Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the clinical results of toric iris-fixated phakic intraocular lens (Artisan®) implantation for the correction of myopia with astigmatism.
Methods
Sixteen eyes of 11 patients underwent toric Artisan® lens implantation between April 2004 and February 2006 and were followed up for 6 months. We analyzed visual acuity, refraction, change in astigmatism, efficacy, safety, predictability, and complications.
Results
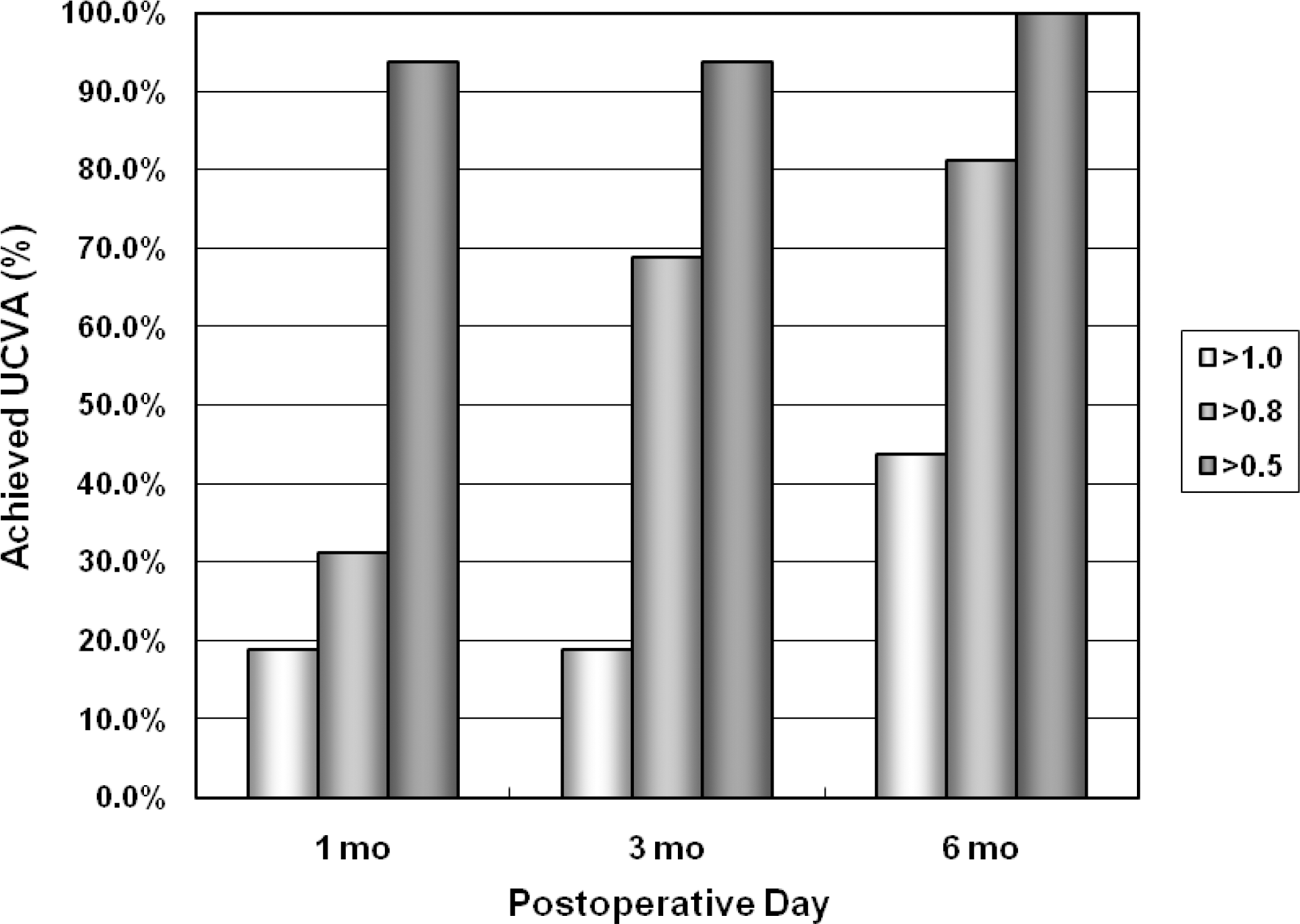
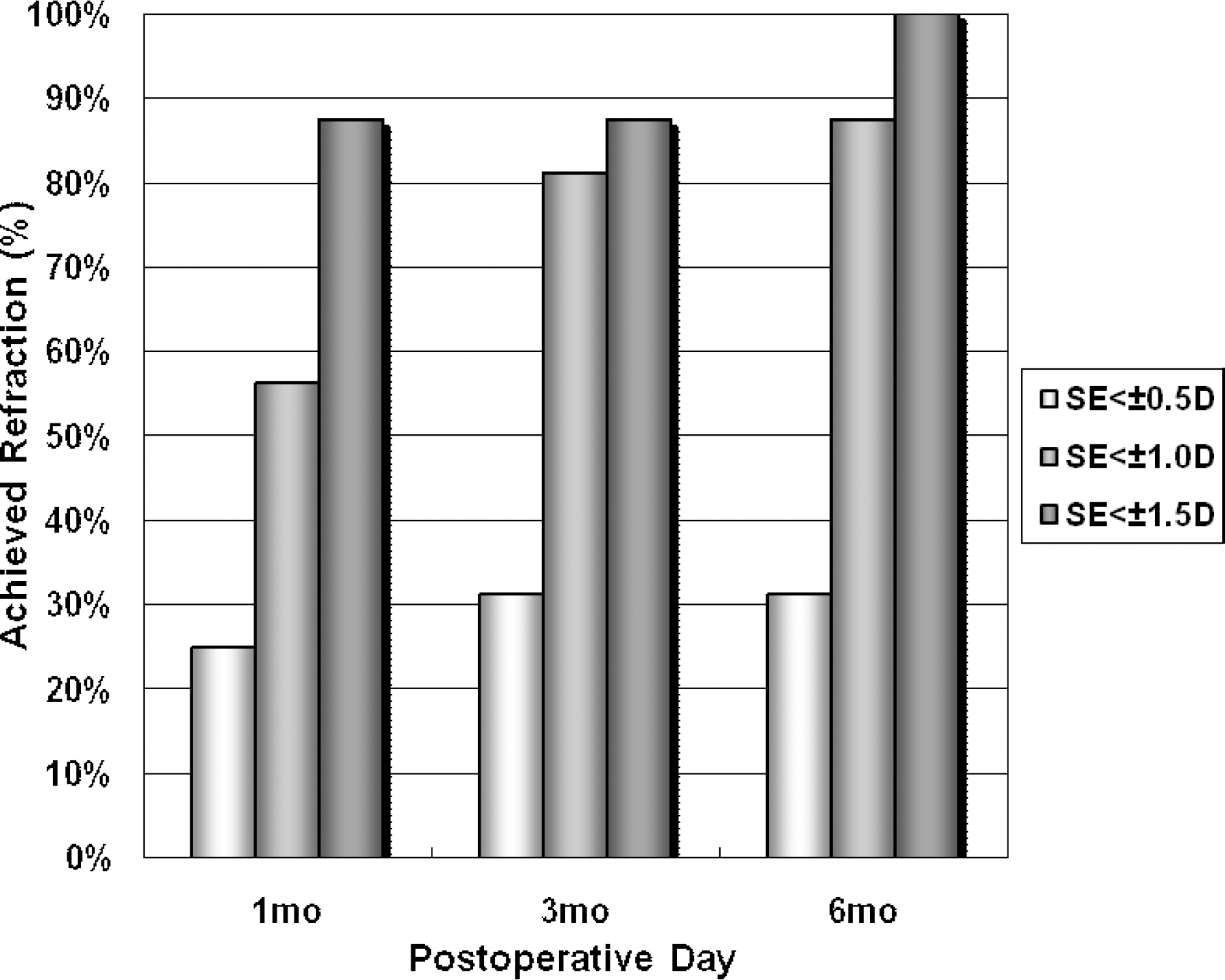
Among 11 patients, 4 were men and 7 were women, with an average age of 30.9 years. The preoperative mean uncorrected visual acuity (UCVA) was 0.02, except for 1 eye with post-LASIK astigmatism (0.4); the mean spherical equivalent refraction was -11.06±4.11D; and the mean astigmatism was -2.91±0.91D. At postoperative 1 month, 3 months, and 6 months, UCVA was more than 0.8 in 31%, 69%, 81% of eyes and more than 0.5 in 94%, 94%, 100% of eyes, respectively. Mean astigmatism decreased to -2.28, -1.37, and -0.73 and the spherical equivalent refraction was within 1.0D in 56%, 81%, 88% of eyes, respectively. For the vector analysis of astigmatic change, a doubled-angle scatterplot revealed that the postoperative 6 month data were located mainly at the center of the plot, which indicated a considerable reduction of astigmatism by magnitude and axis. At postoperative 6 months, the efficacy and safety indices were 99.0% and 114.7%, respectively. Complications included transient elevation of intraocular pressure in 1 eye and nighttime glare or halo in 3 eyes.
Go to : 
References
1. Schallhorn SC, Amesbury EC, Tanzer DJ. Avoidance, recognition, and management of LASIK complications. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006; 141:733–9.

