Abstract
Purpose
The effect of suture presence or position of intraocular lens was evaluated on the astigmatic changes in cataract patients suffering from with-the-rule astigmatism who underwent temporal clear corneal incision cataract surgeries.
Methods
According to the presence or absence of suture and the lens position (either 180˚ or 90˚), 49 eyes of 47 patients were divided into four groups. Astigmatism was determined using an autorefractor and by topography before surgery, and at one day, one week, one month, and two months after surgery.
Results
The suture group showed significant reduction in astigmatism at postoperative day 1 and week 1 by autorefractor and topography compared with the non-suture group. The group with intraocular lens insertion axis at 180˚ did not show significant reduction of astigmatism by autorefractor evaluation. Astigmatism determination by topography in this group was 1.00±0.73D, 1.01±0.77D and 1.01±0.81D at postoperative week 1, month 1, and month 2, respectively, and this showed significant reduction of astigmatism compared with preoperative astigmatism (1.32±1.17D) and group with intraocular lens insertion axis at 90˚. In particular, the group with the sutured temporal incision and with an inserted intraocular lens axis at 180˚ showed significant reduction of astigmatism by autorefraction.
Go to : 
References
1. Tejedor J, Murube J. Choosing the location of corneal incision based on preexisting astigmatism in phacoemulsification. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005; 139:767–76.

2. Khokhar S, Lohiya P, Murugiesan V. Corneal astigmatism correction with opposite clear cornal incisions or single clear corneal incision: Comparative analysis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:1432–37.
3. Bayramlar H, Daglioglu MC, Borazan M. Limbal relaxing incisions for primary mixed astigmatism and mixed astigmatism after cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 23:723–28.

4. Barequet IS, Yu E, Vitale S, et al. Astigmatism outcomes of horizontal temporal versus nasal clear corneal incision cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:418–23.

5. Kaufmann C, Peter J, Oou K, et al. Limbal relaxing incisions versus on-axis incisions to reduce corneal astigmatism at the time of cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:2261–5.

6. Wang L, Misra M, Koch D. Peripheral corneal relaxing incisions combined with cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 23:712–22.

7. Seo JB, Joo CK. Long-term course of induced astigmatism after temporal clear corneal incision in cataract surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:3038–43.
8. Shepherd JR. Induced astigmatism in small incision cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1989; 15:85–8.

9. Cravy TV. Routine use of a lateral approach to cataract extraction to achieve rapid and sustained stabilization of postoperative astigmatism. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1991; 17:415–23.

10. Vasavada A, Singh R. Relationship between lens and capsular bag size. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1998; 24:547–51.

11. Axt JC, McCaffery JM. Reduction of postoperative against the-rule astigmatism by lateral incision technique. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1993; 19:380–86.
12. Maloney WF, Sanders DR, Pearcy DE. Astigmatic keratotomy to correct preexisting astigmatism in cataract patients. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1990; 16:297–304.

13. Muller-Jensen K, Fischer P, Siepe U. Limbal relaxing incisions to correct astigmatism in clear corneal cataract surgery. J Refract Surg. 1999; 15:586–89.
14. Wang L, Misra M, Koch DD. Peripheral corneal relaxing incisions combined with cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:712–22.

15. Ruhswurm I, Scholz U, Zehetmayer M, et al. Astigmatism correction with a foldable toric intraocular lens in cataract patients. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000; 26:1022–27.

16. Sun X-Y, Vicary D, Montgomery P, Griffiths M. Toric intraocular lenses for correcting astigmatism in 130 eyes. Ophthalmology. 2000; 107:1776–81.

17. Kohnen T, Koch DD. Methods to control astigmatism in cataract surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 1996; 7:75–80.

18. Lever J, Dahan E. Opposite clear corneal incision to correct preexisting astigmatism in cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000; 26:803–5.
19. Borasio E, Mehta JS, Maurino V. Torque and flattening effects of clear corneal temporal and on-axis incisions for phacoenul-sification. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:2030–8.
20. Dick HB, Schwenn O, Krummenauer F, et al. Inflammation after sclerocorneal versus clear corneal tunnel phacoemulsification. Ophthalmology. 2000; 107:241–7.

