
1. Myers LL, Nussenbaum B, Bradford CR, et al. Paranasal Sinus Malignancies: An 18-Year Single Institution Experience. Laryngo-scope. 2002; 112:1964–9.

2. Suarez C, Ferlito A, Lund VJ, et al. Management of the orbit in malignant sinonasal tumors: Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Head Neck. 2008; 30:242–50.
3. Imola MJ, Schramm VL. Orbital Preservation in Surgical Management of Sinonasal Malignancy. Laryngoscope. 2002; 112:1357–65.

4. Smith B, Lisman RD, Baker D. Eyelid and orbital treatment following radical maxillectomy. Ophthalmology. 1984; 91:218–28.

5. Gluckman JL. Tumors of nose and paranasal sinuses. Donald PJ, Gluckman JL, Rice DH, editors. The Sinuses. 1st ed. New York: Raven Press;1995. 1:chap. 25.
6. Triana RJ, Uglesic V, Virag M, et al. Microvascular Free Flap Reconstructive Options in Patient with Partial and Total Maxillectomy Defects . Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2000; 2:91–101.
7. Goldberg RA, Joshi AR, McCann JD, Shorr N. Management of severe cicatricial entropion using shared mucosal grafts. Arch Ophthalmol. 1999; 117:1255–60.

8. Takeda A, Shigematsu N, Suzuki S, et al. Late Retinal comp-lacations of radiation therapy for nasal and paranasal malignancies Relationship between irradiated-dose area and severity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999; 44:599–605.
9. Carrau RL, Segas J, Nuss DW, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma of the sinonasal tract invading the orbit. Laryngoscope. 1999; 109:230–5.