2. Malecaze FJ, Hulin H, Bierer P, et al. A randomized paired eye comparison of two techniques for treating moderately high myopia: LASIK and artisan phakic lens. Ophthalmology. 2002; 109:1622–30.

3. Budo C, Hessloehl JC, Izak M, et al. Multicenter study of the Artisan phakic intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000; 26:1163–71.

4. Gonvers M, Bornet C, Othenin-Girard P. Implantable contact lens for moderate to high myopia: relationship of vaulting to cataract formation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:918–24.
5. Menezo JL, Peris-Martinez C, Cisneros AL, Martinez-Costa R. Phakic intraocular lenses to correct high myopia: Adatomed, Staar, and Artisan. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:33–44.
6. Smallman DS, Probst L, Rafuse PE. Pupillary block glaucoma secondary to posterior chamber phakic intraocular lens implantation for high myopia. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:905–7.

7. Kodjikian L, Gain P, Donate D, et al. Malignant glaucoma induced by a phakic posterior chamber intraocular lens for myopia. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:2217–21.

8. Tehrani M, Dick HB, Schwenn O, et al. Postoperative astigmatism and rotational stability after artisan toric phakic intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:1761–6.

9. Maloney RK, Nguyen LH, John ME. Artisan phakic intraocular lens for myopia:short-term results of a prospective, multicenter study. Ophthalmology. 2002; 109:1631–41.
10. Choi BJ, Choi BJ, Son MH, et al. The Clinical Results of 6-mm Iris-Fixated Phakic IOL. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:273–82.
12. Kim HC, Kim HC, Lee SY, et al. The Clinical Results of Iris-Fixed Phakic IOL. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:353–9.
13. Lee ES, Cho YJ, Kim EK. Short-term Change in Corneal Endothelium after Iris-Fixed Phakic Intraocular Lens Insertion. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:410–5.
14. Koch DD, Kohnen T, Obstbaum SA, Rosen ES. Format for reporting refractive surgical data. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1998; 24:285–7.

15. Van der Heijde GL, Rouwen AJ. Optics of intraocular lenses and refractive keratoplasty. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 1990; 1:64–8.

16. Holladay JT, Dudeja DR, Koch DD. Evaluating and reporting astigmatism for individual and aggregate data. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1998; 24:57–65.

17. Dick HB, Alio J, Bianchetti M, et al. Toric phakic intraocular lens: European multicenter study. Ophthalmology. 2003; 110:150–62.
18. Tehrani M, Dick HB. Iris-fixated toric phakic intraocular lens: Three-year follow-up. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:1301–6.

19. Alio JL, Mulet ME, Gutierrez R, Galal A. Artisan toric phakic intraocular lens for correction of astigmatism. J Refract Surg. 2005; 21:324–31.

20. Guell JL, Vazquez M, Malecaze F, et al. Artisan toric phakic intraocular lens for the correction of high astigmatism. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003; 136:442–7.
21. Tehrani M, Dick HB, Schwenn O, et al. Postoperative astigmatism and rotational stability after artisan toric phakic intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:1761–6.

22. Bartels MC, Saxena R, van den Berg TJ, et al. The influence of incision-induced astigmatism and axial lens position on the correction of myopic astigmatism with the Artisan toric phakic intraocular lens. Ophthalmology. 2006; 113:1110–7.

23. Dick HB, Aliyeva S, Tehrani M. Change in pupil size after implantation of an iris-fixated toric phakic intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:302–7.

24. Perez-Torregrosa VT, Menezo JL, Harto MA, et al. Digital system measurement of decentration of Worst-Fechner iris claw myopia intraocular lens. J Refract Surg. 1995; 11:26–30.

