Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the changes of aqueous vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and interleukin (IL)-6 in patients with acute macular edema secondary to recent-onset branch retinal vein occlusion (BRVO) after a single intravitreal injection of triamcinolone acetonide (IVTA)
Methods
Aqueous and plasma levels of VEGF and IL-6 were measured by ELISA in ten controls and thirty patients at the time of IVTA and 3 months afterward. We compared the aqueous levels of VEGF and IL-6 and the clinical course between responders and non-responders.
Results
The aqueous levels of VEGF and IL-6 were significantly higher in non-responders than in responders at baseline measurements (495±259 pg/ml vs. 223±110 pg/ml, P<.001; 36±32 pg/ml vs. 16±19 pg/ml, P=.037, respectively). The aqueous levels of VEGF were still higher in non-responders (303±75 pg/ml) 3 months after IVTA, while the aqueous levels of VEGF in responders returned to normal (77±23 pg/ml, P<.001). The aqueous levels of IL-6 normalized in all patients 3 months after IVTA. In non-responders, central foveal thickness was significantly higher, and foveal ischemia and a wide non-perfused area were more common.
Go to : 
References
1. Aiello LP, Avery RL, Arrigg PG, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor in ocular fluid of patients of diabetic retinopathy and other retinal disorders. N Engl J Med. 1994; 331:1480–7.
2. Cohen T, Nahari D, Cerem LW, et al. Interleukin-6 induces the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1996; 271:736–41.
3. Maruo N, Morita I, Shirao M, Murota S. IL-6 increases endothelial permeability in vitro. Endocrinology. 1992; 131:710–4.

4. Noma H, Funatsu H, Yamasaki M, et al. Pathogenesis of macular edema with branch retinal vein occlusion and intraocular levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and interleukin-6. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005; 140:256–61.

5. Cekic O, Chang S, Tseng JJ, et al. Intravitreal triamcinolone injection for treatment of macular edema secondary to branch retinal vein occlusion. Retina. 2005; 25:851–5.

6. Lee H, Shah GK. Intravitreal triamcinolone as primary treatment of cystoid macular edema secondary to branch retinal vein occlusion. Retina. 2005; 25:551–5.

7. Karacorlu M, Ozdemir H, Karacorlu SA. Resolution of serous macular detachment after intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide treatment of patients with branch retinal vein occlusion. Retina. 2005; 25:856–60.

8. Jonas JB, Akkoyun I, Kamppeter B, et al. Branch retinal vein occlusion treated by intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide. Eye. 2005; 19:65–71.

9. Krepler K, Ergun E, Sacu S, et al. Intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide in patients with macular oedema due to branch retinal vein occlusion: a pilot study. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2005; 83:600–4.

10. Chen SD, Sundaram V, Lochihead J, Patel CK. Intravitreal triamcinolone for the treatment of ischemic macular edema associated with branch retinal vein occlusion. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006; 141:876–83.

11. Jonas JB, Kreissig I, Degenring RF. Intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide for treatment of intraocular proliferative, exudative, and neovascular diseases. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2005; 24:587–611.

12. Thompson JT. Cataract formation and other complications of intravitreal triamcinolone for macular edema. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006; 141:629–37.

13. Chin HS, Kim TH, Moon YS, Oh JH. A convenient method to concentrate triamcinolone acetonide for intravitreal injection. Retina. 2005; 25:1107–8.

14. Aiello LP, Northrup JM, Keyt BA, et al. Hypoxic regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in retinal cells. Arch Ophthalmol. 1995; 113:1538–44.

15. Ali MH, Schlidt SA, Chandel NS, et al. Endothelial permeability and IL-6 production during hypoxia: role of ROS in signal transduction. Am J Physiol. 1999; 277:1057–65.
16. Pai SA, Shetty R, Vijayan PB, et al. Clinical, anatomic, and electrophysiologic evaluation following intravitreal bevacizumab for macular edema in retinal vein occlusion. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007; 143:601–6.

