Abstract
Purpose
To assess the prevalence of A-V pattern strabismus and evaluate the clinical characteristics, surgical methods and outcomes.
Methods
Among 825 patients who underwent horizontal strabismus surgery, the records of patients with A-V pattern strabismus were reviewed retrospectively. The prevalence and clinical characteristics of patients with A-V pattern strabismus were assessed and the surgical methods and outcomes of A-V pattern strabismus were evaluated.
Results
Among 825 patients with horizontal strabismus surgery, 113 (13.7%) patients had A-V pattern. V exotropia was the most common (65.5%) and A esotropia was the least common (7.1%) pattern. A +1.9 inferior oblique overaction in 92.8% of the V-pattern patients and a +1.5 superior oblique overaction in 70.0% of the A pattern patients was found. Among the 113 patients, 64.6% patients underwent oblique muscle surgery and 35.4% patients underwent vertical transposition of horizontal muscle. Vertical incomitance was significantly reduced after surgery in all types of A-V pattern strabismus ( p<0.05) with a surgical success rate of 96.5%.
Go to : 
References
1. Albert DG. Personal communication In Parks MM Annual review Strabismus. Arch Ophthalmol. 1957; 58:152.
2. Von Noorden GK. Binocular Vision and Ocular Motility. 6th. St. Louis: Mosby;2002. p. 396–413.
3. Breinin GM. The physiopathology of the "A" and "V" patterns. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1964; 68:363–74.
4. Knapp P. Vertically incomitant horizontal strabismus: The so-called A and V syndromes. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1959; 57:666–99.
5. Kim SJ, Bae EH, Oh JS. A clinical study on A and V patterns. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1987; 28:1329–38.
6. Woo KI, Chang BL. Treatment of AV Syndrome. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1993; 34:331–6.
7. Chew E, Remaley NA, Tamboli A. . Risk factors for esotropia and exotropia. Arch Ophthalmol. 1994; 112:1349–55.

8. Rah SH, Jun HS, Kim SH. An epidemiologic survey of strabismus among school-children in Korea. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1997; 38:2195–9.
9. Del Monte MA, Parks MM. Denervation and extirpation of the inferior oblique. An improve weakening procedure for marked overaction. Ophthalmology. 1983; 90:1178–85.
11. Costenbader FD. Symposium: The A and V pattern in strabismus. Introduction. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1964; 68:354–5.
12. Breinin G. Symposium: The A and V pattern in strabismus. The physiopathology of the A and V patterns. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1964; 68:363–74.
13. Von Noorden GK, Oslon CL. Diagnosis and surgical management of vertically incomitant horizontal strabismus. Am J Ophthalmol. 1965; 60:434–42.

14. Kushner BJ. The role of ocular torsion on the etiology of A and V patterns. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1985; 22:171–9.

15. Goldstein JH. Monocular vertical displacement of the horizontal rectus muscles in the A and V patterns. Am J Ophthalmol. 1967; 64:265–7.

16. Chang HR, Kim JM. Effect of vertical displacement of bilateral horizontal muscles in AV syndrome. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2000; 41:506–10.
17. Chang BL, Han YB, Kim SY. Inferior oblique muscle recession. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1982; 23:91–4.
18. Knapp P. A and V patterns. In : symposium on strabismus. Transaction of the New Orleans Academy of Ophthalmology, St. Louis: CV Mosby-Year Book;1971. p. 242–54.
19. Caldeira JA. Bilateral recession of the superior oblique graded according to the A pattern: A prospective study of 21 consecutive patients. Binocul Vis Eye Muscle Surg Q. 1995; 10:167–74.
20. Scott WE, Jampolsky AJ, Redmond MR. Superior oblique tenotomy: indications and complications. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 1976; 16:151–9.

21. Prieto-Diaz J. Management of superior oblique overaction in A-pattern deviations. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1988; 226:126–31.

22. Shin GS, Elliott RL, Rosenbaum AL. Posterior superior oblique tenectomy at the scleral insertion for collapse of A-pattern strabismus. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1996; 33:221–8.

23. Wright KW. Superior oblique silicone expander for Brown’s syndrome and superior oblique overaction. J Pediatr Ophthal- mol Strabismus. 1991; 28:101–7.

