Abstract
Purpose
To explore the effects of stimulus duration, stimulus intensity, and background luminance on the amplitude and waveform of the ON- and OFF-responses of photopic ERG and to provide standard parameters of ON- and OFF-responses for normal Korean populations.
Methods
Twenty normal subjects (20 eyes) were enrolled to record photopic ON-and OFF-responses using a contact lens electrode with built-in LEDs and an LED-driver. The influence of stimulus duration on wave amplitudes was studied at flash durations that varied from 5 to 200 ms. The influence of stimulus intensity was studied with 0.4, 0.7, 1.1, 1.4, 1.7, 1.9, 2.0, and 2.1 log cd/m2. In addition, the influence of background luminance was studied with 20, 30, 40, and 50 cd/m2.
Result
Among 20 normal subjects, the d-waves in 16 subjects were isolated from b-waves with more than 50 ms of stimulus duration. The d-wave was observed for a 30-ms stimulus duration in 3 subjects and for a 100-ms duration in 1 subject. The amplitudes of the band d-waves increased as stimulus intensity was increased. The amplitudes of band d-waves decreased as background luminance was increased.
Go to : 
References
1. Marmor MF, Zrenner E. Standard for clinical electroretinography. Doc Ophthalmol. 1995; 89:199–210.

2. Sieving PA. Photopic ON-and OFF-pathway abnormalities in retinal dystrophies. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1993; 91:701–73.
3. Alexander KR, Fishman GA, Peachey NS, et al. ‘ON' response defect in paraneoplastic night blindness with cutaneous malignant melanoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1992; 33:477–83.
4. Quigley M, Roy MS, Barsoum-Homsy M, et al. On- and off-response in the photopic electroretinogram in complete type congenital stationary night blindness. Doc Ophthalmol. 1996–7; 92:159–65.
5. Kabanarou SA, Holder GE, Fitzke FW, et al. Congenital stationary blindness and a “Schubert-Bornschein” type electro-physiology in a family with dominant inheritance. Br J Ophthalmol. 2004; 88:1018–22.
6. Downes SM, Holder GE, Fitzke FW, et al. Autosomal dominant cone and cone-rod dystrophy with mutations in the guanylate cyclase activator 1A gene encoding guanylate cyclase activating protein 1. Arch Ophthalmol. 2001; 119:96–105.
7. Allen LE, Zito I, Bradshaw K, et al. Genotype-phenotype correlation in British families with X-linked congenital stationary night blindness. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003; 87:1413–20.
8. Miyake Y, Yagasaki K, Horiguchi M, et al. On-and off response in photopic electroretinogram in complete and incomplete types of congenital stationary night blindness. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 1987; 31:81–7.
9. Fitzgerald KM, Cibis GW, Giambrone SA, et al. Retinal signal transmission in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: evidence for dysfunction in the photoreceptor/ depolarizing bipolar cell pathway. J Clin Invest. 1994; 93:2425–30.
10. Chen C, Zuo C, Piao C, Miyake Y. Recording rod ON and OFF responses in ERG and multifocal ERG. Doc Opthalmol. 2005; 111:73–81.

11. Usui T, Tanimoto N, Ukei S, et al. Night blindness with depolarizing pattern of ON/OFF response in electroretinogram: a case report. Doc Ophthalmol. 2005; 111:15–21.

13. Falk G. Retinal physiology. Hekenlively JR, Arden GB, editors. Principles and Practice of Clinical Electrophysiology of Vision. St Louis: Mosby;1991. chap. 7.
14. Stell WK, Ishida AT, Lightfoot DO. Structural basis for on-and off-center responses in retinal bipolar cells. Science. 1977; 198:1269–71.
15. Sustar M, Hawlina M, Brecelj J. ON- and OFF-response of the photopic electroretinogram in relation to stimulus characteristics. Doc Ophthalmol. 2006; 113:43–52.

16. Kondo M, Piao CH, Tanikawa A, et al. Amplitude decrease of photopic ERG b-wave at higher stimulus intensities in humans. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2000; 44:20–8.

17. Seiple W, Holopiqian K. The ‘OFF' response of the human electroretinogram does not contribute to the brief flash ‘b-wave'. Vis Neurosci. 1994; 11:667–73.
18. Hogg C. The use of light emitting diodes in electrophysiology and psychophysics. Heckenlively JR, Arden GB, editors. Principles and Practice of Clinical Electrophysiology of Vision. St Louis: Mosby;1991. chap. 28.
19. Kondo M, Piao CH, Tanikawa A, et al. A contact lens electrode with built-in high intensity white light-emmitting diodes. Doc Ophthalmol. 2001; 102:1–9.