25. Nuijts RM, Missier KA, Nabar VA. Phakic toric intraocular lens implantation after flap decentration in laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:259–61.

26. Chung JK, Lee JB, Lee SJ. Artisan phakic intraocular lens implantation after retinal detachment surgery. J Refract Surg. 2006; 22:820–3.

27. Tahzib NG, Cheng YY, Nuijts RM. Three-year follow-up analysis of Artisan toric lens implantation for correction of postkeratoplasty ametropia in phakic and pseudophakic eyes. Ophthalmology. 2006; 113:976–84.

Go to : 
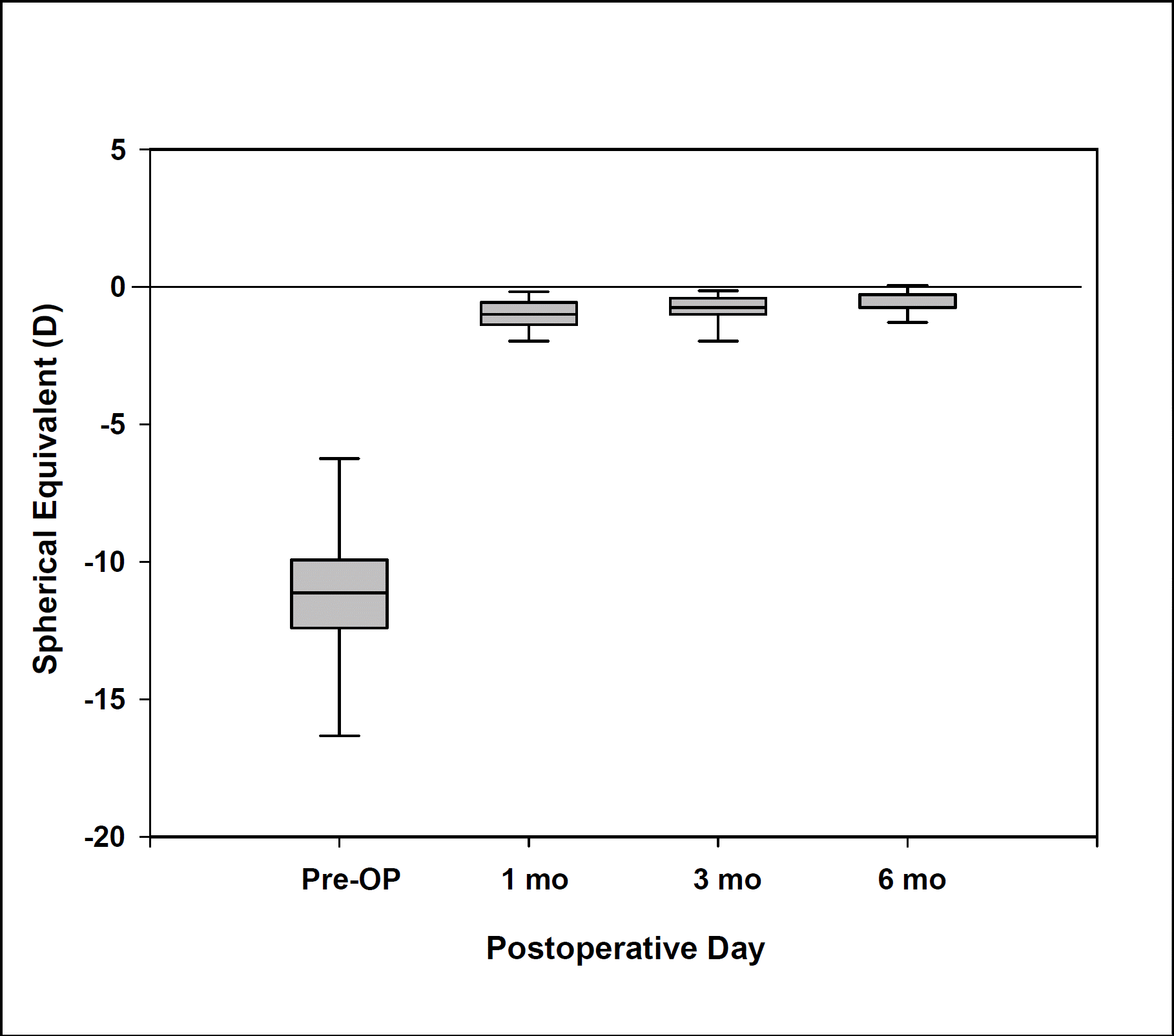 | Figure 2.Reduction in total manifest refraction during preoperative versus postoperative period. Horizontal lines indicate medians and 1st and 3rd quartiles. Vertical extensions indicate 10th/90th percentile values. |
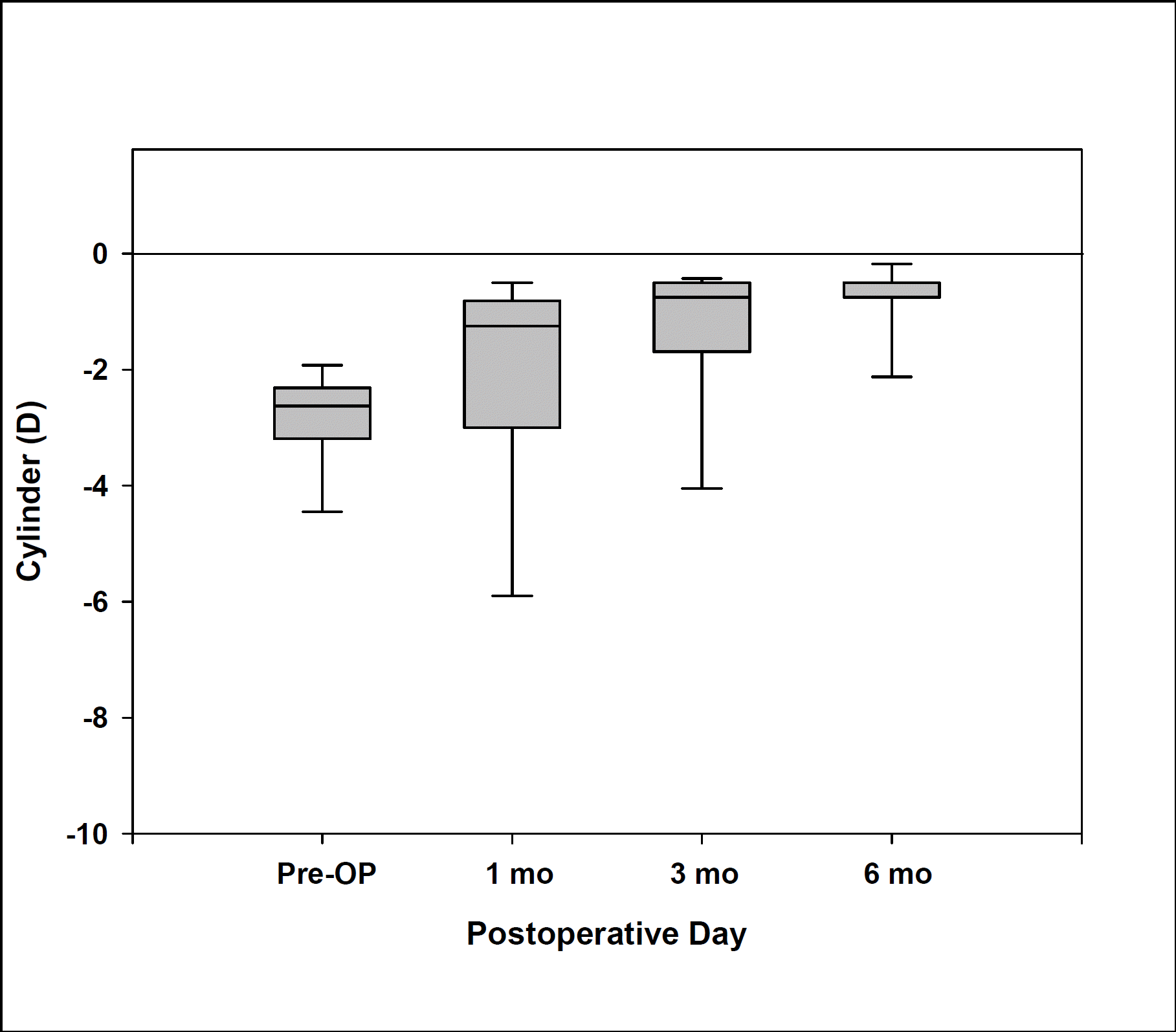 | Figure 3.Reduction in total astigmatism during preoperative versus postoperative period. Horizontal lines indicate medians and 1st and 3rd quartiles. Vertical extensions indicate 10th/90th percentile values. |
