Abstract
Purpose
To compare the clinical outcomes between scleral buckling and vitrectomy in the primary management of pseudophakic retinal detachment with an intact posterior capsule.
Methods
The medical records of 63 eyes that underwent scleral buckling (36 eyes) or vitrectomy (27 eyes) as a primary operation of uncomplicated pseudophakic retinal detachment with intact posterior capsules with a follow-up of more than one year were retrospectively reviewed from 2000 to 2005. We compared the clinical outcomes using anatomical and functional success rates at postoperative one year. Anatomical success was defined by a reattachment rate and functional success was measured by a change of more than 0.3 logMAR.
Results
Anatomical success rates were 86% in the scleral buckling and 82% in the vitrectomy, respectively (p=0.837). Functional success rates were 81% in the scleral buckling and 70% in the vitrectomy, respectively (p=0.065). There were no significant differences of anatomical and functional success rates according to each surgical procedure.
Go to : 
References
1. Boberg-Ans G, Henning V, Villumsen J, la Cour M. Longterm incidence of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment and survival in a defined population undergoing standardized phacoemulsification surgery. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2006; 84:613–8.

2. Russell M, Gaskin B, Russell D, Polkinghorne PJ. Pseudophakic retinal detachment after phacoemulsification cataract surgery: Ten-year retrospective review. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:442–5.
3. Hwang US, Kim JI, Park JM. Clinical evaluation of pseudophakic retinal detachment. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2001; 42:991–6.
4. Koo YM, Lee MS, Yoon IH. Comparison of clinical findings between phakic retinal and pseudophakic retinal detachment. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1998; 39:2995–3002.
5. Devenyi RG, de Carvalho Nakamura H. Combined scleral buckle and pars plana vitrectomy as a primary procedure for pseudophakic retinal detachments. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 1999; 30:615–8.

7. Park CS, Song SJ, Park YH. Surgical results of segmental scleral buckling in pseudophakic retinal detachments. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2004; 45:570–5.
8. Arya AV, Emerson JW, Engelbert M, et al. Surgical management of pseudophakic retinal detachments: a meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 2006; 113:1724–33.
9. Brazitkos PD, Androudi S, Christen WG, Stangos NT. Primary pars plana vitrectomy versus scleral buckle surgery for the treatment of pseudophakic retinal detachment: a randomized clinical trial. Retina. 2005; 25:957–64.
10. Ahmadieh H, Moradian S, Faghihi H, et al. Anatomic and visual outcomes of scleral buckling versus primary vitrectomy in pseudophakic and aphakic retinal detachment: six-month follow-up results of a single operation–report no. 1. Ophthalmology. 2005; 112:1421–9.
11. Weichel ED, Martidis A, Fineman MS, et al. Pars plana vitrectomy versus combined pars plana vitrectomy-scleral buckle for primary repair of pseudophakic retinal detachment. Ophthalmology. 2006; 113:2033–40.

12. Martinez-Castillo V, Zapata MA, Boixadera A, et al. Pars plana vitrectomy, laser retinopexy, and aqueous tamponade for pseudophakic rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. Ophthalmology. 2007; 114:297–302.

13. Martinez-Castillo V, Verdugo A, Boixadera A, et al. Management of inferior breaks in pseudophakic rhegmatogenous retinal detachment with pars plana vitrectomy and air. Arch Ophthalmol. 2005; 123:1078–81.

14. Sharma YR, Karunanithi S, Azad RV, et al. Functional and anatomic outcome of scleral buckling versus primary vitrectomy in pseudophakic retinal detachment. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2005; 83:293–7.

15. Le Rouic JF, Behar-Cohen F, Azan F, et al. Virtectomy without scleral buckle versus ab-externo approach for pseudophakic retinal detachment: comparative retrospective study. J Fr Ophthalmol. 2002; 25:240–5.
16. Retna P, Kivela T. Functional and anatomic outcome of retinal detachment surgery in pseudophakic eyes. Ophthalmology. 2002; 109:1432–40.

17. Halberstadt M, Chatterjee-Sanz N, Brandenberg L, et al. Primary retinal reattachment surgery: anatomical and functional outcome in phakic and pseudophakic eyes. Eye. 2005; 19:891–8.

