Abstract
Purpose
To develop a screening test based on the difference (Diff) between the anterior corneal surface and the anterior best‐ fit sphere in the central region of the Orbscan IIz topography as a way of detecting previous myopic photorefractive surgery.
Methods
From 1623 patients who had no refractive surgery and no corneal disease, 3132 topographies were defined as normal. From 120 patients who had Orbscan IIz topography after myopic photorefractive surgery, 238 topographies were defined as eyes that had undergone refractive surgery. The first objective was to determine the difference (Diff) between the anterior corneal surface and the anterior best‐ fit sphere in the central region. The second objective was to classify the anterior elevation map of Orbscan IIz topography.
Results
The Diff value of the center of the anterior cornea surface averaged 0.008±0.003 mm in normal eyes, and all values were over 0 mm. However, in eyes that had previous refractive surgery, the average was 0.014±0.009 mm, and all values in this group were less than 0. The specificity and sensitivity was 100 % in both groups. The spherical equivalent of the degree of myopic correction and the Diff value of the center of the anterior cornea surface showed a linear relationship. Consequently, we could derive a formula to determine the degree of myopic correction with a known Diff value of the center of the anterior corneal surface.
References
1. Sandoval HP, de Castro LE, Vroman DT, Solomon KD. Refractive Surgery Survey 2004. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:221–33.

2. Solomon KD, Fernandez de Castro LE, Sandoval HP, et al. Refractive surgery survey 2003. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:1556–69.

3. Solomon KD, Holzer MP, Sandoval HP, et al. Refractive Surgery Survey 2001. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:346–55.

4. Pepose JS, Lim‐ Bon‐ Siong R, Mardelli P. Future shock: the long‐ term consequences of refractive surgery. Br J Ophthalmol. 1997; 81:428–9.

5. Hamilton DR, Hardten DR. Cataract surgery in patients with prior refractive surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2003; 14:44–53.

6. Mifflin M, Kim M. Penetrating keratoplasty using tissue from a donor with previous LASIK surgery. Cornea. 2002; 21:537–8.

7. Mootha VV, Dawson D, Kumar A, et al. Slitlamp, specular, and light microscopic findings of human donor corneas after laser‐ assisted in situ keratomileusis. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004; 122:686–92.
8. Laliberte JF, Meunier J, Hick S, Brunette I. Topography-based screening for previous laser in situ keratomileusis to correct myopia and hyperopia. Cornea. 2005; 24:167–77.

9. Vavra DE, Enzenauer RW. Predictive value of slitlamp examinations in screening donor corneas for prior refractive surgery. Arch Ophthalmol. 2005; 123:707–8.

10. Jeong SY, Chin HS, Oh JH. Anterior elevation maps as the screening test for the ablation power of previous myopic refractive surgery. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2006; 20:13–7.