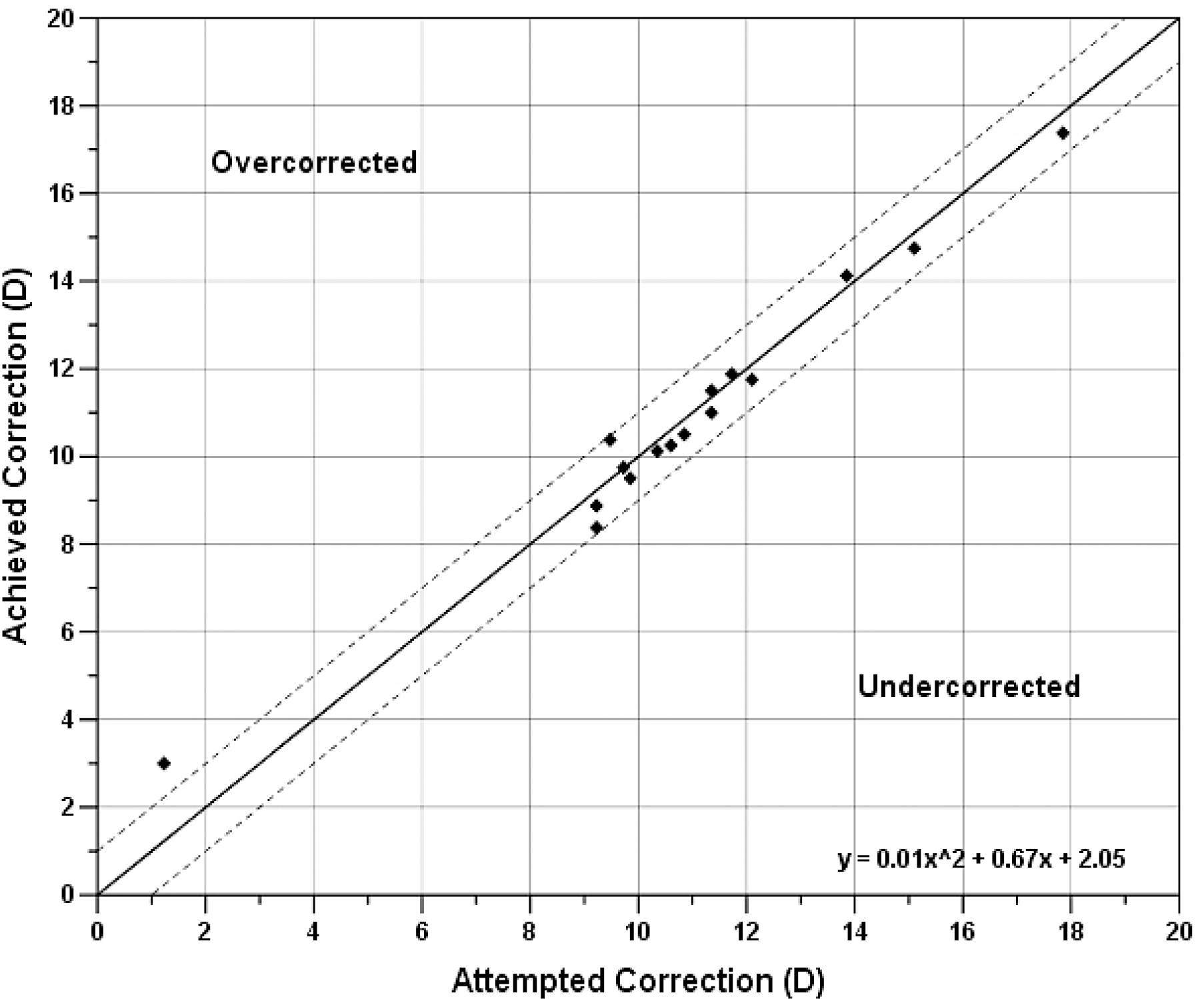 | Figure 5.Scattergram of achieved refraction (spherical equivalent) against intended refraction at 6 months. The diagonal line show equality and overcorrection and undercorrection by 1 diopter; D=diopters. |
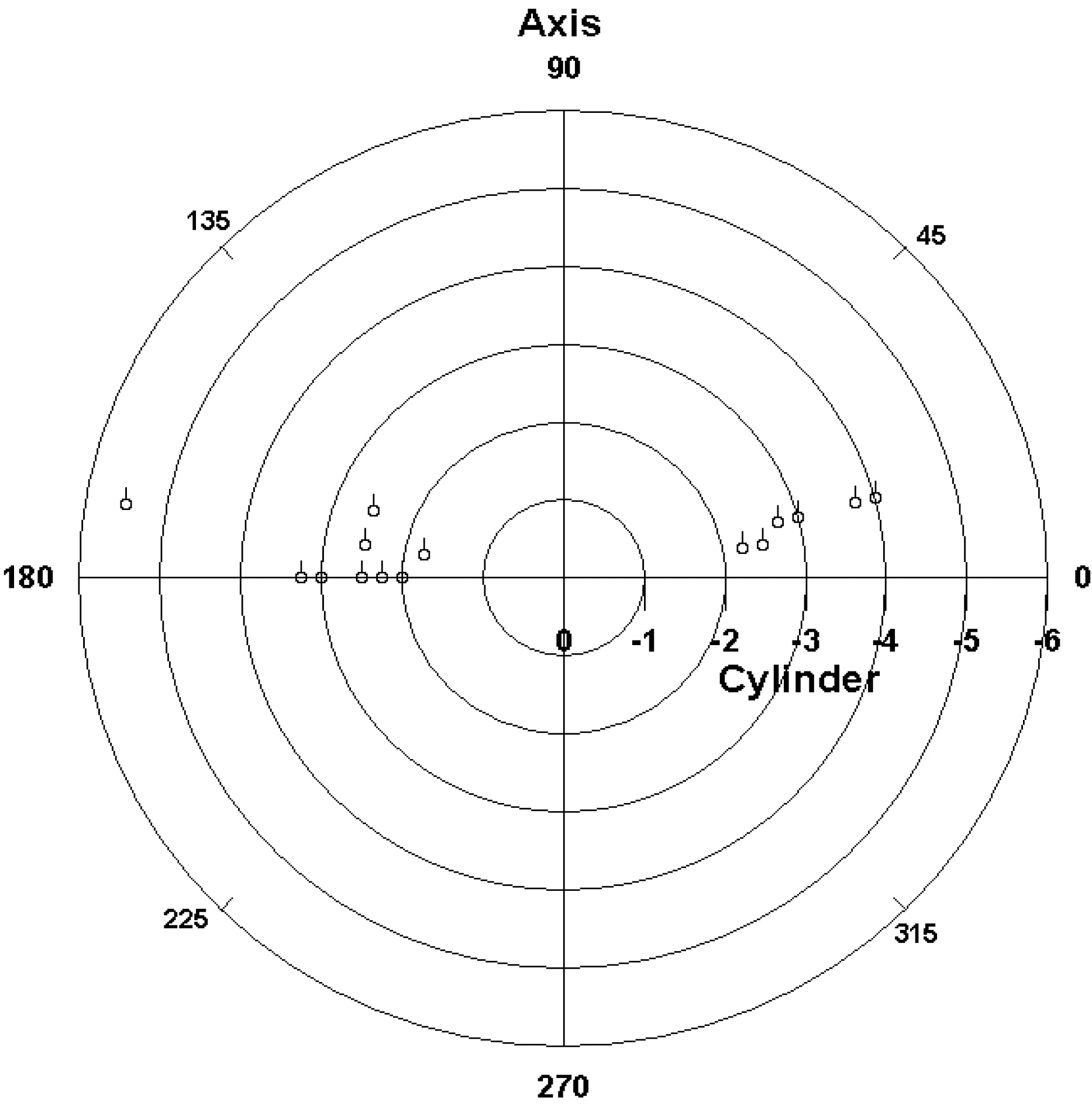 | Figure 6.Doubled‐ angle scatterplot showing a polar plot of the preoperative spectacle plane refractive astigmatism at a vertex distance of 12 mm by using the value of cylinder for the magnitude and the axis of the astigmatism for the angle. The 