Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the accuracy of measuring ultrasonic axial lengths using A-scan (Ocuscan®, Alcon, USA) on opaque intraocular lenses after hydrophilic lens (ACRL-160®, Ophthalmed, USA) implantation.
Methods
We measured axial length through ultrasonic biometry prior to intraocular lens exchange. Twelve eyes of 14 patients who had intraocular lens opacity following hydrophilic acryl lens implantation were examined in a clinical study. We compared pre-cataract operative axial lengths to pre-IOL exchange axial lengths. The pre-IOL exchange axial lengths were measured in aphakic and pseudophakic modes. In the pseudophakic mode, the ultrasound velocity through an IOL was set at a rate ranging between 1,500 m/sec to 2,200 m/sec.
Results
The pre-IOL exchange axial lengths in the pseudophakic mode at the rate of 1,600 m/sec in lens velocity were the closest to pre-cataract operative values ( p=0.88).
Conclusions
When pre-cataract operative axial length is known with a hydrophilic acrylic intraocular lens, previous values may be used for IOL exchange of an opacity patient. If not, however, the closest values to pre-cataract operative axial lengths may be obtained by setting the velocity in the pseudophakic mode to a lens velocity rate of 1,600 m/sec.
Go to : 
References
1. Kohnen T. The variety of foldable intraocular lens material. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1996; 22:1255–8.
2. Ursell PG, Spalton DJ, Pande MV. . Relationship between intraocular lens biomaterials and posterior capsular opacification. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1998; 24:352–60.
3. Saika S, Miyamoto T, Ohnishi Y. Histology of anterior capsule opacification with a poly HEMA/HOHEXMA hydrophilic hydrogel intraocular lens compared to poly(methyl methacrylate), silicone, and acrylic lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:1198–203.
4. Chang BY, Davey KG, Gupta M. . Late clouding of an acrylic intraocular lens following routine phacoemulsification. Eye. 1999; 13:807–8.

5. Werner L, Apple DJ, Kaskaloglu M, Pandey SK. Dense opacification of the optical component of a hydrophilic acrylic intraocular lens: a clinicopathological analysis of 9 explanted lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001; 27:1485–92.
6. Frohn A, Dick HB, Augustin AJ, Grus FH. Late opacification of the folderble hydrophilic acrylic lens SC60B-OUV. Ophthalmology. 2001; 108:1999–2004.
7. Werner L, Apple DJ, Escobar-Gomez M. . Postoperative deposition of calcium on the surfaces of a hydrogel intraocular lens. Ophthalmology. 2000; 107:2179–85.
8. Lee DH, Seo Y, Joo CK. Progressive opacification of hydrophilic acrylic intraocular lenses in diabetic patients. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:1271–5.