Go to : 
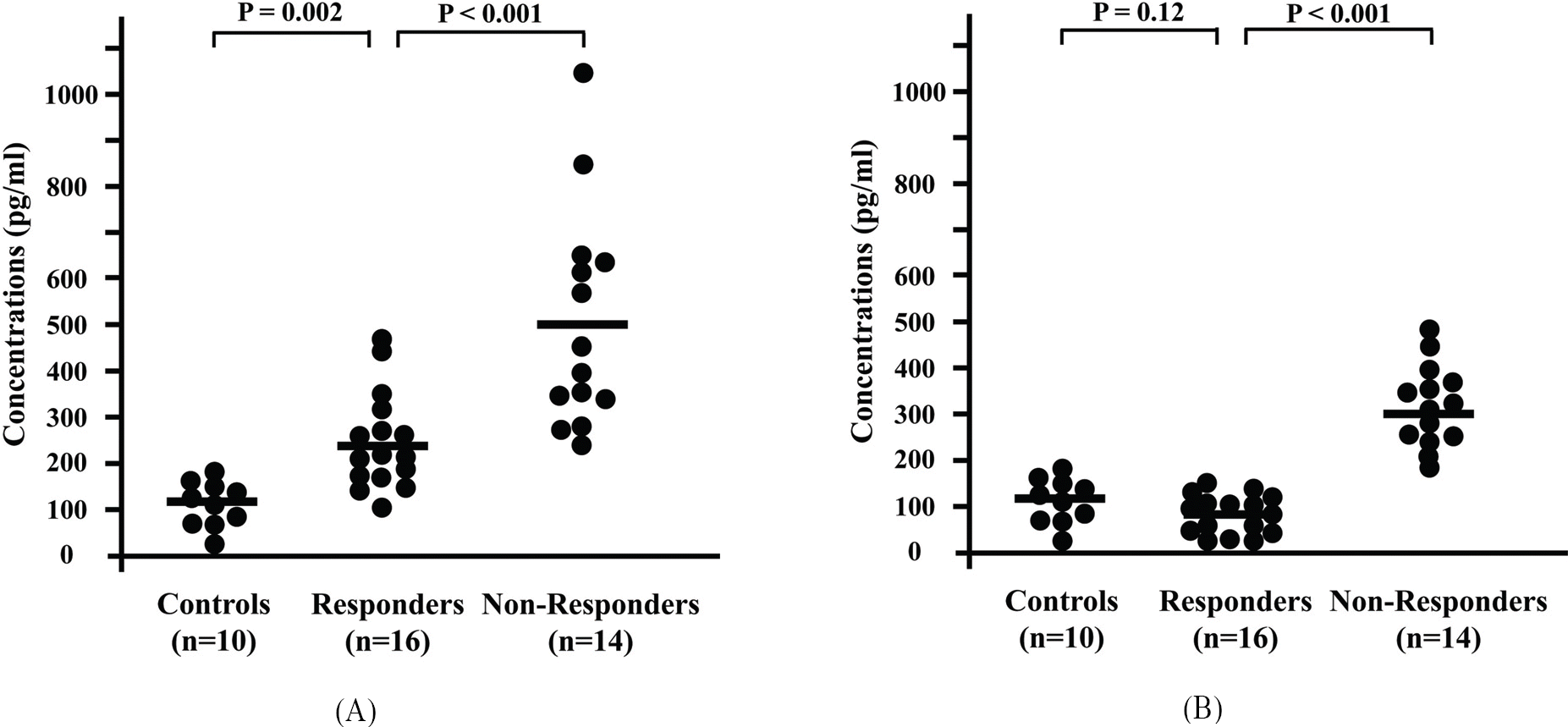 | Figure 1.Aqueous levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) at the time of intravitreal injection of triamcinolone acetonide (A) and 3 months later (B). The horizontal bars indicate the mean values at each measurement. |
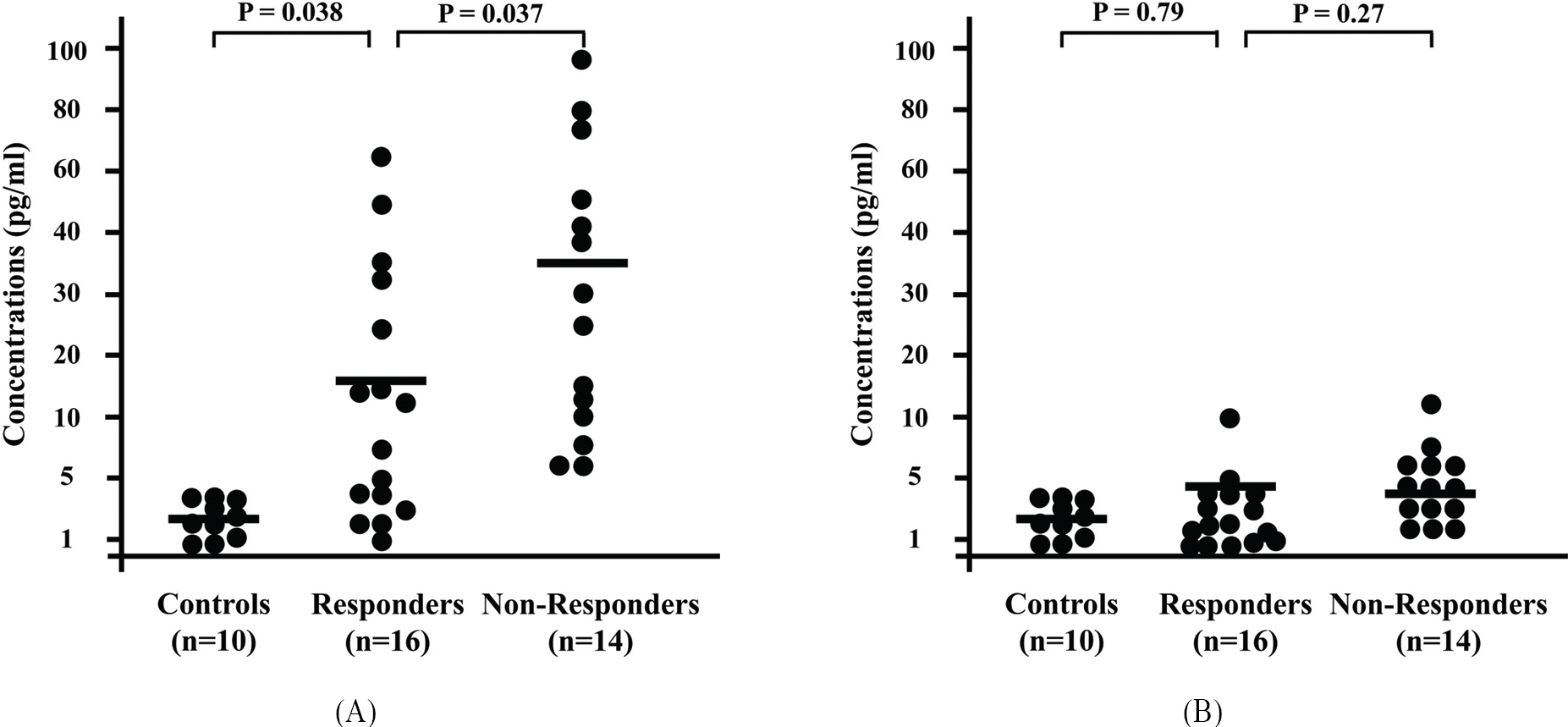 | Figure 2.Aqueous levels of interleukin-6 at the time of intravitreal injection of triamcinolone acetonide (A) and 3 months later (B). The horizontal bars indicate the mean values at each measurement. |
Table 1.
Demographic characteristics of patients with branch retinal vein occlusion (BRVO) and control subjects
| Variables | Patients w | ith BRVO | Healthy controls |
|---|---|---|---|
| Responders (n=16) | Non-responders* (n=14) | (n=10) | |
| Age, yrs (mean±SD) | 57.2±7.9 | 58.7±7.4 | 62.6±9.5 |
| Gender (male:female) | 14:4 | 7:5 | 4:6 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 14 (78) | 8 (75) | 6 (60) |
Table 2.
Clinical outcomes of patients with branch retinal vein occlusion after single intravitreal injection of triamcinolone acetonide (IVTA) according to the therapeutic response
Table 3.
Aqueous and plasma levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and interleukin (IL)-6 in p retinal vein occlusion after single intravitreal injection of triamcinolone acetonide (IVTA) patients with branch




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download