10. Daniel MA. Metastatic and Secondary Orbital Tumors. John JW, Peter AR, George BB, editors. Principles and Practice of Ophthalmology. 3rd ed.Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier;2008. 3:chap. 239.
11. Kim JS, Jang SO, Lim HH, et al. Paranasal sinus tumor. No HJ, editor. Head and Neck surgery II. Seoul: Iljogac;2002. 2:chap. 22.
Figure 1.
A patient had adenocarcinoma in the maxillary sinus. Photograph shows severe enophthalmos after total maxillectomy. Also it shows the inferior orbital rim and suture materials through the thin skin.
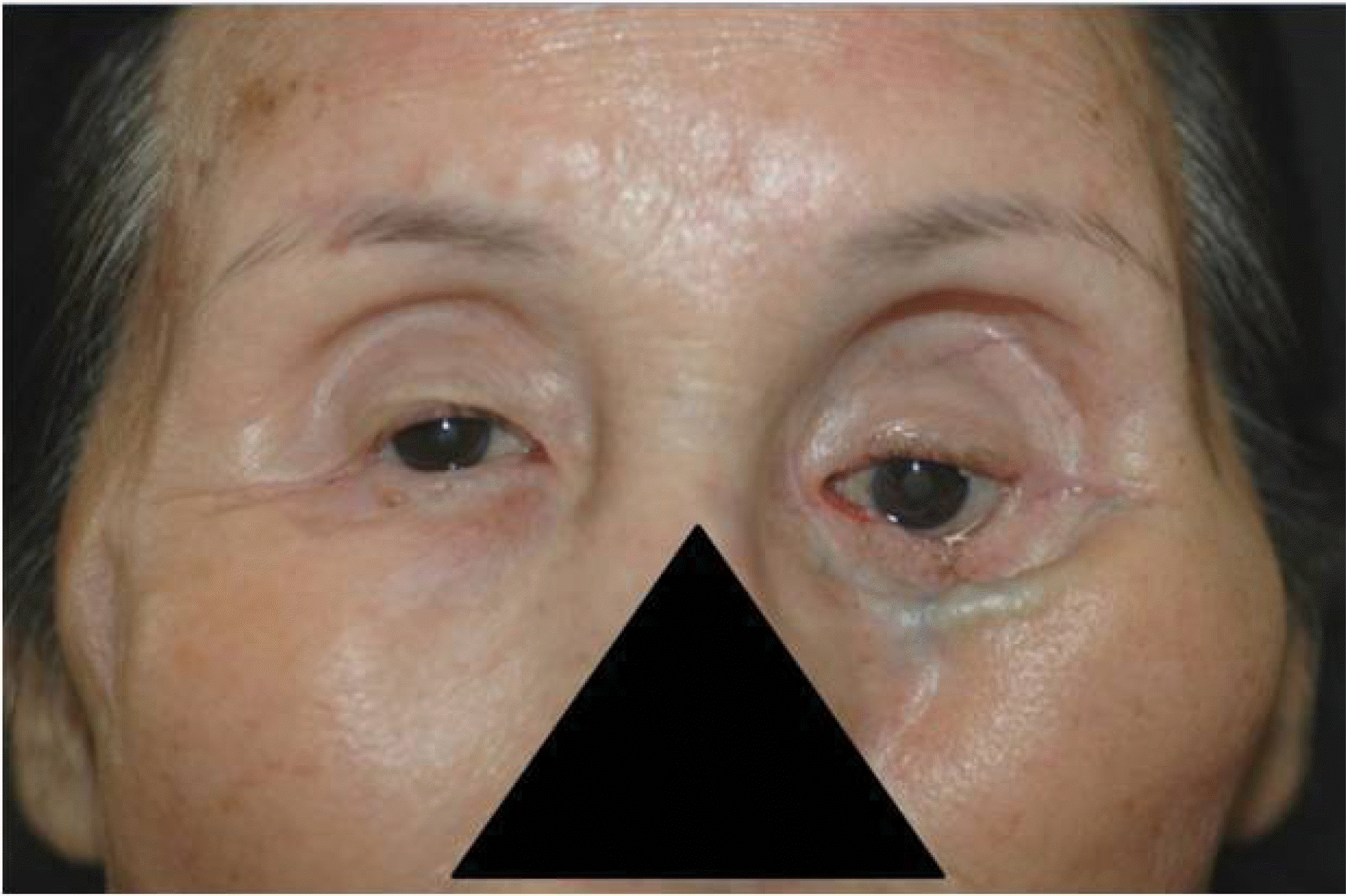
Figure 2.
(A) The preoperative computed tomograph shows the mass lesion that was maxillary sinus squamous cell carcinoma. It invaded the hard plate and inferior orbital wall. (B) It shows the lower lid retraction that occurred one week after total maxillectomy. (C) After 3 months, the left lower lid retraction gets worst by scarring of recon-structed orbital floor.
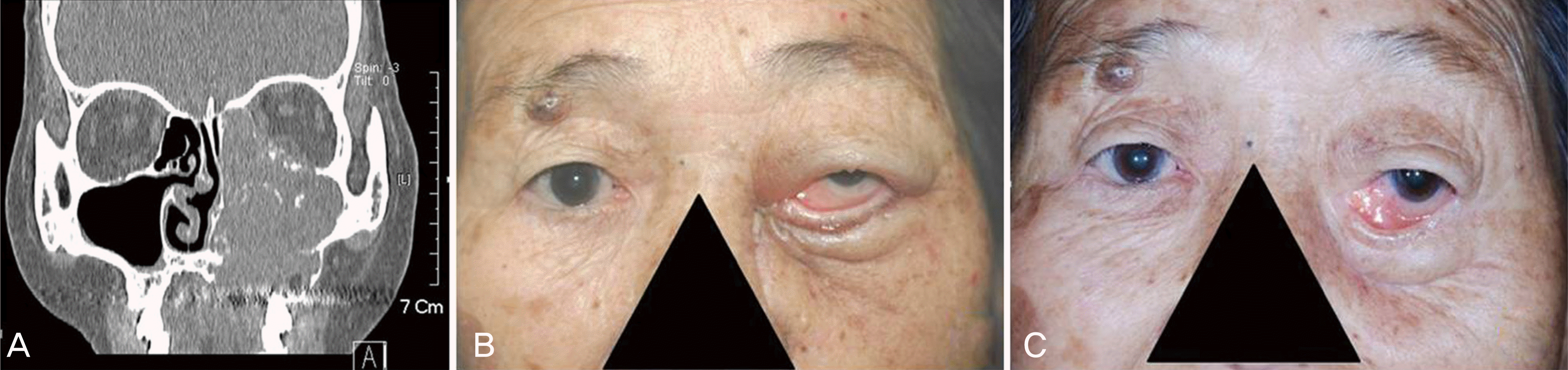
Figure 3.
(A) She first visited the ophthalmic clinic with mild Rt. exophthalmos. The diagnosis was delayed for 4 month due to nonspecific ocular pain. (B) Computer tomography finding at the diagnosis. The malignant tumorous lesion turned out to be ethmoidal sinus squamous cell carcinoma.