18. Oshima Y, Yamanishi S, Sawa M, et al. Two-year follow-up study comparing primary vitrectomy with scleral buckling for macula-off rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2000; 44:538–49.

19. Lee MV, Moon CS, Yang HS, et al. Factor influencing anatomical failure of simple rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:407–14.
20. Stangos AN, Petropoulos IK, Brozou CG, et al. Pars plana vitrectomy alone vs vitrectomy with scleral buckling for primary rhegmatogenous pseudophakic retinal detachment. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004; 138:952–8.
Go to : 
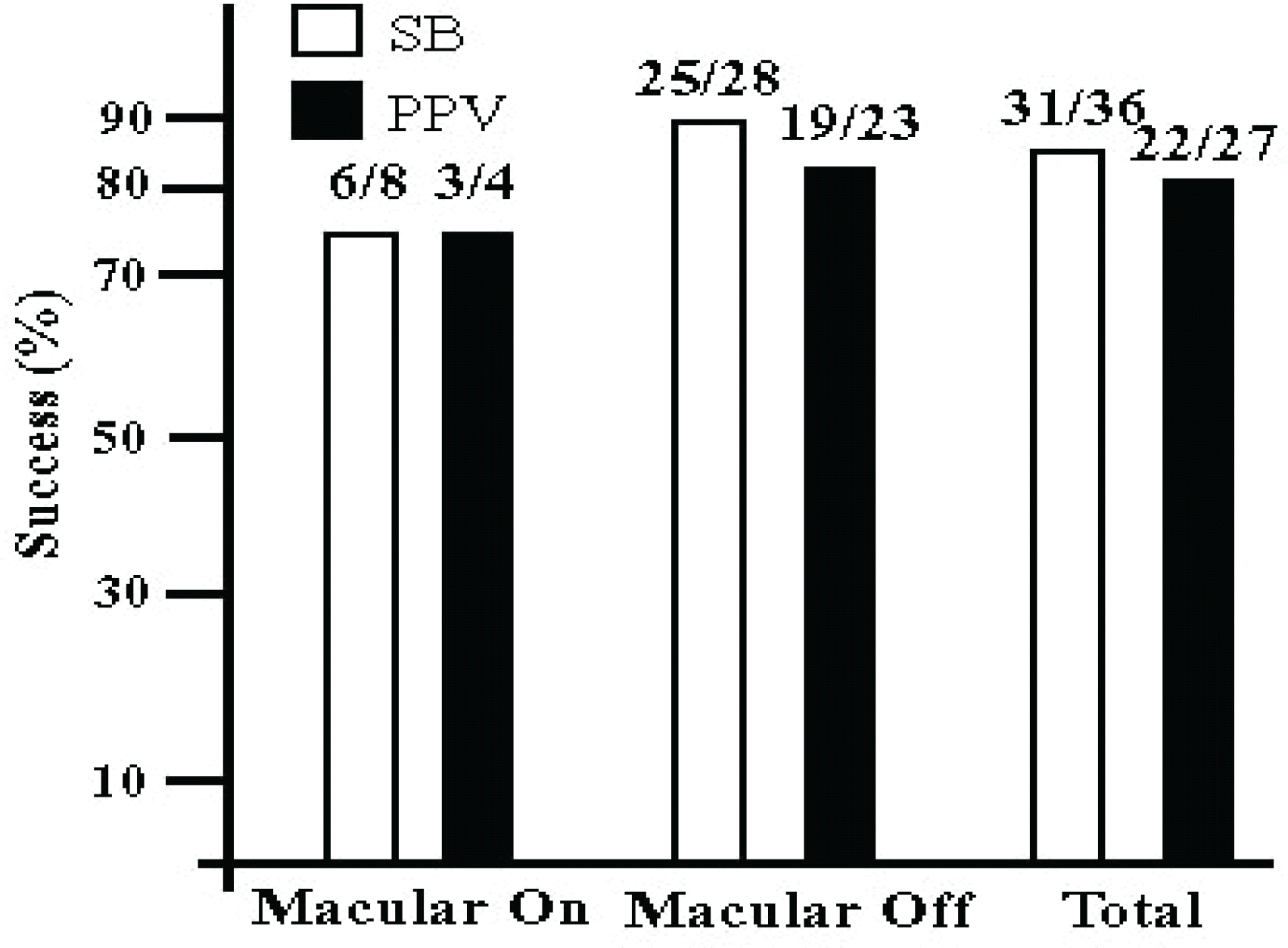 | Figure 1.One-year anatomical outcomes after surgical procedures in uncomplicated pseudophakic retinal detachment with intact posterior capsule.
SB=scleral buckling; PPV=pars plana vitrectomy.
|
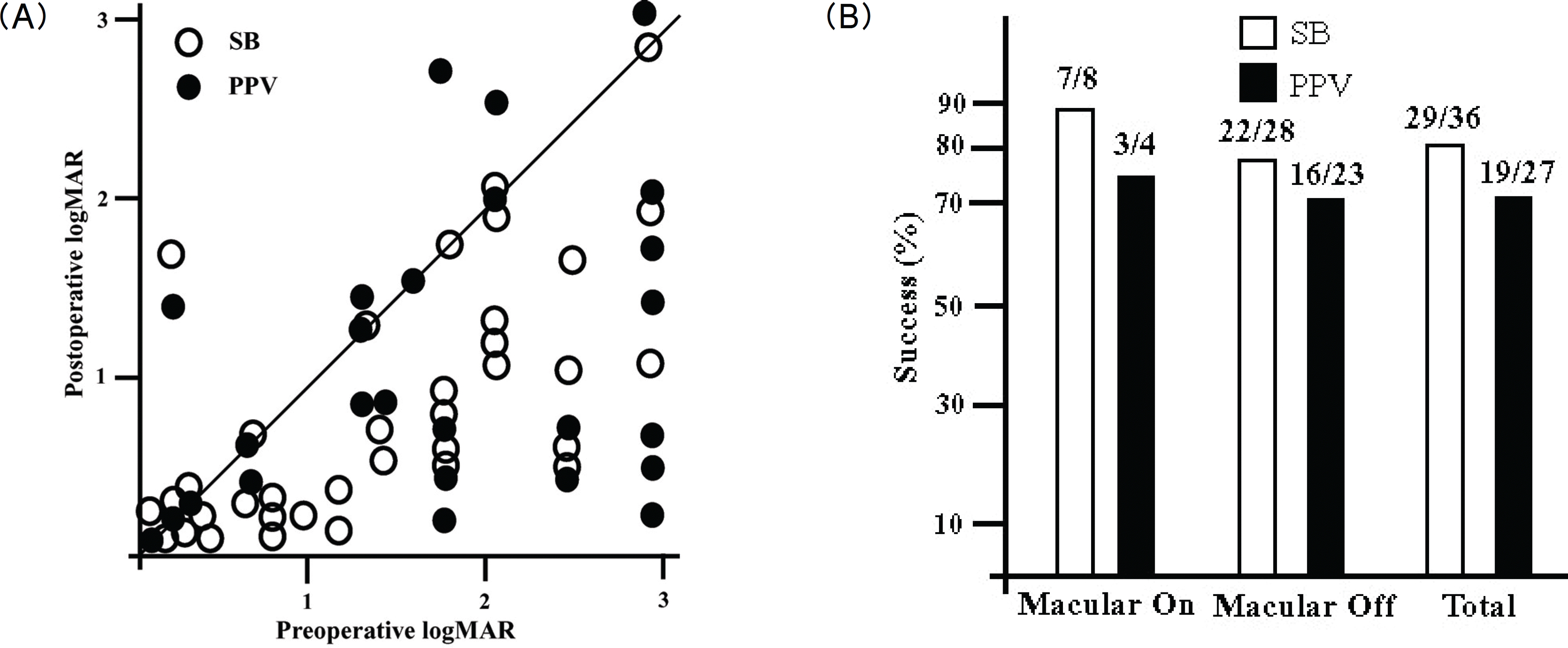 | Figure 2.Visual outcomes after surgical procedures in uncomplicated pseudophakic retinal detachment with intact posterior capsule. (A) Scatterplot of preoperative vs. postoperative one-year visual acuity. (B) Comparison between the two surgical methods SB=scleral buckling; PPV=pars plana vitrectomy. |
Table 1.
Patient Characteristics




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download