21. Moon SC, Mohamed T, Fine IH. Comparison of surgically induced astigmatisms after clear corneal incisions of different sizes. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2007; 21:1–5.

22. Pfleger T, Skorpik C, Menapace R, et al. Long-term course of induced astigmatism after clear corneal incision cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1996; 22:72–7.

23. Axt JC, McCaffery JM. Reduction of postoperative against-the-rule astigmatism by lateral incision technique. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1993; 19:380–6.

24. Cillno S, Morreale D, Mauceri A. Temporal versus superior approach phacoemulsification: Short-term postoperative astigmatism. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1997; 23:267–71.
25. Rao SN, Konowal A, Murchison AE, Epstein RJ. Enlargement of the temporal clear corneal cataract incision to treat preexisting astigmatism. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 18:463–67.

26. Barequet IS, Yu E, Vitale S, Cassard S, et al. Astigmatism outcomes of horizontal temporal versus nasal clear corneal incision cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:418–23.

27. Masket S. Keratorefractive aspects of the scleral pocket incision and closure method for cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1989; 15:70–7.

28. Gimbel HV, Sun R. Postoperative astigmatism following phacoemulsification with sutured versus unsutured wound. Can J Ophthalmol. 1993; 28:259–62.
29. Pham DT, Wollensak J, Drosch S. Early postoperative corneal astigmatism. Comparison of various suture techniques. Ophthalmologe. 1992; 89:305–9.
Go to : 
 | Figure 1.Sheme of intraocular lens insertion axis of a patient's right eye. Imaginary line of haptic-optic-haptic lying horizontally is defined to be inserted at 180° axis (Left) and vertically is defined to be at 90° axis (Right). |
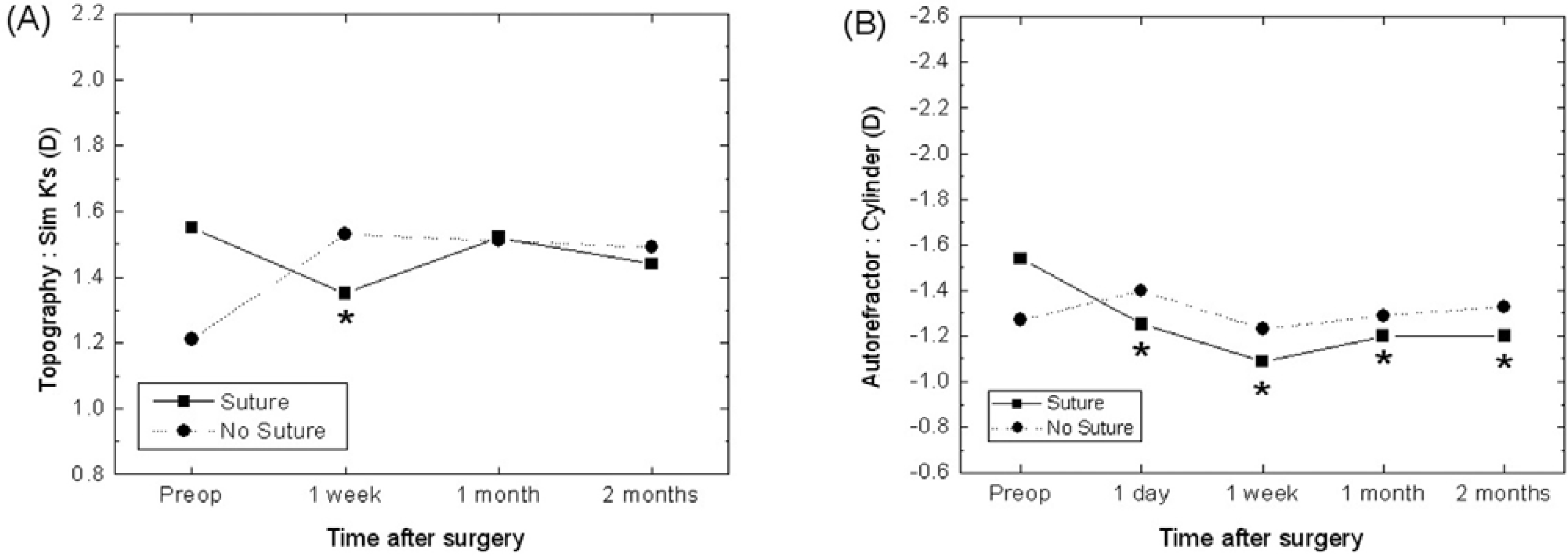 | Figure 2.The changes of mean astigmatism in suture and no suture groups by topography measurement (A), autorefractor measurement (B). (* P<0.05) |
