Abstract
Purpose
To compare the safety and efficacy of polypropylene and silicone Ahmed glaucoma valves (AGVs).
Methods
The medical records of 62 consecutive refractory glaucoma patients who had undergone AGV implantion from March 2003 to December 2005 were reviewed retrospectively. Among the 62 patients, 32 patients underwent polypropylene AGV implantation (group P) and the other 30 patients underwent silicone AGV implantation (group S). Postoperative IOP, the complication rate, and the success rate were compared between the two groups.
Results
The life-table success rates for the group P were 81.3% at 6 months and 71.2% at 12 months, and the success rates for the group S were 89.9% at 6 months and 78.6% at 12 months, showing no significant difference between the two groups. Complications, including non-tube-related complications, were observed more frequently in the group S, but there was no significant difference between the two groups.
Go to : 
References
1. El-Sayyad F, el-Maghraby A, Helal M, et al. The use of releasable sutures in Molteno glaucoma procedures to reduce postoperative hypotony. Ophthalmic Surg. 1991; 35:82–4.
2. Kook MS, Jeon SK. Clinical results of Ahmed glaucoma implantation in refractory glaucoma. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1996; 37:1893–901.
3. Kim JM, Lee DH. Clinical experience with the Ahmed Glaucoma Valve. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:1332–8.
4. Hu CH, Lee YG, Hong YJ. Ahmed glaucoma valve implant in refractory glaucoma. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1997; 38:259–66.
5. Coleman AL, Hill R, Wilson MR, et al. Initial clinical experience with the Ahmed glaucoma valve implant. Am J Ophthalmol. 1995; 120:23–31.

6. Taglia DP, Perkins TW, Gangnon R, et al. Comparison of the Ahmed glaucoma valve, the Krupin eye valve with disk, and the double plate Molteno implant. J Glaucoma. 2002; 11:347–53.
7. Ayyala RS, Zurakowski D, Monshizadeh R, et al. Comparison of double plate Molteno and Ahmed glaucoma valve in patients with advanced uncontrolled glaucoma. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 2002; 33:94–101.
8. Ayyala RS, Harman LE, Michelini-Norris B, et al. Comparison of different biomaterials for glaucoma drainage devices. Arch Ophthalmol. 1999; 117:233–6.

9. Ayyala RS, Michelini-Norris B, Flores A, et al. Comparison of different biomaterials for glaucoma drainage devices: part2. Arch Opthalmol. 2000; 118:1081–4.
10. Rollett M, Moreau M. Traitement dele hypopyon par le drainage capillaire de chamber anterieure. Rev Gen Ophthalmol. 1906; 35:481.
11. Molteno AC. New implant for drainage in glaucoma. Clinical trial. Br J Ophthalmol. 1969; 53:606–15.

12. Schocket SS, Lakhanpal V, Richards RD. Anterior chamber tube shunt to an encircling band in the treatment of neovascular glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 1982; 89:1188–94.

13. Lloyd MA, Baerveldt G, Heuer DK, et al. Initial clinical experience with the Baerveldt implant in complicated glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 1994; 101:640–50.
14. Ahn BH, Kim CS, Kim YB. Use of e-PTFE membrane for glaucoma drainage surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1990; 31:603–14.
15. Krupin T, Podos SM, Becker B. Valve implants in filtering surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 1976; 81:232–5.

16. Joseph NH, Sherwood MB, Trantas G, et al. A one-piece drainage system for glaucoma surgery. Trans Ophthalmol Soc U K. 1986; 105:657–64.
17. White TC. Clinical results of glaucoma surgery using the White glaucoma pump shunt. Ann Ophthalmol. 1992; 24:365–73.
18. Prata JA, Mermoud A, LaBree L, et al. In vitro and in vivo flow characteristics of glaucoma drainage implants. Ophthalmology. 1995; 102:894–904.