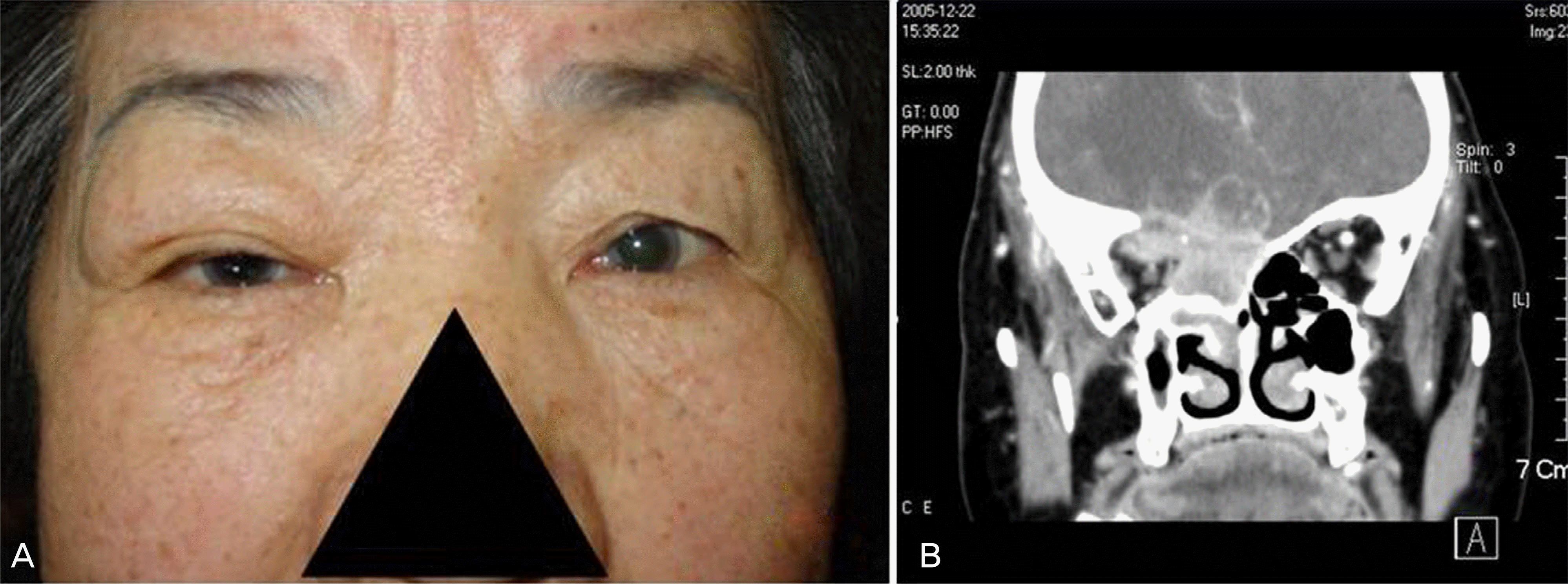
Table 1.
Distribution of paranasal cancer in patients treated with ocular preservation
| Histologic subtype | MS* | ES† | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 12 | 1 | 13 |
| Adenocarcinoma | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Plasmocytoma | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Malignant schwanomma | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Undifferenciated carcinoma | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Total | 16 | 3 | 19 |
Table 2.
Overall incidence of functional ocular sequelae in paranasal cancer treated with ocular preservation (total 19 patients)
| Ocular sequelae | Incidence (No. of affected eyes) | Onset‡ (month) |
|---|---|---|
| Enophthalmos | 12 | 4∼6 |
| Lid malposition* | 6 | 4∼6 |
| Epiphora | 4 | 4∼10 |
| Inflammation† | 3 | 2∼3 |
| Drynesss | 3 | 2∼3 |
| Strabismus | 2 | 1 |
| Cataract | 1 | 6 |
| Optic atrophy | 1 | 4 |
Table 3.
Enophthalmos after orbit-preserving surgical management for paranasal sinus cancer
| Degree of enophthalmic status* | Enophthalmic eyes (Total 19 eyes) |
|---|---|
| 0∼2 | 7 |
| 2∼4 | 10 |
| More than 4 | 2 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download