Go to : 
 | Figure 1.(A) LED-driver (size 20W×16D×6H cm, weight 800 gm; Mayo Co., Nagoya, Japan), (B) contact lens electrode with build-in white LEDs. |
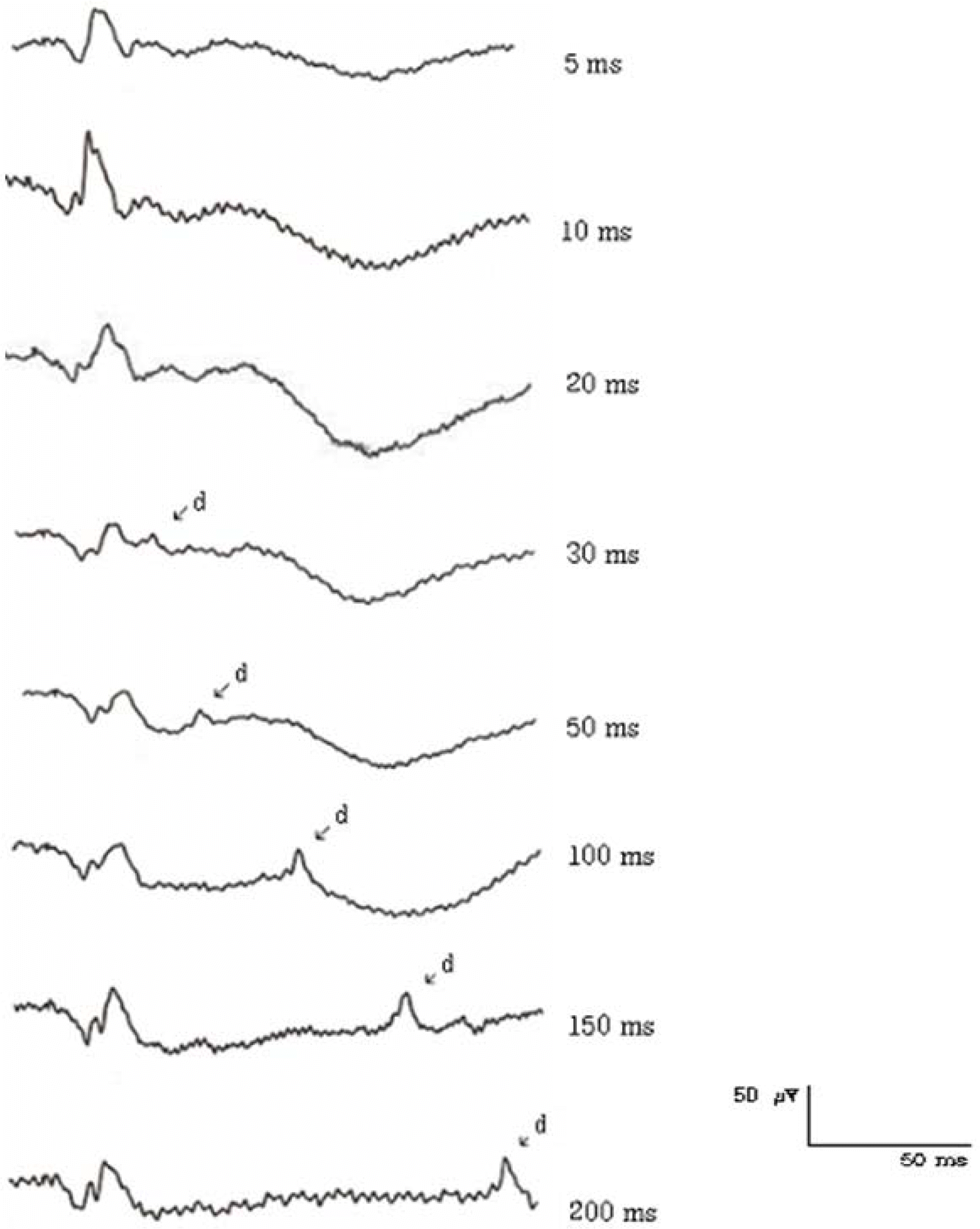 | Figure 2.The ON- & OFF-responses of a normal human subject elicited with different stimulus durations. (2.1 log cd/m2 intensity, 40 cd/m2 background luminance) |
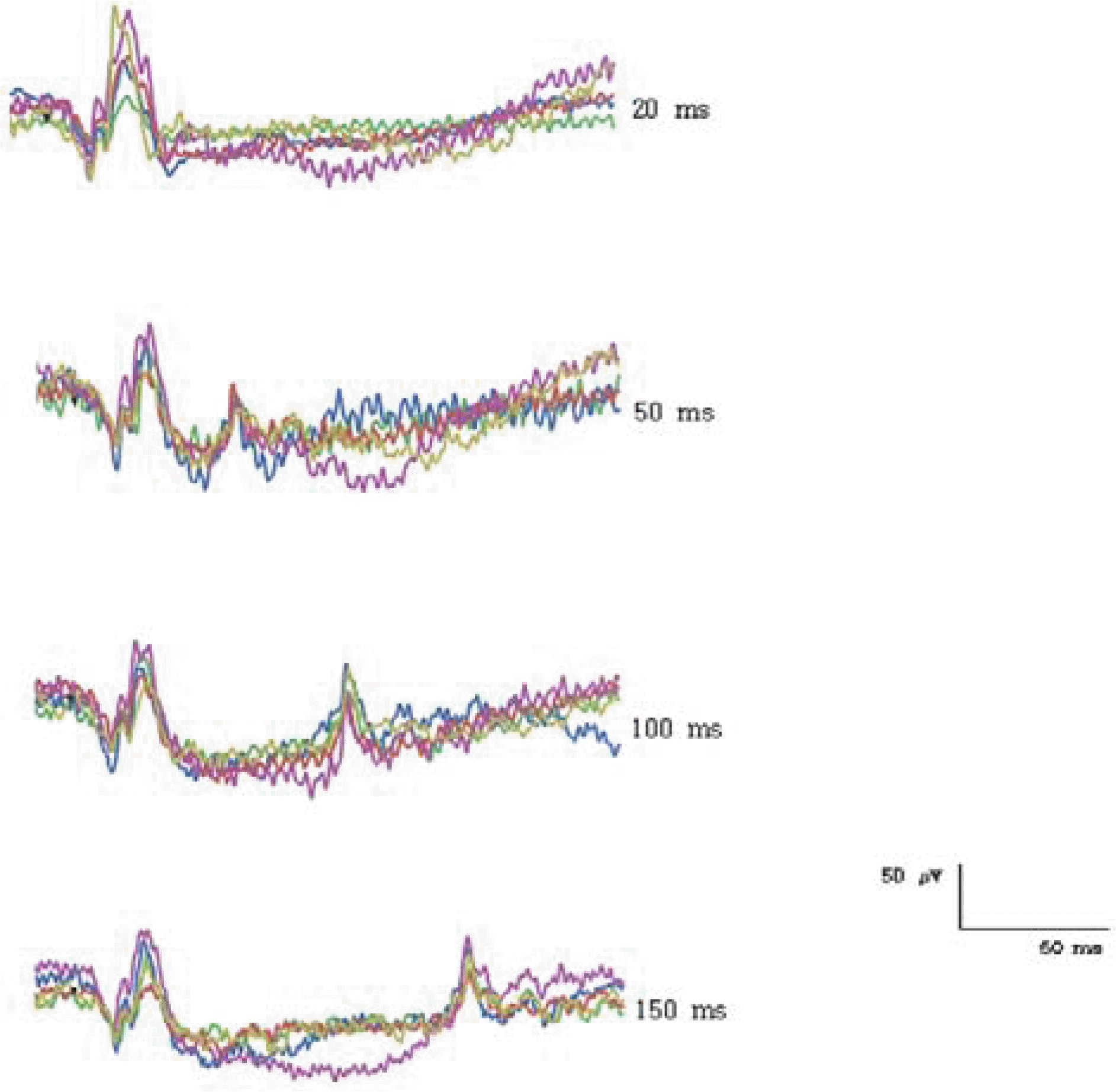 | Figure 3.Consistency of ON- & OFF-responses