19. Lee YW, Yim JH, Lee SB, et al. Factors associated with the success of Ahmed glaucoma valve implantation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:1509–17.
20. Law SK, Nguyen A, Coleman AL, et al. Comparison of safety and efficacy between silicone and polypropylene Ahmed glaucoma valves in refractory glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 2005; 112:1514–20.

Go to : 
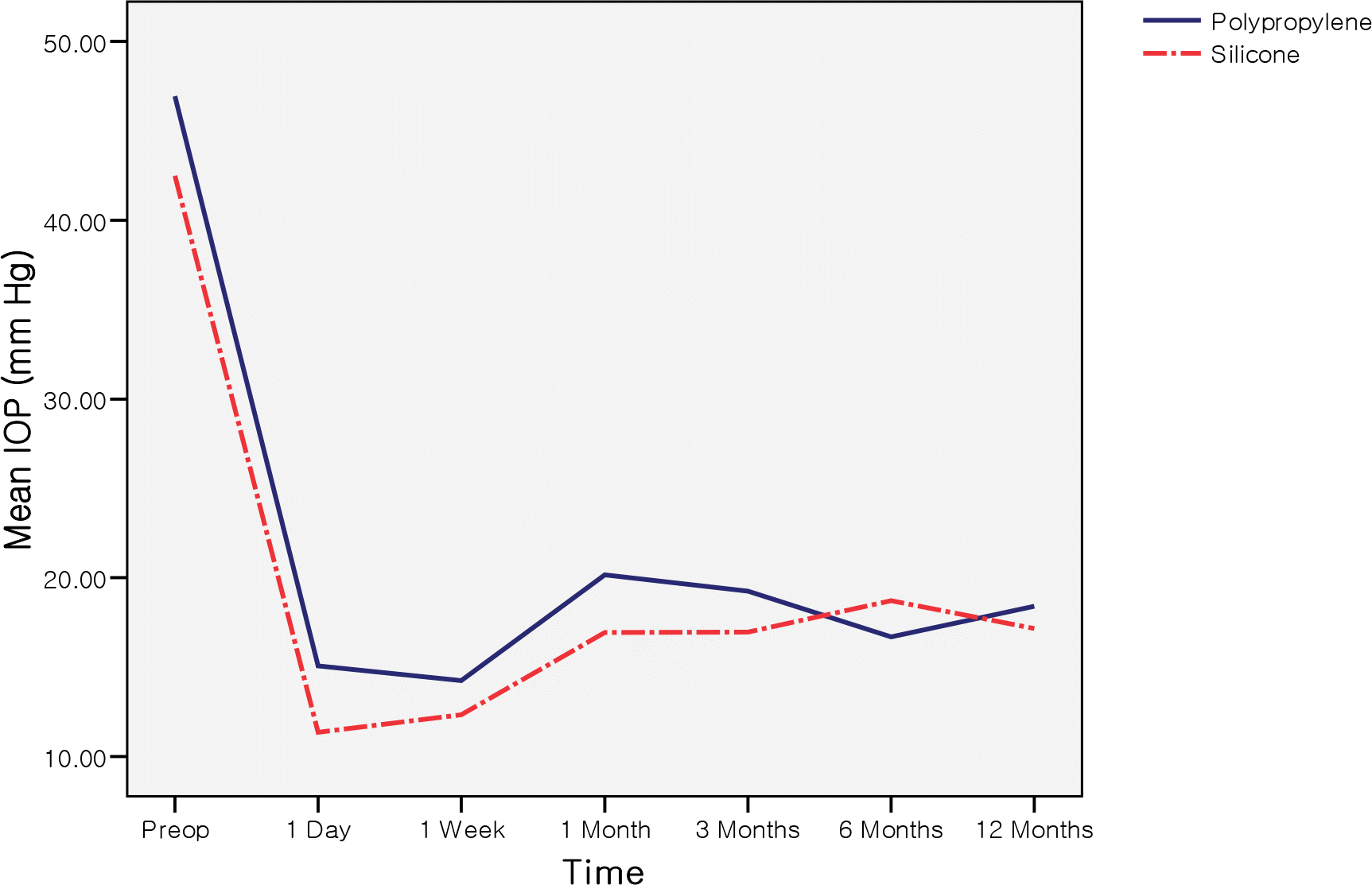 | Figure 1.Comparison of the mean intraocular pressure between polypropylene and silicone AGV during one-year followup. There were no statistically significant differences between groups (P>0.05). Preop = before surgery. |
