Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the correlation between optic disc size and retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness in healthy subjects and patients with normal tension glaucoma (NTG).
Methods
Optical coherence tomography was performed on 50 eyes of 50 healthy subjects and on 50 eyes of 50 NTG patients.
Results
The optic disc size showed a significant correlation with the RNFL thickness in healthy subjects and in patients with NTG. Significant correlations were observed between the optic disc size and the ratio of superior-to-total RNFL thickness (r=-0.283, p=0.049) and the ratio of nasal to total RNFL thickness (r=0.403, p=0.004) in healthy subjects. In patients with NTG, significant correlations were observed between the optic disc size and the ratio of superior to total RNFL thickness (r=-0.314, p=0.029) and the ratio of inferior to total RNFL thickness (r=-0.302, p=0.034).
Go to : 
References
1. Levene RZ. Low tension glaucoma: a critical review and new material. Surv Ophthalmol. 1980; 24:621–64.

2. Quigley HA, Miller NR, George T. Clinical evaluation of nerve fiber layer atrophy as an indicator of glaucomatous optic nerve damage. Arch Ophthalmol. 1980; 98:1564–71.

3. Quigley HA, Dunkelberger GR, Green WR. Retinal ganglion cell atrophy correlated with automated perimetry in human eyes with glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1989; 107:453–64.

4. Sommer A, Katz J, Quigley HA, et al. Clinically detectable nerve fiber atrophy precedes the onset of glaucomatous field loss. Arch Ophthalmol. 1991; 109:77–83.

5. Schuman JS, Hee MR, Arya AV, et al. Optical coherence tomography: a new tool for glaucoma diagnosis. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 1995; 6:89–95.

6. Nouri-Mahdavi K, Hoffman D, Tannenbaum DP, et al. Identifying early glaucoma with optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004; 137:228–35.

7. Kanamori A, Nakamura M, Escano MF, et al. Evaluation of the glaucomatous damage on retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003; 135:513–20.

8. Savini G, Zanini M, Carelli V, et al. Correlation between retinal nerve fibre layer thickness and optic nerve head size: an optical coherence tomography study. Br J Ophthalmol. 2005; 89:489–92.

9. Ha DW, Sung K, Kim S, et al. Interocular comparison of nerve fiber layer thickness and its relation with optic disc size in normal subjects. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2002; 16:8–12.

10. Funaki S, Shirakashi M, Abe H. Relation between size of optic disc and thickness of retinal nerve fiber layer in normal subjects. Br J Ophthalmol. 1998; 82:1242–5.
11. Mikelberg FS, Yidegiligne HM, White VA, Schulzer M. Relation between optic nerve axon number and axon diameter to scleral canal area. Ophthalmology. 1991; 98:60–3.

12. Varma R, Skaf M, Barron E. Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in normal human eyes. Ophthalmology. 1996; 103:2114–9.

13. Tuulonen A, Airaksinen PJ. Optic disc size in exfoliative, primary open angle, and low tension glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 1992; 110:211–3.
14. Quigley HA, Brown AE, Morrison JD, Drance SM. The size and shape of the optic disc in normal human eyes. Arch Ophthalmol. 1990; 108:51–7.

15. Jonas JB, Fernandez MC, Naumann GO. Correlation of the optic disc size to glaucoma susceptibility. Ophthalmology. 1991; 98:675–80.

16. Repka MX, Quigley HA. The effect of age on normal human optic nerve fiber number and diameter. Ophthalmology. 1989; 96:26–32.
17. Schuman JS, Hee MR, Puliafito CA, et al. Quantification of nerve fiber layer thickness in normal and glaucomatous eyes using optical coherence tomography. Arch Ophthalmol. 1995; 113:586–96.