of normal human subjects elicited with different stimulus durations. (2.1 log cd/m2 intensity, 40 cd/m2 background luminance) |
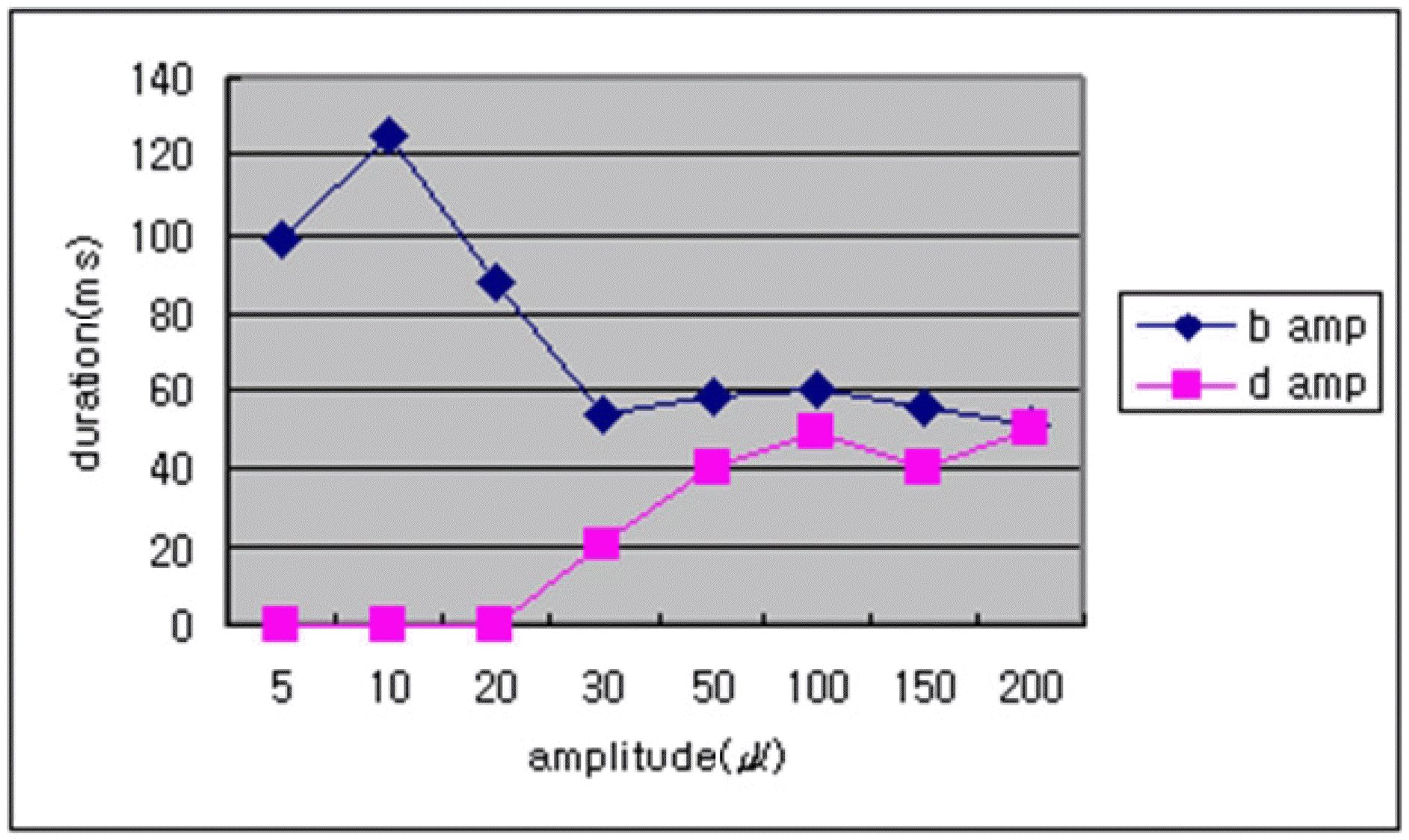 | Figure 4.The averages of b- and d-wave amplitudes shown at different stimulus durations. (2.1 log cd/m2 intensity, 40 cd/m2 background luminance) (n=20) |
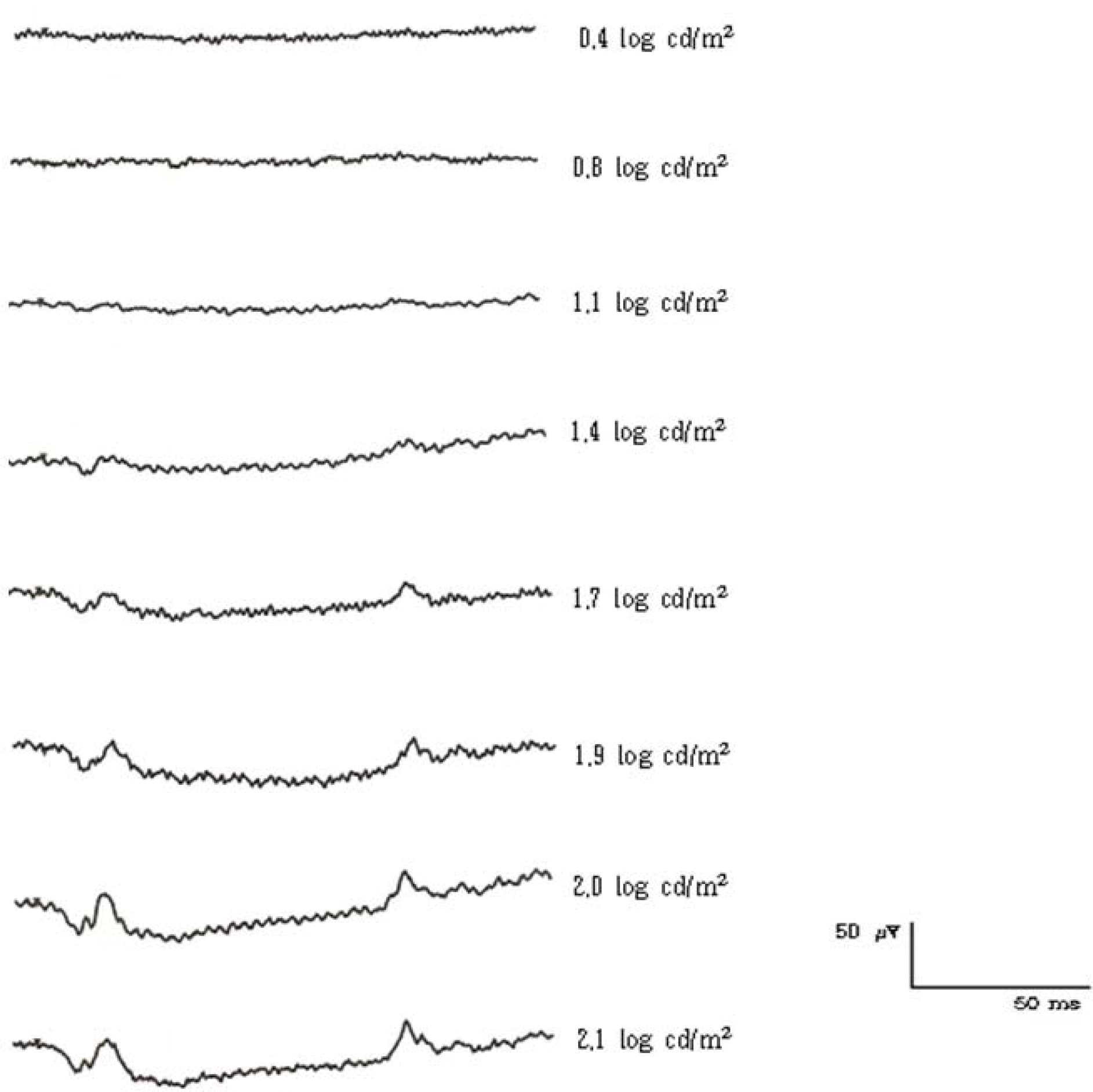 | Figure 5.The ON- & OFF-responses of a normal human subject