0° and 180° locations are the same, just as 0° and 180° are the same for the axis of refraction. |
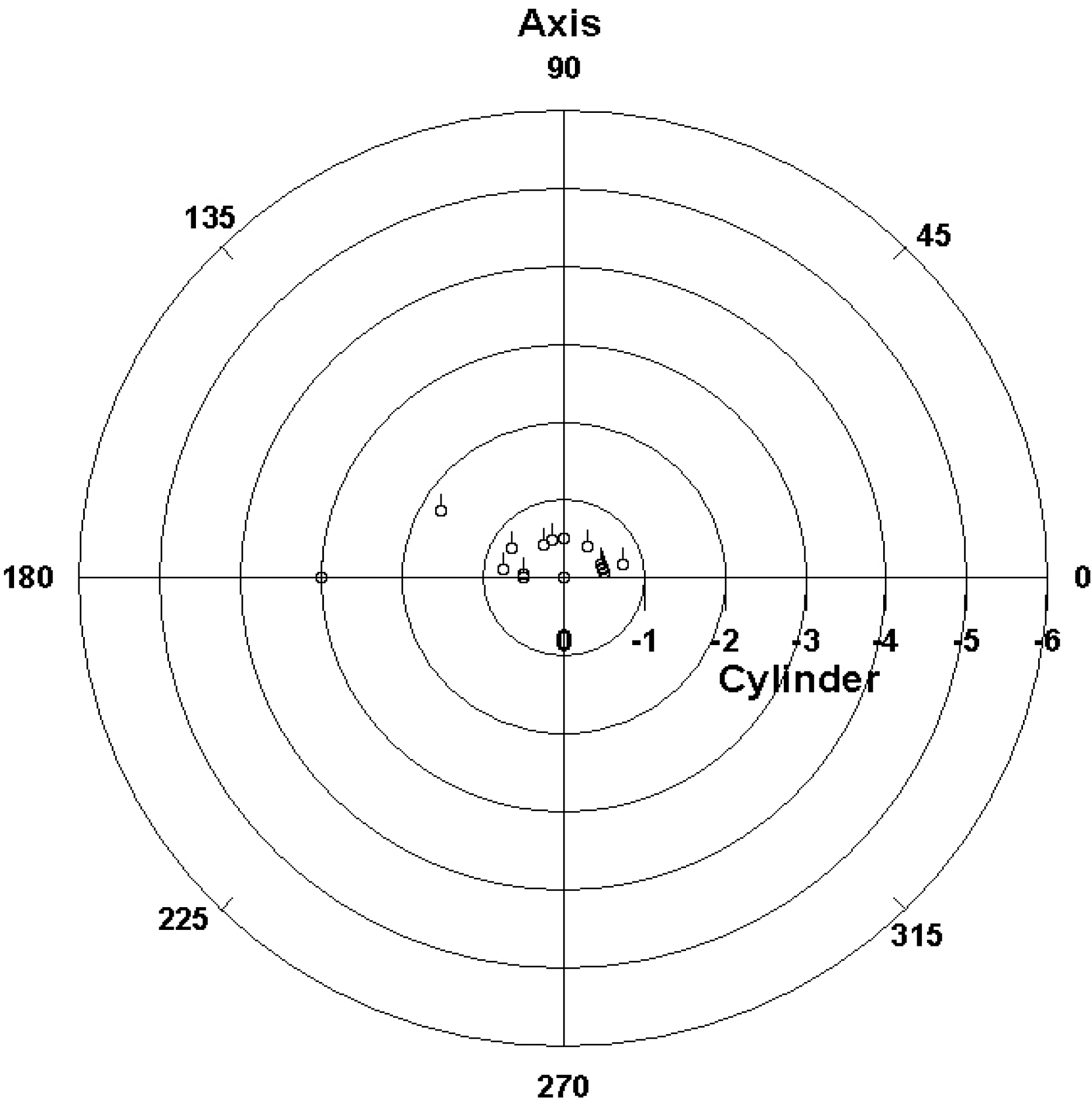 | Figure 7.Doubled‐ angle scatterplot showing a polar plot of the 6‐ month‐ postoperative spectacle plane refractive astigmatism at a vertex distance of 12 mm by using the value of cylinder for the magnitude and the axis of the astigmatism for the angle. The postoperative data are located at the center of the plot, which illustrates the great reduction of preoperative astigmatism by the implantation of toric phakic intraocular lenses. |
Table 1.
Summary of preoperative patient data for patients undergoing implantation of toric phakic intraocular lenses
Table 2.
Preoperative and postoperative mean uncorrected visual acuity, best spectacle corrected visual acuity, spherical equivalent and cylinder
Table 3.
Preoperative and postoperative results of two patients who received Artisan lens in the right eye and toric Artisan lens in the left eye




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download