11. Destrempes F, Brunette I, Meunier J, et al. Topography‐ based screening for previous laser in situ keratomileusis to correct myopia. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:1644–50.
Figure 2.
‘Diff’ value in the anterior corneal center of a normal and the correction of myopia.(A) ‘Diff ’ value in the anterior corneal center in a normal.(B) ‘Diff ’ value in the anterior corneal center in a correction of myopia.(C) Percent distribution of ‘Diff ’ value in the anterior corneal center in a normal and correction of myopia.
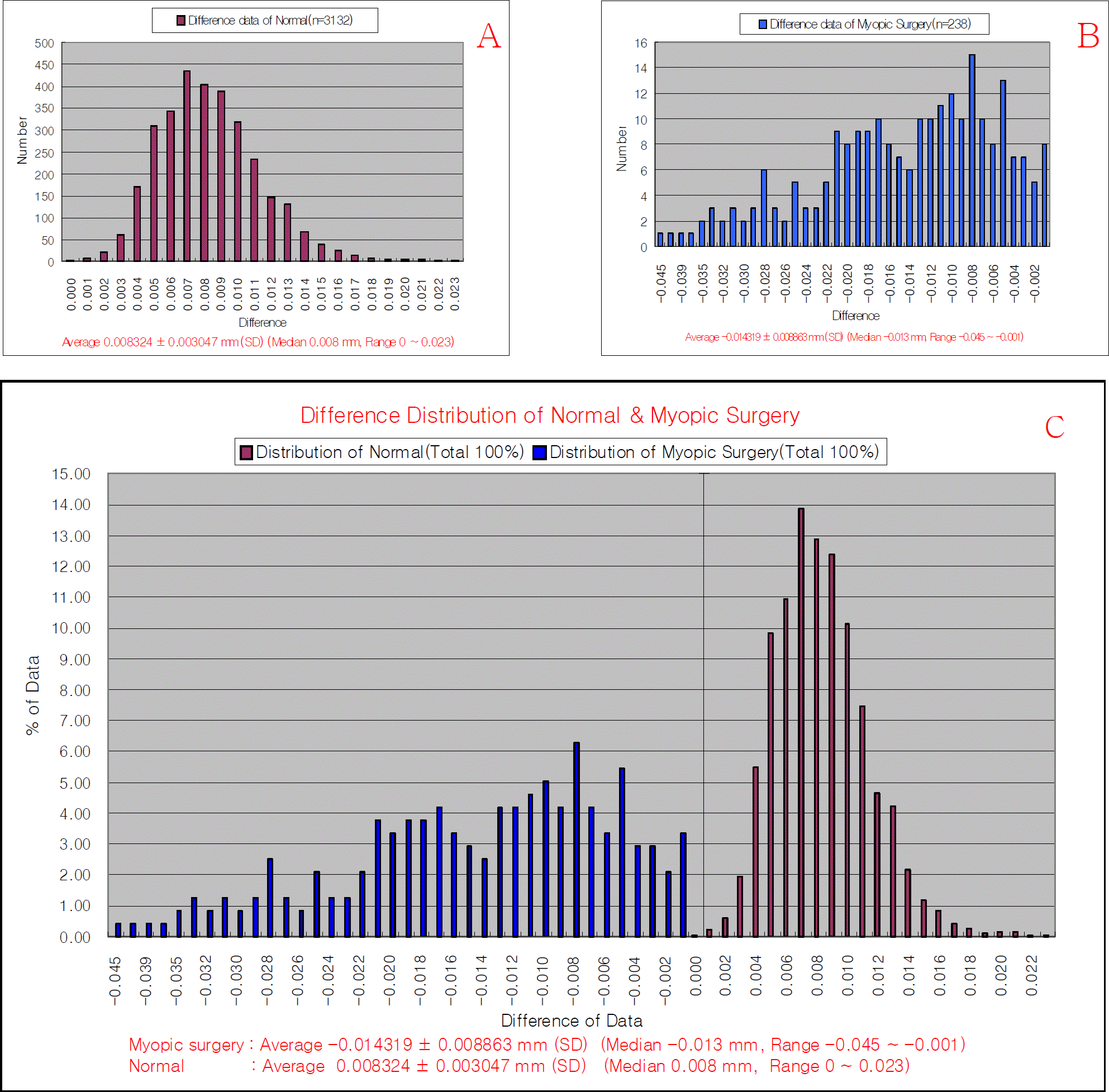
Figure 3.
Plot diagram of the point for the correlation of ablation power for myopic correction and ‘Diff’ value in the anterior corneal center. (A) Post-operative ‘Diff ’ value in the anterior corneal center and amount (spherical) of myopic correction (r=0.8667, p<0.001). (B) Post-operative ‘Diff’ value in the anterior corneal center and amount (spherical equivalent) of myopic correction (r=0.8732, p<0.001).
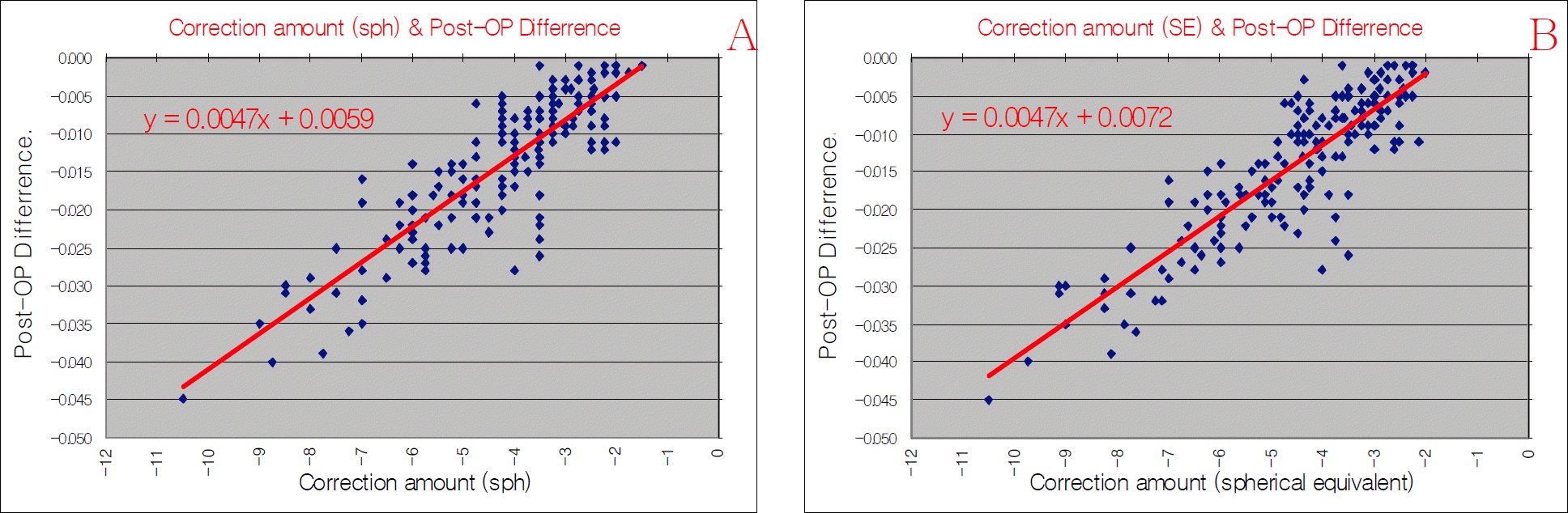
Table 1.
Population characteristics and surgical parameters
| Classification |
Normal (N=3132) |
Classification |
Myopic correction (N=238) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean±SD* | Median, Range | Mean±SD* | Median, Range | ||
| Best Correction Spherical equivalent (D†) | 0.53±3.76 | 0.50, | Myopic correction Spherical equivalent (D†) | -4.61±1.76 | -4.25, |
| -12.75 ∼ 8.50 | -2.00 ∼ -10.50 | ||||
| Best Correction spherical (D†) | 0.07±2.17 | 0.00, | Myopic correction spherical (D†) | )-4.30±1.74 | -4.00, |
| -12.00 ∼ 8.25 | -1.50 ∼ -9.00 | ||||
| Best Correction Cylinder (D†) | 0.71±1.12 | 0.75 | Myopic correction Cylinder (D†) | -0.60±0.66 | -0.50, |
| 0 ∼ 7.25 | 0 ∼ -3.00 | ||||
| Center Pachymetry | 535.12±35.27 | 537, | Center Pachymetry (Pre-OP) | 532.98±28.06 | 537, |
| 412 ∼ 723 | 461 ∼ 582 | ||||




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download