18. Yamagami J, Araie M, Shirato S. A comparative study of optic nerve head in low and high tension glaucomas. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1992; 230:446–50.
19. Caprioli J, Spaeth GL. Comparison of the optic nerve head in high and low tension glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 1985; 103:1145–9.
Go to : 
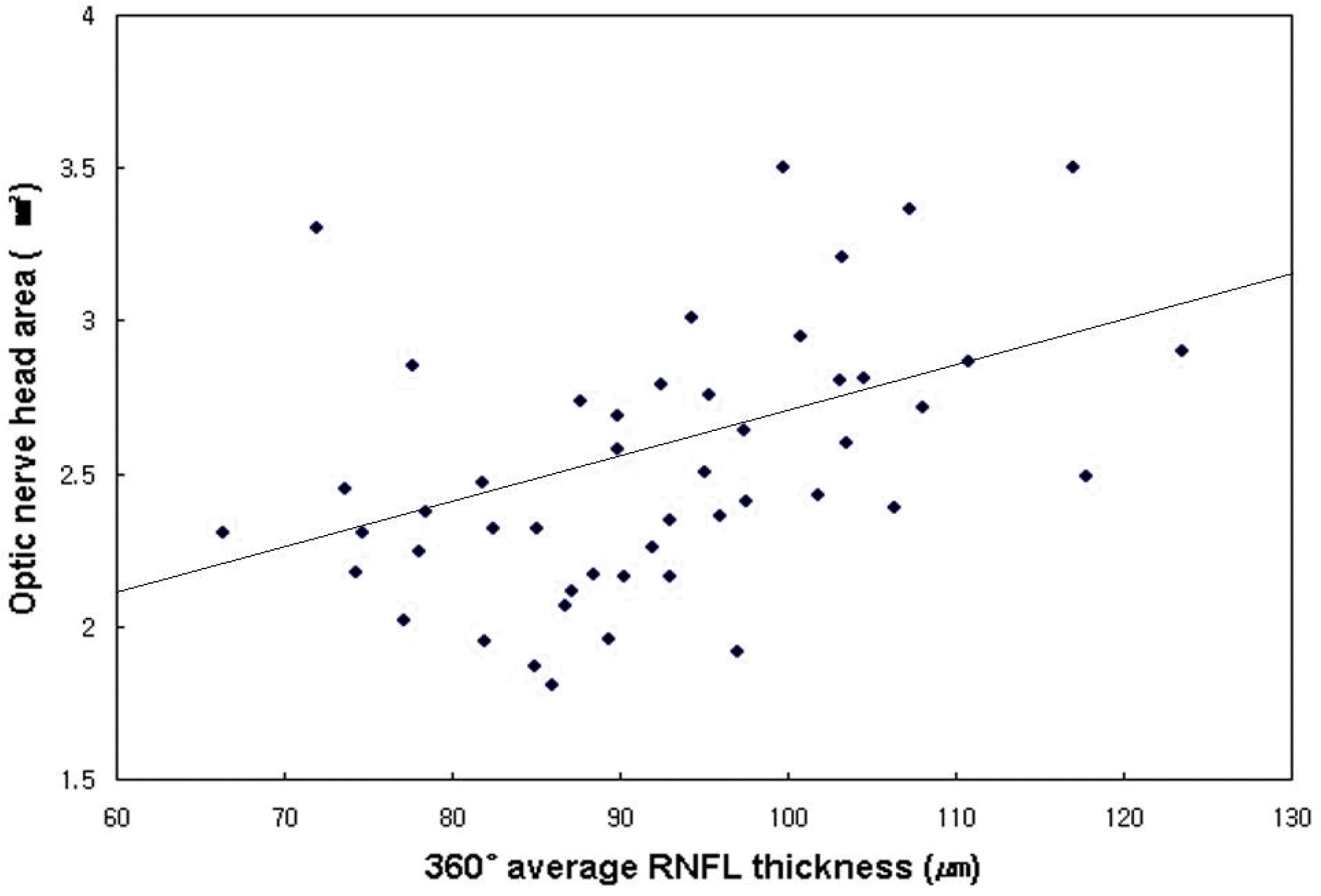 | Figure 1.Scatter plot of correlation between optic nerve head area and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in normal eyes (R=0.425, P=0.001). |
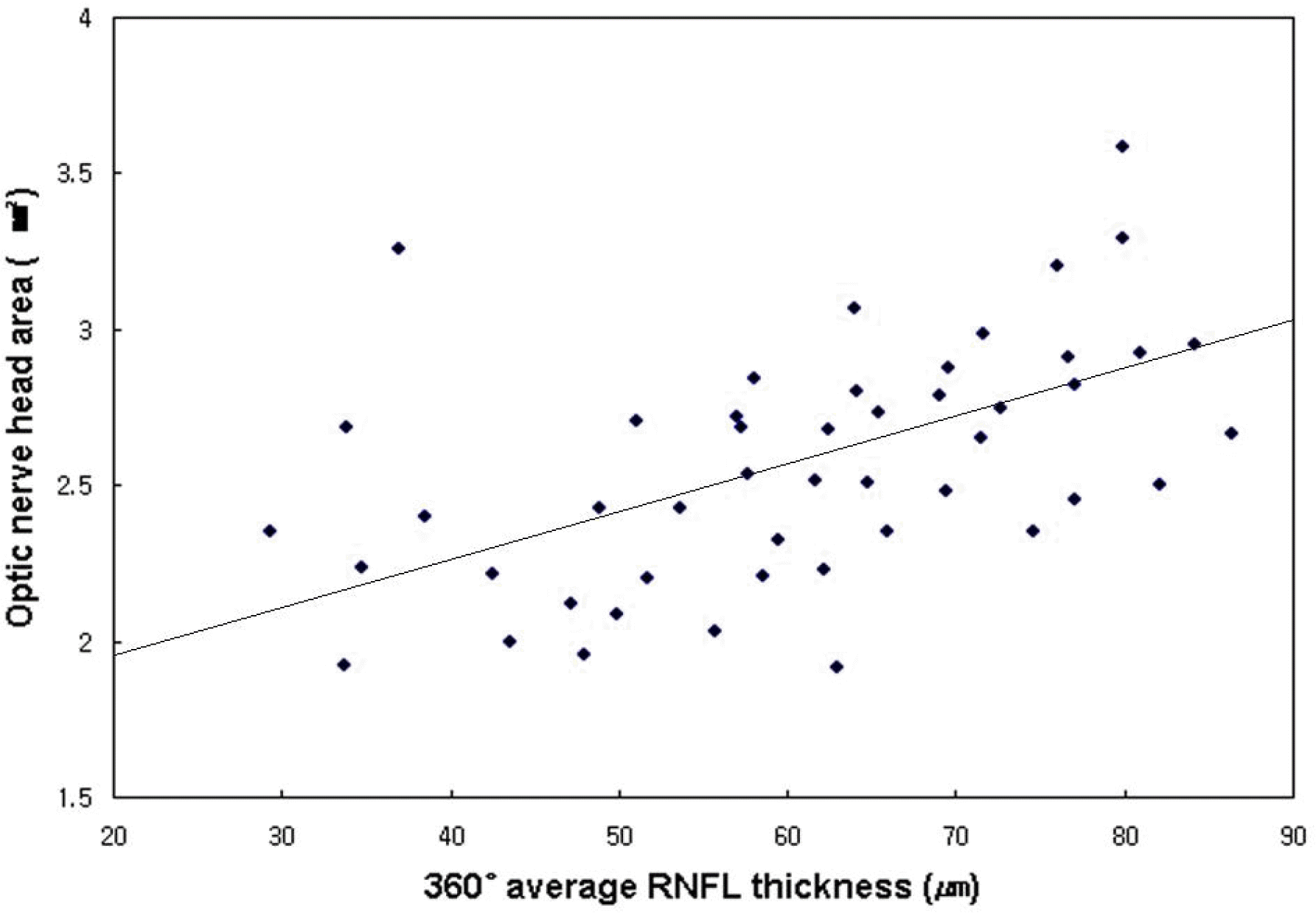 | Figure 2.Scatter plot of correlation between optic nerve head area and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in normal tension glaucoma eyes (R=0.451, P=0.001). |
Table 1.
Comparison of demographic and visual field global indicies between normal eyes and normal tension glaucoma eyes
| Normal (n=50) | Normal Tension Glaucoma (n=50) | ∗ P-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 49.88±10.45 | 62.84±9.54 | 0.032 |
| Best Corrected Visual Acuity | 0.81±0.16 | 0.89±0.20 | 0.661 |
| Spherical Equivalent (diopter) | -1.59±1.85 | -1.20±2.54 | 0.392 |