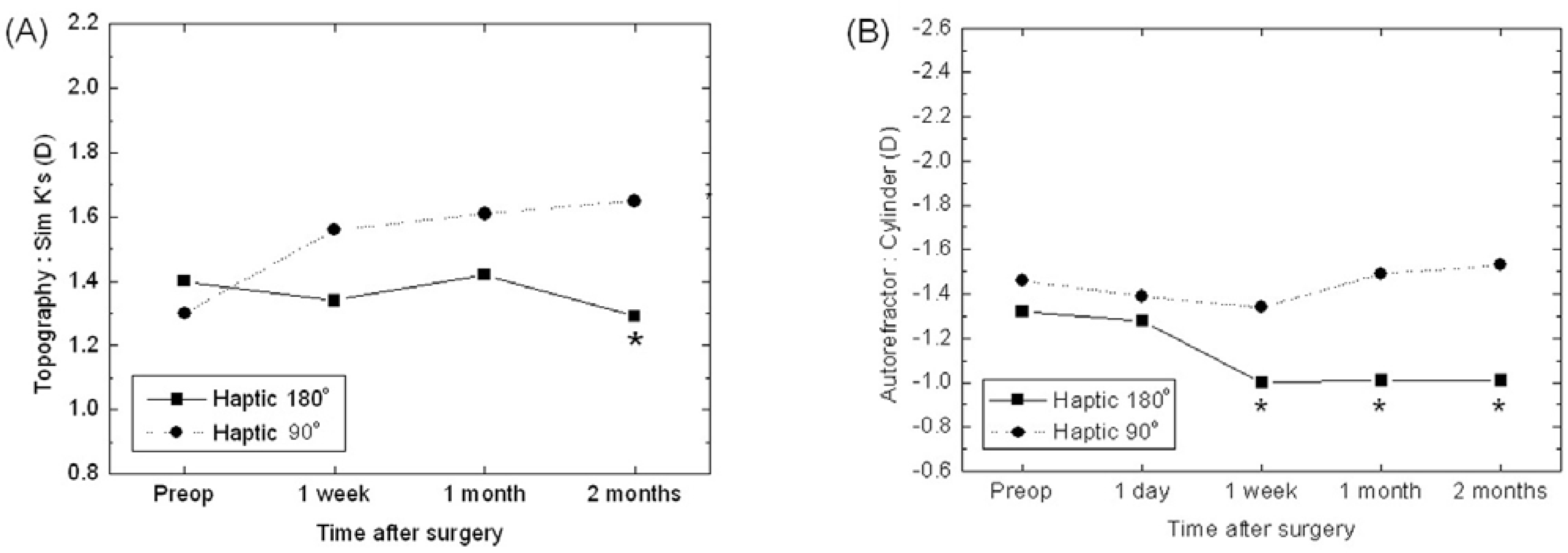 | Figure 3.The changes of mean astigmatism in 180° axis IOL and 90° axis IOL group by topography measurement (A), autorefractor measurement (B). (* P<0.05) |
 | Figure 4.The changes of mean astigmatism in each groups by autorefractor measurement. (* P<0.05) Group I=suture+Haptic 180° group. Group II=suture+Haptic 90° group. Group III=no suture+Haptic 180° group. Group IV=no suture+Haptic 90° group. |
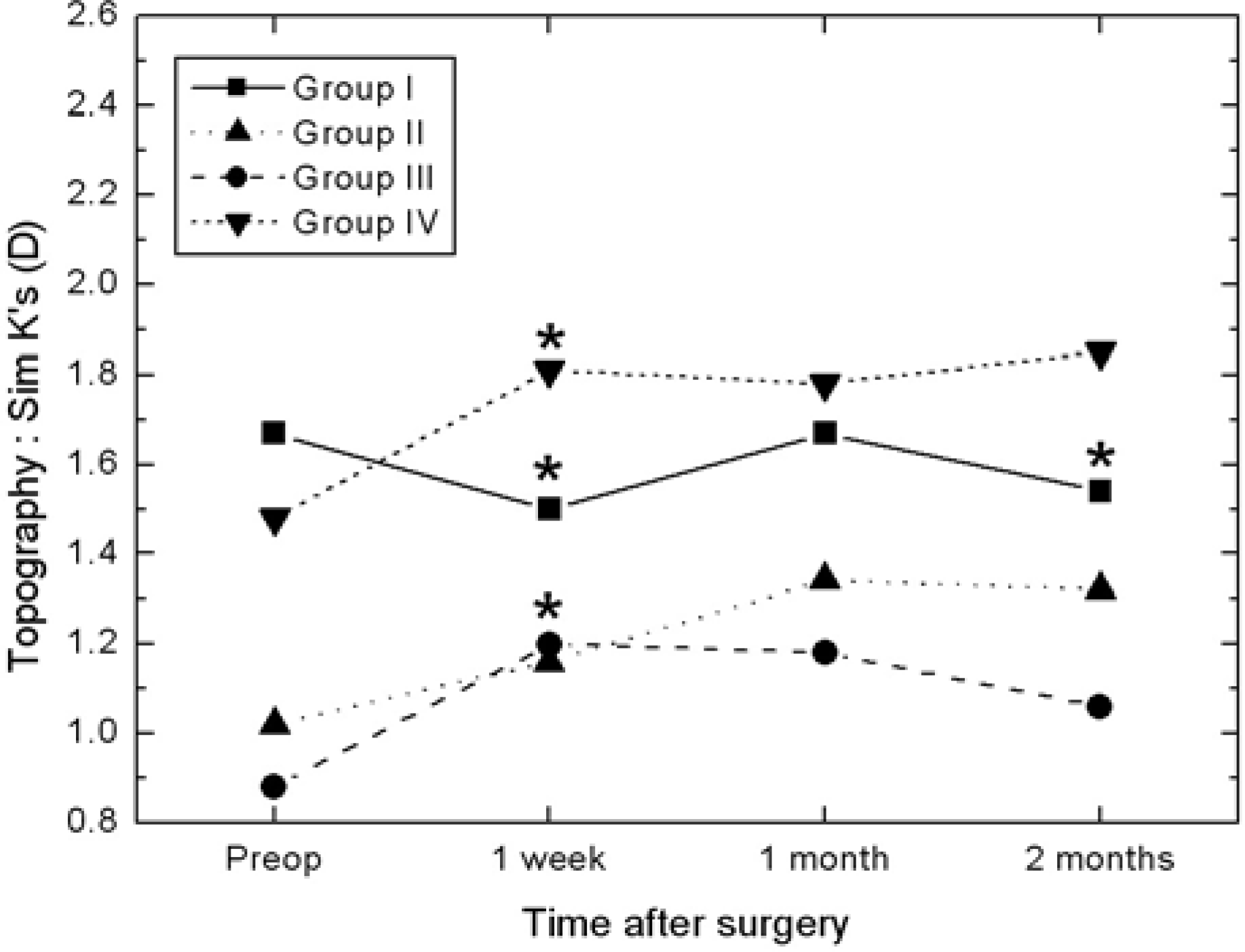 | Figure 5.The changes of mean astigmatism in each group by keratometric measurement. (* P<0.05) Group I=suture+Haptic 180° group. Group II=suture+Haptic 90° group. Group III=no suture+Haptic 180° group. Group IV=no suture+Haptic 90° group. |
Table 1.
Dermographics and preoperative astigmatism of each group
Table 2.
The change of mean astigmatism in suture and no suture groups by autorefractor and topography measurement (Diopter)
Table 3.
The change of mean astigmatism in IOL insertion axis groups by autorefractor and topography measurement (Diopter)




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download