Abstract
Purpose
To compare the surgical outcomes of recession-resection (R&R) on the contralateral eye and medial rectus re-resection surgery for recurrent intermittent exotropia in patients who previously underwent unilateral recess-resection.
Methods
A retrospective analysis was performed on patients who underwent either R&R on the contralateral eye or medial rectus re-resection surgery for recurrent intermittent exotropia who had unilateral R&R previously with a minimum follow-up period of at least 12 months.
Results
Thirty-nine patients underwent contralateral R&R surgery and 13 patients underwent medial rectus re-resection surgery. The satisfactory surgical result was considered between −5 (prism diopters, PD) and +10PD. The success rate of the contralateral R&R group and medial rectus re-resection group was 84.6% and 100% (p=0.317) at postoperative 1 week, 79.5% and 46.2% (p=0.034) at postoperative 6 months, 69.2% and 38.5% (p=0.048) at postoperative 12 months, and 51.3% and 7.7% (p=0.006) at the last follow-up visit.
Go to : 
References
1. Chia A, Seenyen L, Long QB. Surgical experiences with two-muscle surgery for the treatment of intermittent exotropia. J AAPOS. 2006; 10:206–11.

2. Jeoung JW, Lee MJ, Hwang JM. Bilateral lateral rectus recession versus unilateral recess-resect procedure for exotropia with a dominant eye. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006; 141:683–8.

3. Fiorelli VM, Goldchmit M, Uesugui CF, Souza-Dias C. Intermittent exotropia: comparative surgical results of lateral rectirecession and monocular recess-resect. Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2007; 70:429–32.

4. Mauro T, Kubota N, Sakaue T, Usui C. Intermittent exotropia surgery in children: long term outcome regarding changes in binocular alignment. A Study of 666 Cases. Binocul Vis Strabismus Q. 2001; 16:265–70.
5. Oh J-Y, Hwang JM. Survival analysis of 365 patients with exotropia after surgery. Eye. 2006; 20:1268–72.

6. Yazdian Z, Ghiassi G. Re-recession of the lateral rectus muscles in patients with recurrent exotropia. J AAPOS. 2006; 10:164–7.

7. Kim SJ, Choi DG. The clinical analysis after reoperation for recurrent intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:321–7.
8. Mun HJ, Kim MM. Comparison of surgical results between bilateral recession and unilateral recession-resection in 25PD intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002; 43:2202–7.
9. Figueira EC, Hing S. Intermittent exotropia: comparison of treatments. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2006; 34:245–51.

10. Hahm IR, Yoon SW, Baek SH, Kong SM. The clinical course of recurrent exotropia after reoperation for exodeviation. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2005; 19:140–4.

11. Mims JL 3rd. Outcome of 5 mm resection of one medial rectus extraocular muscle for recurrent exotropia. Binocul Vis Strabismus Q. 2003; 18:143–50.
12. Olitsky SE, Kelly C, Lee H, Nelson LB. Unilateral rectus resectionin the treatment of undercorrected or recurrent strabismus. J Pediatr Ophthalmol strabismus. 2001; 38:349–53.
13. Kim SC, Kim MM. The efficacy of unilateral rectus resection in the reoperation of strabismus. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:904–10.
14. Kim MM, Cho ST. Long – term surgical results of intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1994; 35:1321–6.
15. Koo NK, Lee YC, Lee SY. Clinical study for the undercorrection factor in intermittent exotropia. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2006; 20:182–7.

16. Roh JH, Paik HJ. Clinical study on factors associated with recurrence and reoperation in intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:1114–9.

