Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the accuracy of biometry and intraocular lens (IOL) power calculation using partial coherence interferometry (IOL Master®) in highly myopic patients with axial lengths of 26 mm or greater.
Methods
Patients with axial lengths equal to or greater than 26 mm who had undergone cataract surgery were enrolled. IOL power was calculated using IOL Master and/or applanation ultrasonography with the SRK/T formula. Twenty-seven eyes using both IOL Master and applanation ultrasonography were included in a paired group, and forty-eight eyes using the IOL Master only and twenty-five eyes using applanation ultrasonography only were included in unpaired groups. The differences between the predicted refraction and the actual refraction were compared and analyzed.
Results
In the paired study, the axial lengths in patients using IOL Master (29.14±2.32 mm) were significantly longer than those of patients using applanation ultrasonography (28.57±2.23 mm) ( p<0.05). The mean absolute error (MAE) of the IOL Master and applanation ultrasonography groups were 0.62±0.58D and 0.87±0.49D, respectively ( p>0.05). In the unpaired study, the MAEs of the IOL Master and applanation ultrasonography groups were 0.61±0.61D and 0.65±0.63D, respectively.
Go to : 
References
1. Olsen T. Sources of error in intraocular lens power calculation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1992; 18:125–9.

2. Connors R 3rd, Boseman P 3rd, Olson RJ. Accuracy and reproducibility of biometry using partial coherence interfero metry. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:235–8.
3. Drexler W, Findl O, Menapace R, et al. Partial coherence interferometry: a novel approach to biometry in cataract surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 1998; 126:524–34.

4. Rajan MS, Keilhorn I, Bell JA. Partial coherence laser interferometry vs conventional ultrasound biometry in intraocular lens power calculations. Eye. 2002; 16:552–6.

5. Findl O, Drexler W, Menapace R, et al. Improved prediction of intraocular lens power using partial coherence interferometry. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001; 27:861–7.

6. Rose LT, Moshegov CN. Comparison of the Zeiss IOLMaster and applanation A-scan ultrasound: biometry for intraocular lens calculation. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2003; 31:121–4.

7. Zaldivar R, Shultz MC, Davidorf JM, Holladay JT. Intraocular lens power calculations in patients with extreme myopia. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000; 26:668–74.

8. MacLaren RE, Sagoo MS, Restori M, Allan BD. Biometry accuracy using zero- and negative-powered intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:280–90.

9. Tsang CS, Chong GS, Yiu EP, Ho CK. Intraocular lens power calculation formulas in Chinese eyes with high axial myopia. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:1358–64.

10. Sanders DR, Retzlaff JA, Kraff MC, et al. Comparison of the SRK/T formula and other theoretical and regression formulas. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1990; 16:341–6.

11. Vogel A, Dick HB, Krummenauer F. Reproducibility of optical biometry using partial coherence interferometry : intraobserver and interobserver reliability. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001; 27:1961–8.
12. Choi JH, Roh KH. The Reproducibility and Accuracy of Biometry Parameter Measurement from IOL Master. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2004; 45:1665–73.
13. Haigis W, Lege B, Miller N, Schneider B. Comparison of immersion ultrasound biometry and partial coherence interferometry for intraocular lens calculation according to Haigis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2000; 238:765–73.