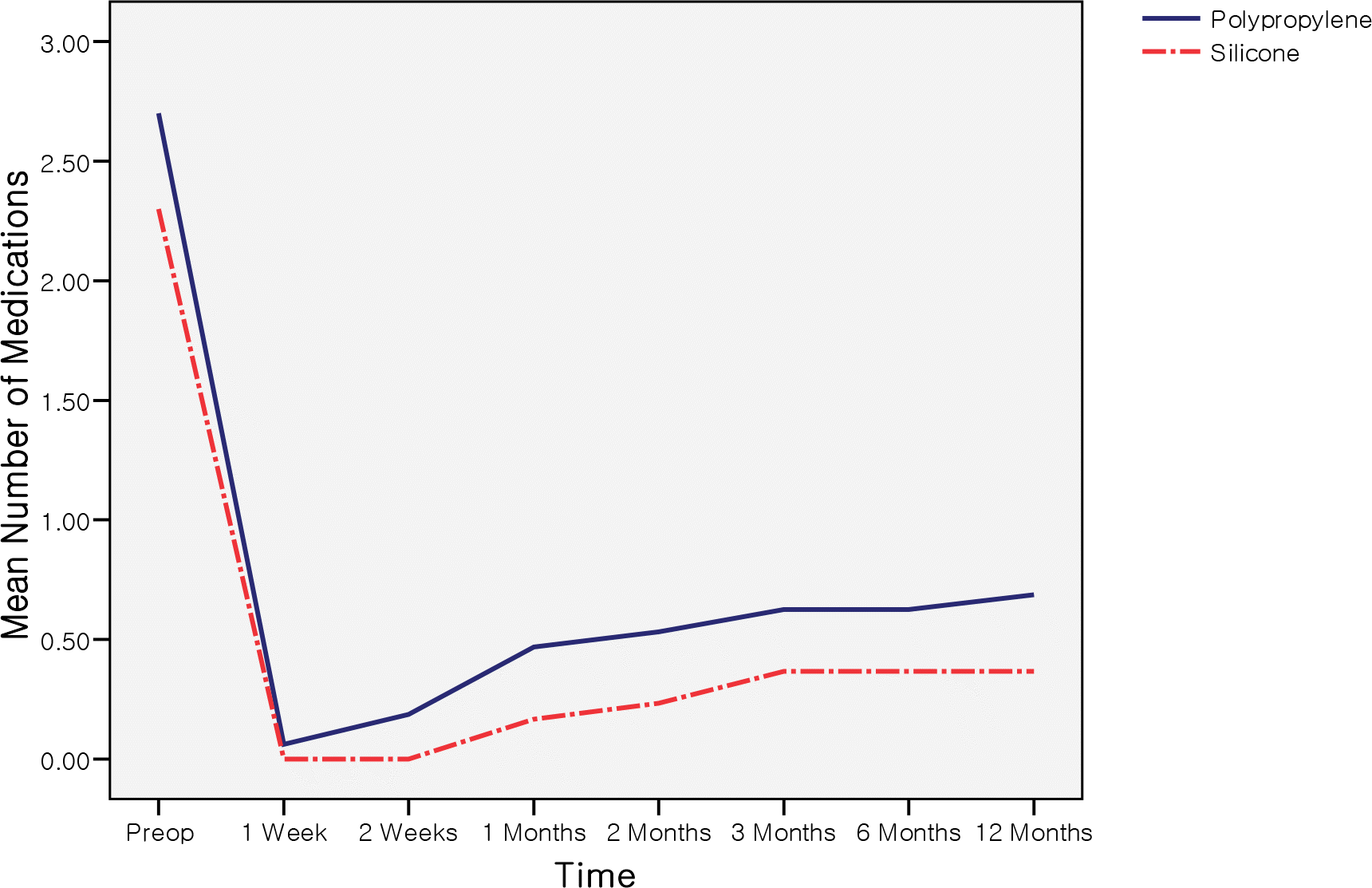 | Figure 2.Comparison of the mean number of glaucoma medications between polypropylene and silicone AGV during one-year followup. There were no statistically significant differences between groups (P>0.05). Preop = before surgery. |
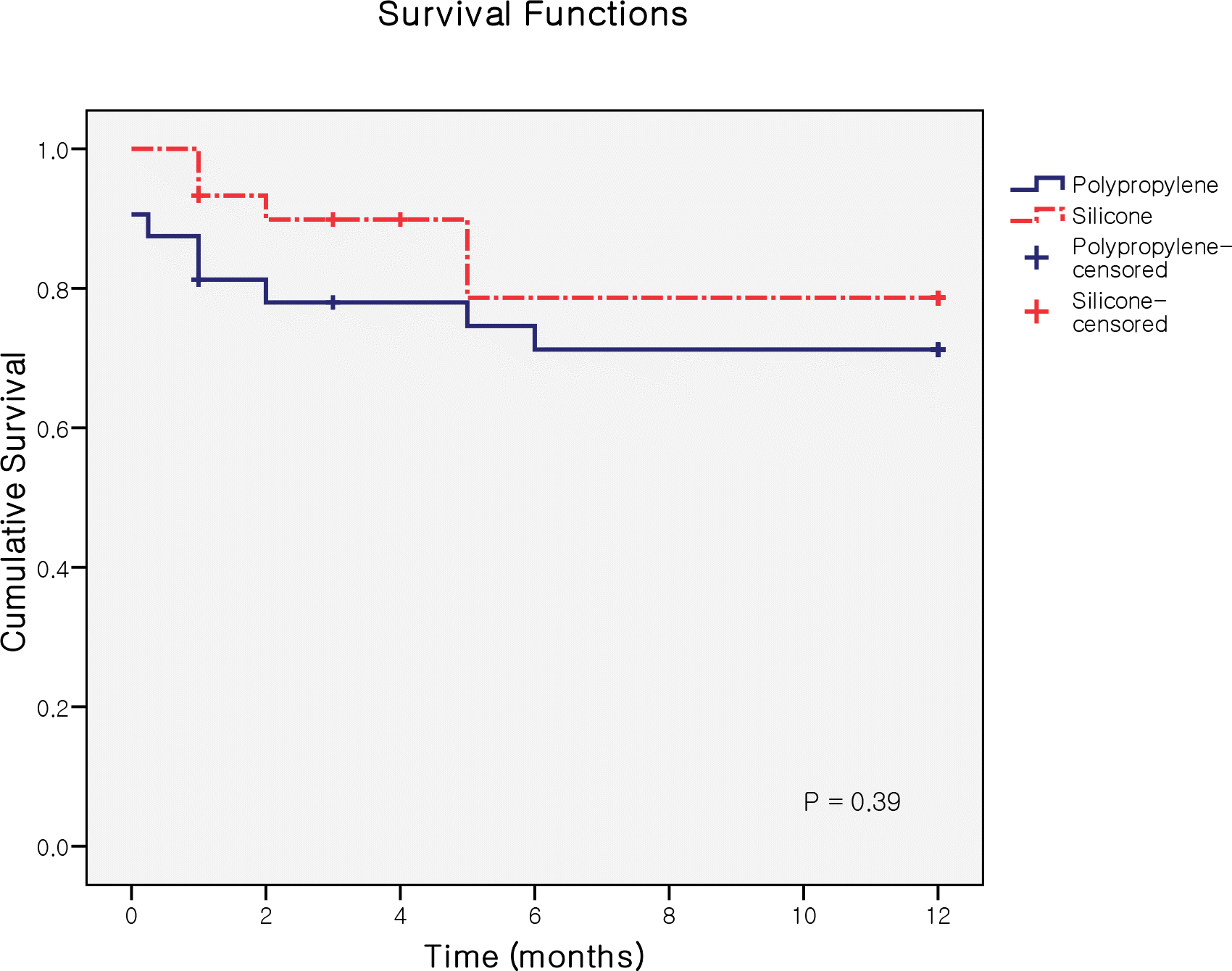 | Figure 3.Graph demonstrating the Kaplan-Meier survival curves according to surgical success definition after implantation of the polypropylene and the silicone AGVs. There were no statistically significant differences between groups. |
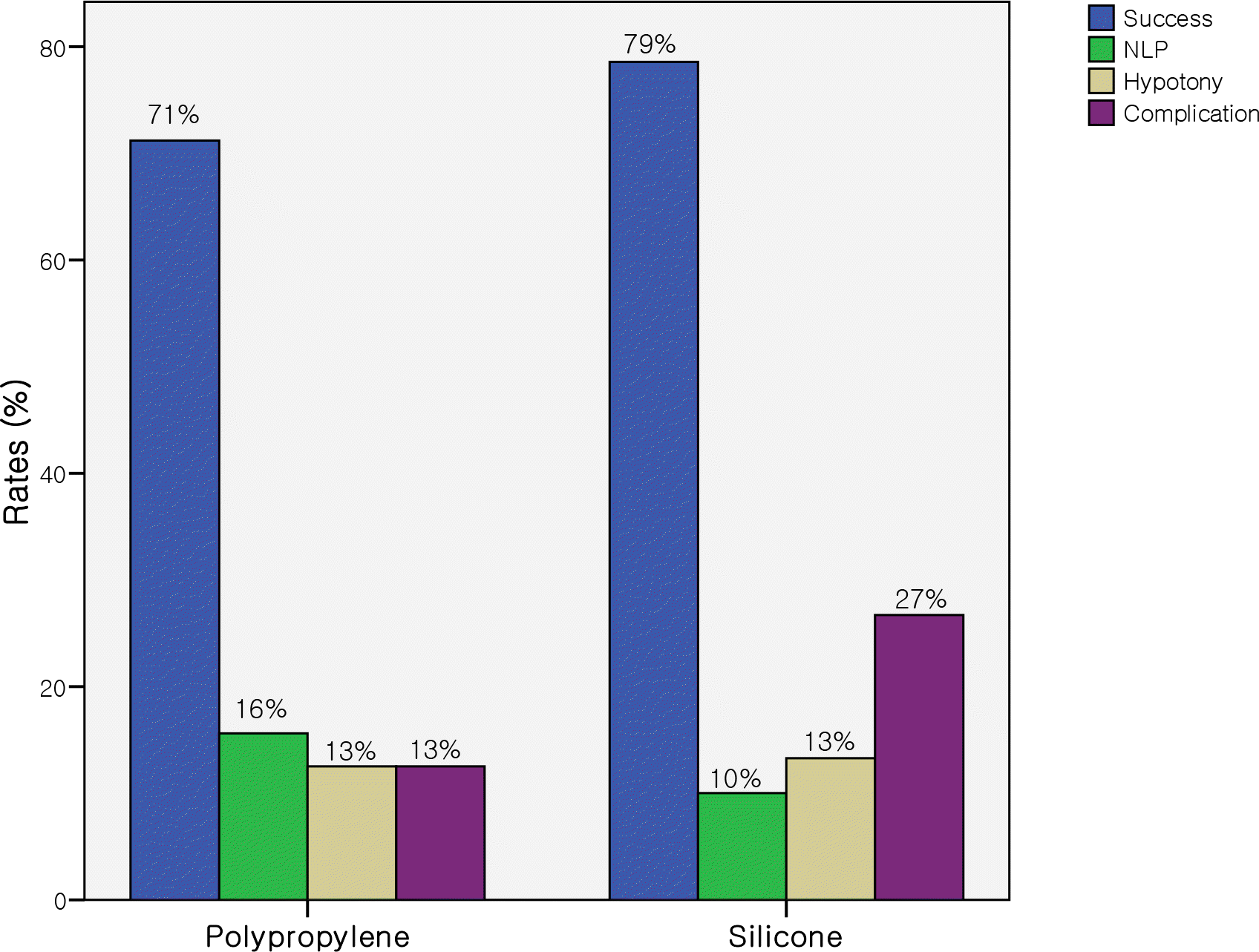 | Figure 4.Comparison of rates of success (12 months), NLP (loss of light perception), hypotony, and complication between polypropylene and silicone AGVs. |