elicited with different stimulus intensities. (150 ms duration, 40 cd/m2 background luminance) |
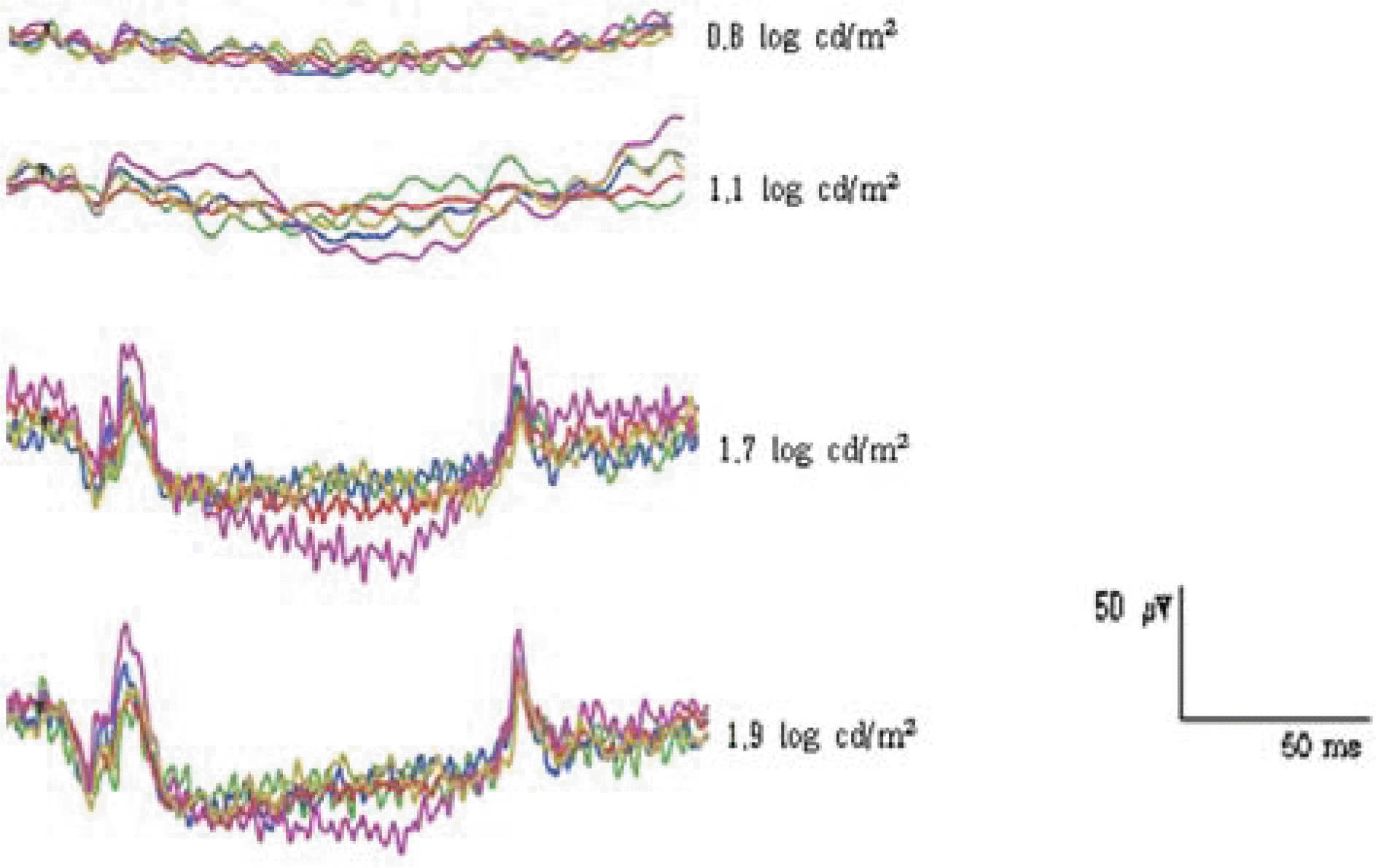 | Figure 6.Consistency of ON- & OFF-responses of normal human subjects elicited with different stimulus intensities. (150 ms duration, 40 cd/m2 background luminance) |
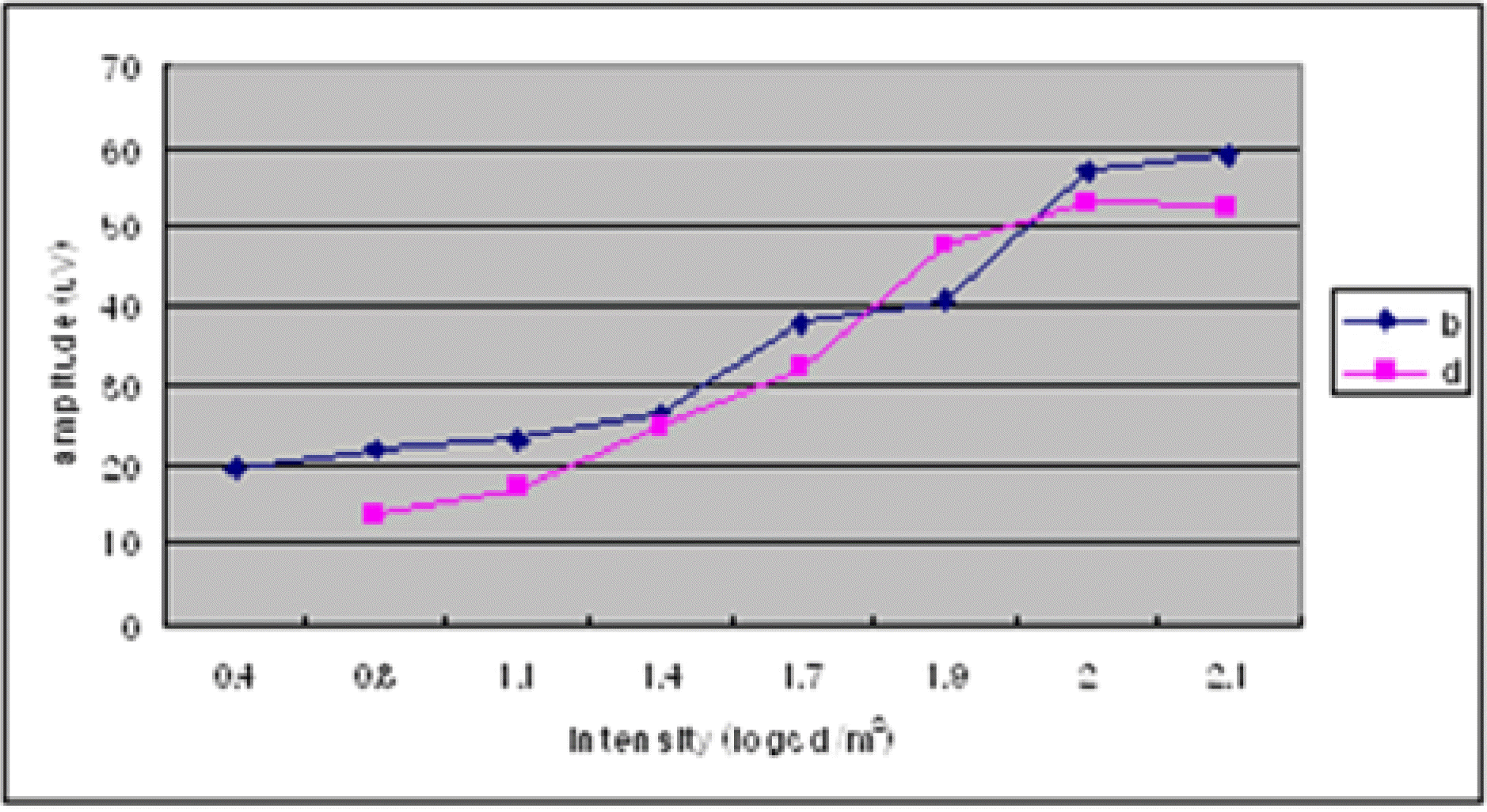 | Figure 7.The averages of b- and d-wave amplitudes shown at different stimulus intensities. (150 ms duration, 40 cd/m2 background luminance) (n=20) |