14. Eleftheriadis H. IOL Master biometry: refractive results of 100 consecutive cases. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003; 87:960–3.
15. Song BY, Yang KJ, Yoon KC. Accuracy of Partial Coherence Interferometry in Intraocular Lens Power Calculation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:775–80.
16. Chung JK, Choe CM, You YS, Lee SJ. Biometry with Partial Coherence Interferometry and Ultrasonography in High Myopes. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:355–61.
17. Tehrani M, Krummenauer F, Kumar R, Dick HB. Comparison of biometric measurements using partial coherence interfero metry and applanation ultrasound. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:747–52.
18. Lee JT, Song JS, Kim HM. The Accuracy of Axial Length Measurement Using Partial Coherence Interferometry. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:812–7.
Go to : 
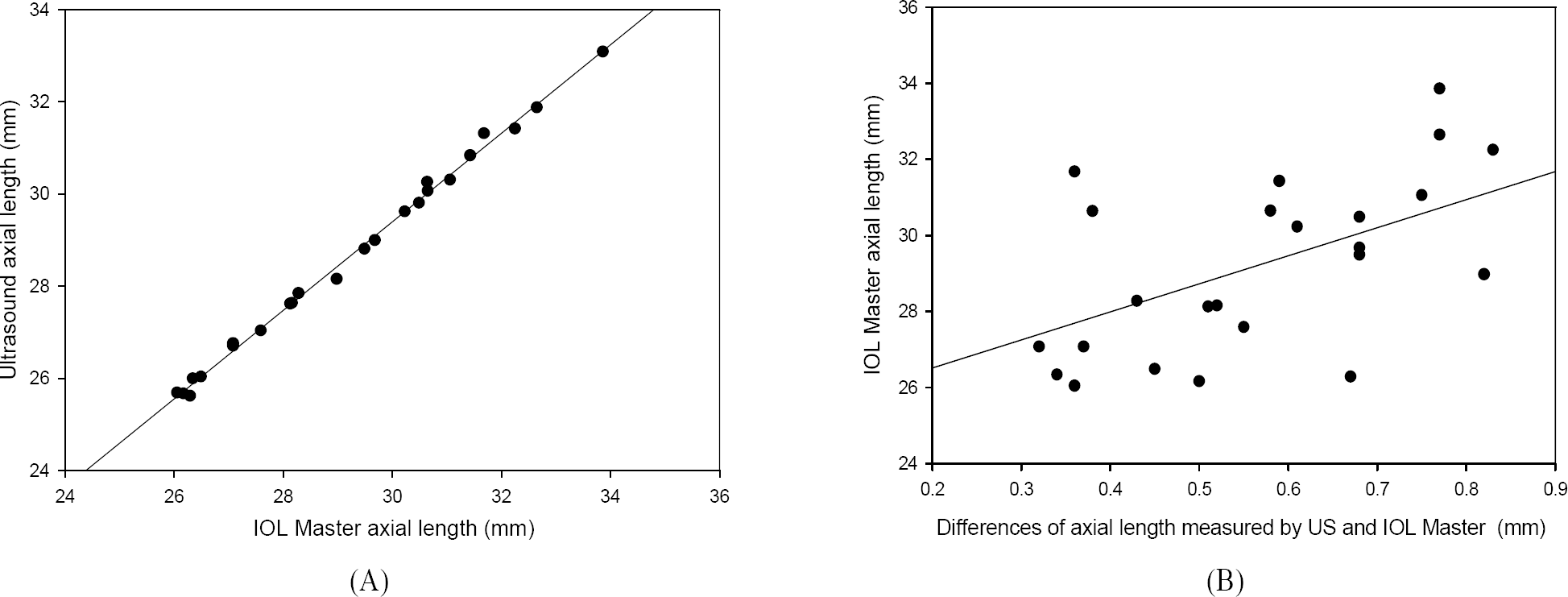 | Figure 1.(A) Correlation between axial lengths measured by the IOL Master and ultrasound with correlation coefficient of 0.99, P<0.001. (B) Correlation between the axial length and differences of axial length measured by the two methods with correlation coefficient of 0.60, P<0.05. |
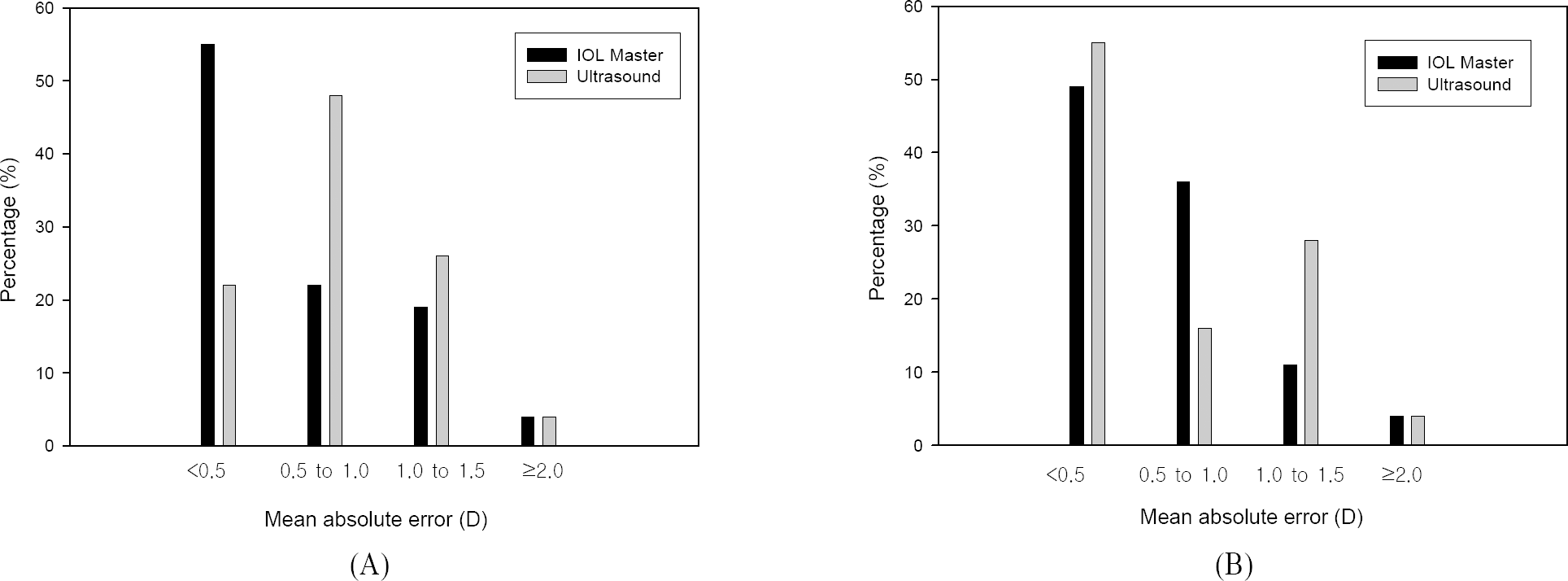 | Figure 2.(A) Mean absolute error in paired group. (B) Mean absolute error in unpaired group. |
Table 1.
Patient characteristics
| Parameters | Paired group | Unpaired group | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paired group | IOL Master | Ultrasound | |
| No. of eyes (patients) | 27 (19) | 47 (38) | 25 (20) |
| Sex (Male/Female) | 5/14 | 19/19 | 10/10 |
| Mean age | 57.00±10.80 | 54.87±12.03 | 54.82±10.32 |
| Preoperative SE* (D) | -13.08±5.83 | -10.76±5.06 | -8.76±4.83 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download