Table 1.
Patient demographics
| Polypropylene group (N=32) | Silicone group (N=30) | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) (mean±SD) | 53.6±13.5 | 53.7±13.7 | 0.96∗ |
| Sex (M/F) | 17/15 | 17/13 | 0.21† |
| Followup (months) (mean±SD) | 9.3±4.3 | 10.9±3.1 | 0.11∗ |
| Glaucoma subtype | 0.69† | ||
| POAG | 2 (6.3%) | 1 (3.3%) | |
| SOAG | 7 (21.9%) | 9 (30.0%) | |
| NVG | 23 (71.9%) | 20 (66.7%) |
Table 2.
Preoperative data of polypropylene and silicone Ahmed glaucoma valve groups
| Polypropylene group | Silicone group | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of prior operations (mean±SD) | 1.2±1.1 | 1.5±1.3 | 0.28∗ |
| No. of preoperative medications (mean±SD) | 2.5±0.8 | 2.3±0.6 | 0.09∗ |
| Preoperative IOP (mean±SD) | 46.9±10.1 | 42.5±8.7 | 0.07† |
Table 3.
IOP comparison of polypropylene and silicone Ahmed glaucoma valve (AGV) implantation
| Interval | Polypropylene group (N=32) IOP (mean±SD) | Silicone group (N=30) IOP (mean±SD) | P-value∗ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preoperative IOP | 46.9±10.1 | 42.5±8.7 | 0.71 |
| 1 day | 15.1±11.5 | 11.4±5.1 | 0.11 |
| 1 week | 14.3±9.2 | 12.3±5.5 | 0.32 |
| 1 month | 20.2±9.9 | 16.9±8.1 | 0.18 |
| 3 months | 19.3±8.9 | 16.9±7.2 | 0.29 |
| 6 months | 16.7±7.9 | 18.7±13.7 | 0.51 |
| 12 months | 18.4±8.1 | 17.1±8.9 | 0.61 |
Table 4.
Postoperative complications after polypropylene and silicone AGV implantation
| Polypropylene group (N=32) N (%) | N (%) Silicone group (N=30) | P-value∗ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Complications | 4 (12.5%) | 8 (26.7%) | 0.115 |
| Tube-related | 3 (9.4%) | 3 (10.0%) | 0.329 |
| Blocked tube | 0 | 1 | |
| Tube migration | 1 | 0 | |
| Exposed tube | 2 | 2 | |
| Non-tube related | 1 (3.1%) | 5 (16.7%) | 0.085 |
| Flat anterior chamber (required reformation) | 1 | 2 | |
| Large choroidal effusion | 0 | 1 | |
| Hypotony maculopathy | 0 | 1 | |
| Total hyphema | 0 | 1 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download