24. Choi HY, Roh YB. Posterior tenotomy and tenectomy of superior oblique muscle in "A"pattern strabismus. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1996; 37:1073–9.
Go to : 
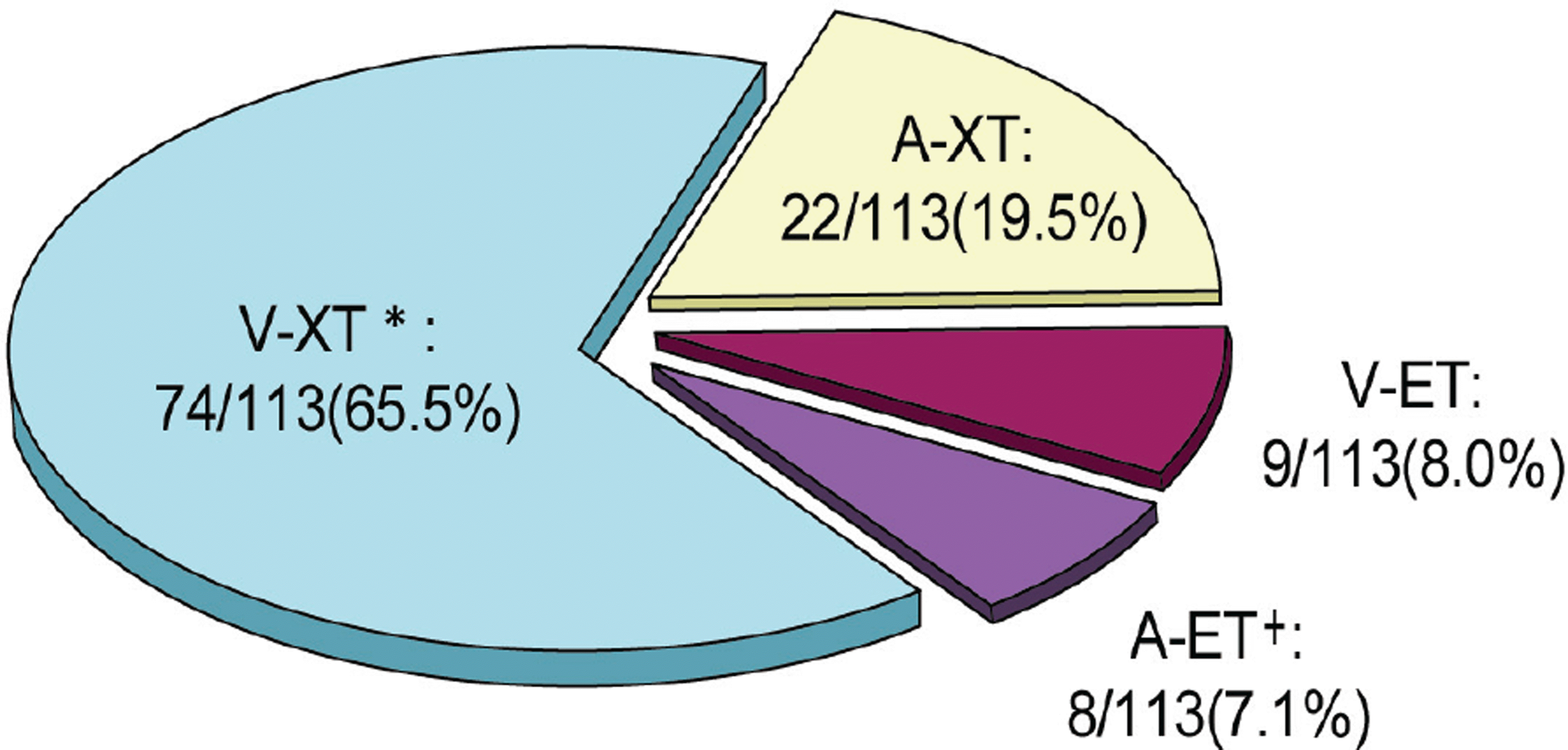 | Figure 1.Distribution of A-V pattern strabismus among 113 patients; * XT=exotropia; † ET=esotropia. |
Table 1.
Distribution of A-V pattern strabismus in different reports in Korea
Table 2.
Relative frequency of A and V pattern strabismus among 113 patients
| V pattern (%) | A pattern (%) | Total (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exotropia | 74 (65.5) | 22 (19.5) | 96 (85.0) |
| Esotropia | 9 (8.0) | 8 (7.1) | 17 (15.1) |
| Total | 83 (73.5) | 30 (26.5) | 113 (100) |
Table 3.
Characteristics of patients with A-V pattern strabismus
| V-exotropia | A-exotropia | V-esotropia | A-esotropia | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | ) | 15.4±11.2 | 17.4±14.0 | 19.2±19.1 | 19.0±17.1 |
| Sex (M/F∗) | 33/41 | 7/13 | 4/5 | 6/2 | |
| BCVA† | OD‡ | 0.9±0.2 | 0.9±0.3 | 0.8±0.2 | 0.7±0.2 |
| OS | 0.9±0.2 | 1.0±0.1 | 0.7±0.4 | 0.9±0.1 | |
| R.E§ | OD | -0.7±1.8 | -0.3±1.7 | 0.2±2.8 | -0.5±2.0 |
| OS | -0.8±2.2 | -0.3±1.3 | 0.7±3.0 | -0.4±1.7 | |
| Amblyopia | 7/64 (10.9%) | 4/13 (30.8%) | 3/9 (33.3%) | 2/8 (25.0%) | |
| Titmus∏ | 364.7±845.7 | 869.5±1193.5 | 548.9±948.9 | 1166.7±1594.8 | |
| AHP# | 19/64 (29.7%) | 6/13 (46.1%) | 2/9 (22.2%) | 2/8 (25.0%) |
Table 4.
Preoperative and postoperative measurements in A-V pattern strabismus
Table 5.
Frequency and grade of oblique muscle dysfunction in A-V pattern strabismus
| Oblique muscle dysfunction (%) | Grade of oblique muscle dysfunction | |
|---|---|---|
| V-exotropia | 68/74 (91.8) | +2.0±1.2 (IOOA∗) |
| A-exotropia | 17/22 (77.3) | +1.9±1.5 (SOOA†) |
| V-esotropia | 9/9 (100.0) | +1.7±1.0 (IOOA) |
| A-esotropia | 4/8 (50.0) | +1.0±1.1 (SOOA) |
Table 6.
Surgical methods for A-V pattern strabismus
Table 7.
Collapse of pattern after surgery for A-V pattern strabismus
Table 8.
Amount of decrease in A or V pattern after surgery
| Amount of decrease in A or V pattern | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Oblique muscle surgery | Vertical transposition of horizontal rectus muscle | P-value† | |
| V-exotropia | 17.5±6.6∗ | 17.0±4.8 | 0.128 |
| A-exotropia | 12.9±7.1 | 11.8±3.4 | 0.400 |
| V-esotropia | 16.9±5.9 | 15.8±3.9 | 0.815 |
| A-esotropia | 12.0±0.1 | 12.7±6.1 | 0.889 |
| Total | 14.8±7.0 | 14.3±4.5 | 0.558 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download