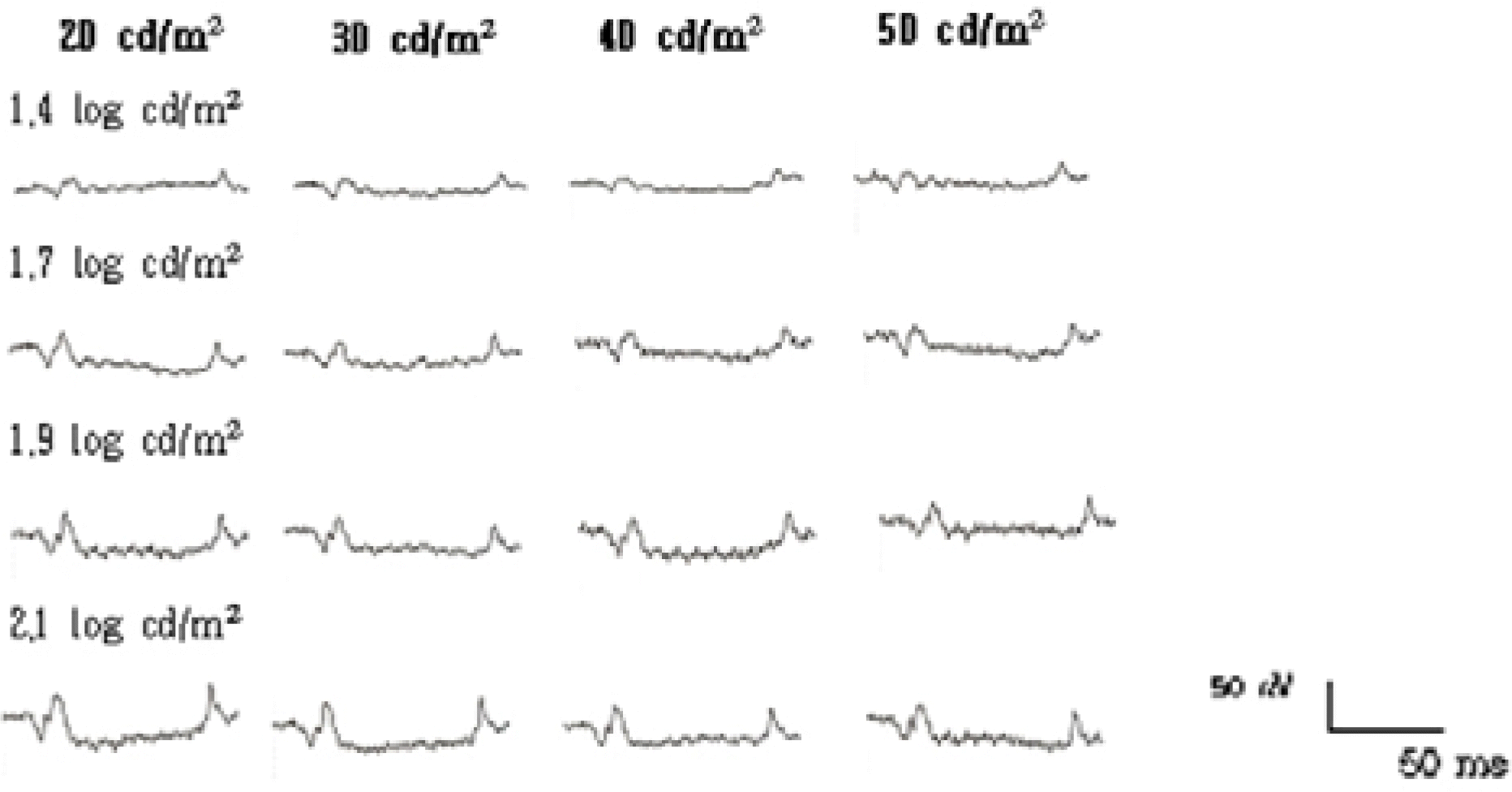 | Figure 8.The ON- & OFF-responses of a normal human subject elicited with different background luminances and intensities. (150 ms duration) |
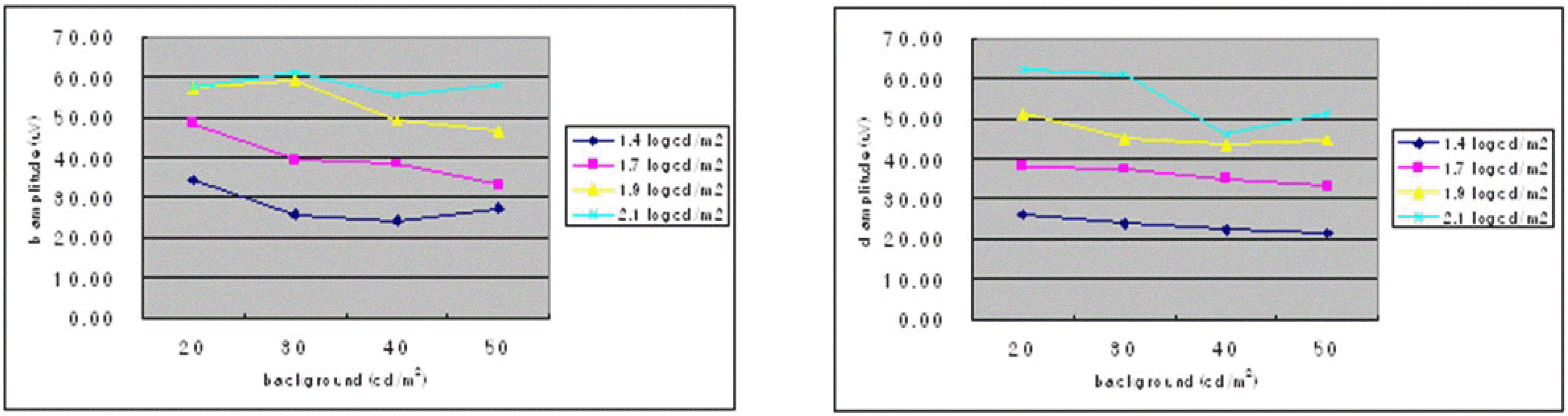 | Figure 9.The average amplitudes of (a) b-wave and (b) d-wave amplitudes shown at different background luminances and intensities. (150 ms duration) (n=20) |