17. Lee SY, Lee YC. Comparison of surgical results by initial postoperative alignment following bilateral lateral rectus recession and unilateral lateral rectus recession-medial rectus resection in intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:2604–10.
Go to : 
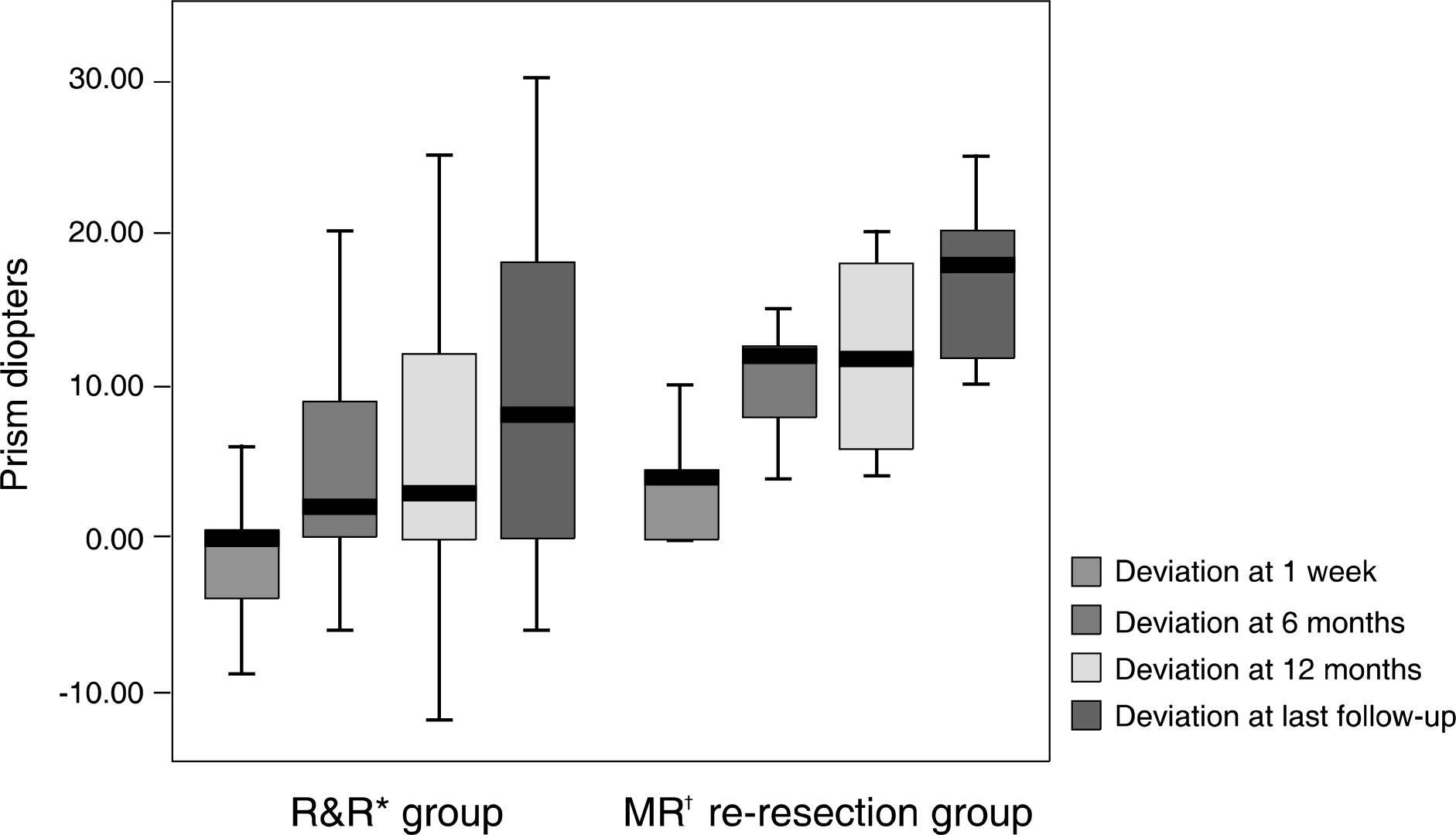 | Figure 1.Comparison of mean angle of deviation after operation according to type of surgery.* R&R=unilateral lateral rectus recession and medial rectus resection; † MR=medial rectus muscle. |
Table 1.
Characteristics of patients
| | R&R* group | MR† re-resection group | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patient | 39 | 13 | − |
| Sex (male:female) | 15:24 | 5:8 | 1.000‡ |
| Age (years, mean± SD) | 8.1±3.7 | 7.6±1.65 | 0.684§ |
| Preoperative deviation (PD∏, mean± SD) | 25.0±2.0 | 23.1±3.3 | 0.063§ |
Table 2.
Mean angle of deviation after operation according to type of surgery
| | R&R* group | MR† re-resection group | p-value‡ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preoperative deviation (PD§) | 25.0±2.0 | 23.1±3.3 | 0.063 |
| Deviation at 1 week | −0.2±6.6 | 3.0±3.3 | 0.107 |
| Deviation at 6 months | 4.5±6.2 | 10.0±3.4 | 0.000 |
| Deviation at 12 months | 5.9±7.9 | 12.1±5.9 | 0.011 |
| Deviation at last F/U∏ | 9.8±9.5 | 18.7±8.5 | 0.004 |
Table 3.
Success rates according to type of surgery
| |
Number of patients (success rate, %) |
p-value‡ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| R&R* group (n=39) | MR† re-resection group (n=13) | ||
| 1 week | 33/39 (84.6) | 13/13 (100) | 0.317 |
| 6 months | 31/39 (79.5) | 6/13 (46.2) | 0.034 |
| 12 months | 27/39 (69.2) | 5/13 (38.5) | 0.048 |
| Last F/U§ | 20/39 (51.3) | 1/13 (7.7) | 0.006 |
Table 4.
Statistical correlation factors in R&R group
| Factors | p-value* | Odds ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | 0.669 | 1.420 |
| Age at repeat operation | 0.290 | 0.886 |
| Preoperative deviation | 0.110 | 0.690 |
| Deviation at post-operation 1 week | 0.107 | 1.256 |
| Overcorrection at post-operation 1 week | 0.096 | 0.129 |
Table 5.
Average correction for medial rectus re-resection at postoperative 1 week
| Resection (mm) | Number of cases | Average corrected deviation /mm (PD*) |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | 7 | 4.7±0.9 |
| 5 | 5 | 4.1±0.9 |
| 6 | 1 | 4.3 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download