| Intraocular Pressure (mmHg) | 14.06±3.24 | 14.80±2.52 | 0.206 |
| Mean Deviation (dB) | -0.96±0.95 | -7.11±5.54 | <0.001 |
| Pattern Standard Deviation (dB) | 1.70±0.45 | 7.82±4.40 | <0.001 |
Table 2.
Comparison of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness between normal eyes and normal tension glaucoma eyes
| Normal (n=50) | Normal Tension Glaucoma (n=50) | ∗ P-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 360˚ Average (µm) | 99.56±16.92 | 73.62±21.21 | <0.001 |
| Sup Quadrant (µm) | 122.44±24.77 | 88.17±28.31 | <0.001 |
| Temp Quadrant (µm) | 72.80±13.80 | 57.20±20.37 | <0.001 |
| Inf Quadrant (µm) | 127.00±27.01 | 87.74±32.45 | <0.001 |
| Nasal Quadrant (µm) | 75.68±16.41 | 61.02±15.34 | <0.001 |
Table 3.
Comparison of optic nerve head analysis between normal eyes and normal tension glaucoma eyes
| Normal (n=50) | Normal Tension Glaucoma (n=50) | ∗ P-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Disc Area (mm2) | 2.60±0.59 | 2.60±0.60 | 0.996 |
| Cup Area (mm2) | 1.31±0.69 | 1.95±0.76 | <0.001 |
| Rim Area (mm2) | 1.28±0.52 | 0.64±0.42 | <0.001 |
| Cup/Disc Area Ratio | 0.49±0.21 | 0.74±1.89 | <0.001 |
| Cup/Disc Horizontal Ratio | 0.73±0.17 | 0.87±1.32 | <0.001 |