Table 1.
The averages of ON-and OFF-responses of 20 normal subjects with different stimulus durations (2.1 log cd/m2 intensity 40 cd/m2 background luminance)
Table 2.
The averages of ON-and OFF-ERG responses of 20 normal subjects with different stimulus intensities (150 ms duration, 40 cd/m2 background luminance)
Table 3.
The averages of ON-and OFF-responses of 20 normal subjects with different background luminances, intensities, and 150 ms duration
|
background luminance (cd/m2) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20† | 30 | 40 | 50 | ||
|
|
|||||
| stimulus intensity (log cd/m2) | |||||
| 1.4 | |||||
| b amp* (µV) | 34.04±22.19 | 25.61±11.54 | 24.35±8.90 | 27.22±9.74 | |
| d amp* (µV) | 26.07±8.29 | 23.94±11.30 | 22.20±7.93 | 21.68±7.94 | |
| 1.7 | |||||
| b amp* (µV) | 48.63±22.44 | 39.29±24.39 | 38.43±20.33 | 32.94±26.29 | |
| d amp* (µV) | 37.99±15.43 | 37.30±17.95 | 34.94±15.48 | 33.07±15.17 | |
| 1.9 | |||||
| b amp* (µV) | 57.41±25.96 | 59.21±26.38 | 49.19±20.60 | 46.41±16.70 | |
| d amp* (µV) | 51.16±18.48 | 44.81±14.91 | 43.61±17.72 | 44.74±17.09 | |
| 2.1 | |||||
| b amp* (µV) | 57.54±22.15 | 61.09±19.48 | 55.20±24.79 | 58.16±25.15 | |
| d amp* (µV) | 62.40±21.01 | 61.04±18.33 | 46.30±13.23 | 51.07±17.97 | |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download