| Cup/Disc Vertical Ratio | 0.64±0.15 | 0.82±0.13 | <0.001 |
Table 4.
Correlation between optic disc size and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in normal eyes and normal tension glaucoma eyes
|
Normal (n=50) |
Normal Tension Glaucoma (n=50) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R∗ | P† Value | R∗ | P† Value | |
| 360˚ Average (µm) | 0.425 | 0.001 | 0.451 | 0.001 |
| Sup Quadrant (µm) | 0.345 | 0.025 | 0.352 | 0.012 |
| Temp Quadrant (µm) | 0.307 | 0.031 | 0.298 | 0.039 |
| Inf Quadrant (µm) | 0.412 | 0.002 | 0.329 | 0.020 |
| Nasal Quadrant (µm) | 0.323 | 0.022 | 0.327 | 0.021 |
Table 5.
Correlation between optic disc size and the ratio of each quadrant to the total retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in normal eyes and normal tension glaucoma eyes
|
Normal (n=50) |
Normal Tension Glaucoma (n=50) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R∗ | P† Value | R∗ | P† Value | |
| Sup / Total | -0.283 | 0.049 | -0.314 | 0.029 |
| Temp / Total | 0.057 | 0.694 | 0.165 | 0.273 |
| Inf / Total | -0.217 | 0.130 | -0.302 | 0.034 |
| Nasal / Total | 0.403 | 0.004 | 0.184 | 0.210 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download