9. Holladay JT, Prager TC. Accurate Ultrasonic Biometry in Pseudophakia. Am J Ophthalmol. 1993; 115:536–7.

10. Lee SB, Choi SH. Ultrasonic Determination of Axial Length in Pseudophakia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2000; 41:1164–9.
11. Lee JH, Choi SH, Kim CS. The Difference in Post-operative Refractive Error between In-the-bag and Sulcus Intraocular Lens Implantation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002; 43:2144–50.
12. Hoffer KJ. Ultrasound velocities for axial eye length measurement. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1994; 20:554–62.
13. Kim HG, Lee SH, Choi YJ. Late Postoperative Opacification of the Foldable Hydrophilic Acrylic Intraocular Lens, ACRL-160. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:315–20.
14. Lee JY, Joo KM, Kim SH. Late Opacification of Hydrophilic Acrylic Intraocular Lenses. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002; 43:2419–29.
Go to : 
 | Figure 2. (A) Ultrasonic analyzer 5601A (Panametric, USA) measures for the measurement of ultrasonic velocity in hydrophilic acrylic lens (ACRL-C160®, Ophthalmed, USA). (B) Result of the measurement: Ultrasonic velocity shows 2008 m/sec. |
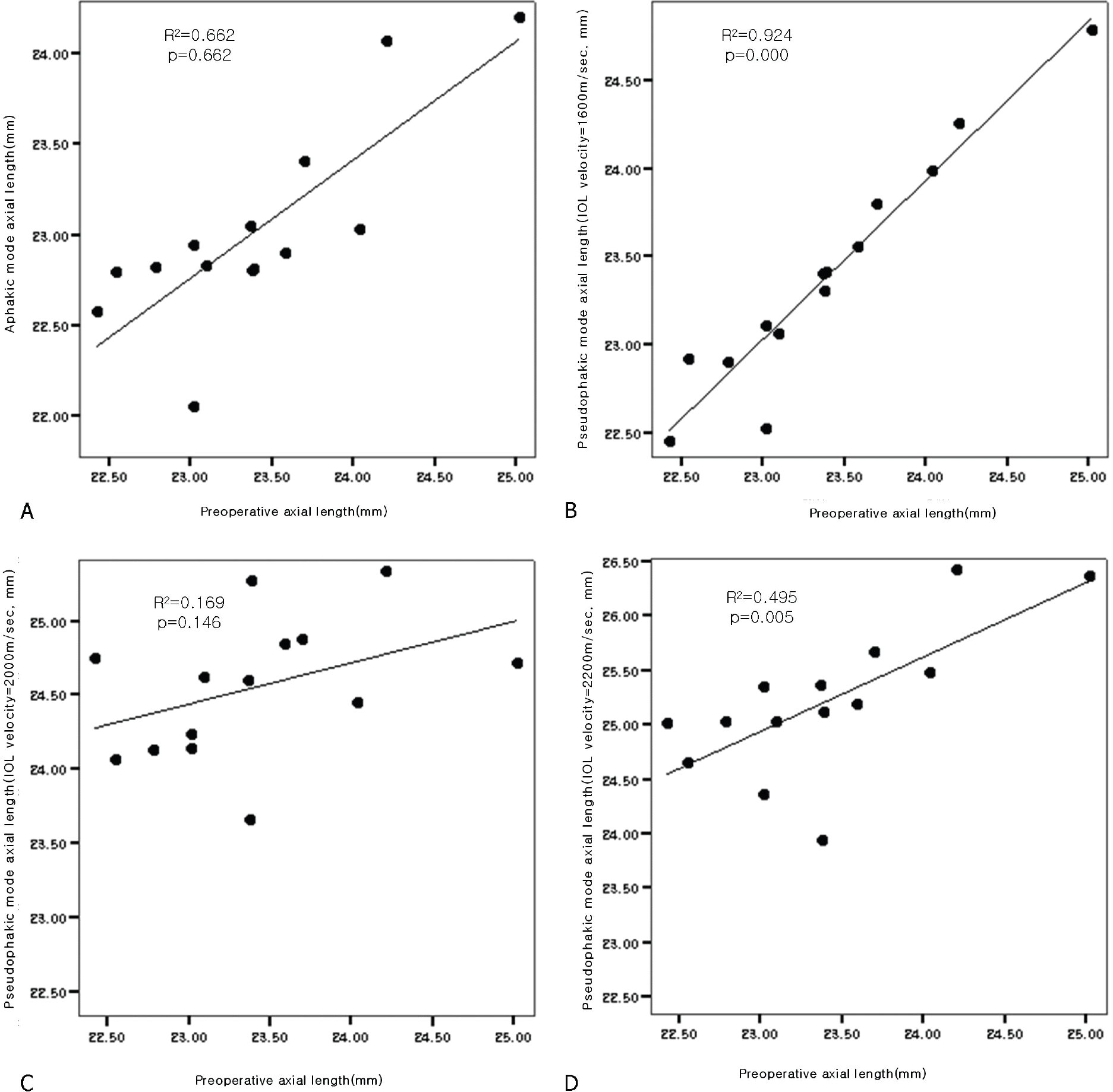 | Figure 3.The result of axial length measurement at pre-cataract operation and pre-IOL exchange (aphakic/pseudophakic mode). (A)=aphakic mode; (B)=pseudophakic mode (lens velocity, 1,600 m/sec); (C)=pseudophakic mode (lens velocity, 2,000 m/sec); (D)=pseudophakic mode (lens velocity, 2,200 m/sec). |
Table 1.
Visual acuity at presentation of pre- and post-IOL exchange
| Visual acuity∗ | pre-IOL exchange | post-IOL exchange | p-value† | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visual acuity∗ | No. of eyes〔 n (%)〕 | No. of eyes〔 n (%)〕 | p-value | |
| <0.1 | 2 (14.3) | 1 (7.1) | ||
| 0.1-0.2 | 11 (78.6) | 1 (7.1) | ||
| 0.3-0.4 | 1 (7.1) | 1 (7.1) | ||
| 0.5-0.6 | 3 (21.4) | |||
| 0.7-0.8 | 6 (42.9) | |||
| >0.8 | 2 (14.3) | |||
| Average | (LogMAR) | 0.75±0.15 | 0.33±0.32 | 0.01 |
Table 2.
The results of measurement of axial length in opaque IOL (Mean±SD)
| Axial length (mm) | p-value∗ | |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Cataract op. | 23.40±0.69 | |
| IOL opacity | ||
| Aphakic mode | 23.01±0.56 | 0.01 |
| Pseudophakic mode | ||
| 1,500 m/sec | 23.05±0.57 | 0.02 |
| 1,550 m/sec | 23.25±0.63 | 0.27 |
| 1,600 m/sec | 23.39±0.65 | 0.88 |
| 1,650 m/sec | 23.59±0.70 | 0.12 |
| 1,700 m/sec | 23.69±0.57 | 0.04 |
| 1,750 m/sec | 23.86±0.62 | 0.02 |
| 1,800 m/sec | 24.01±0.57 | 0.00 |
| 1,850 m/sec | 24.16±0.63 | 0.00 |
| 1,900 m/sec | 24.33±0.60 | 0.00 |
| 2,000 m/sec | 24.55±0.47 | 0.02 |
| 2,200 m/sec | 25.21±0.67 | 0.03 |
Table 3.
The results of axial length and keratometry at pre-cataract op. and post-IOL exchange
Table 4.
Comparison between expected refractive error by axial length measured at pre-cataract, pre-IOL exchange (psuedophaki mode, 1,600 m/sec) and manifested refractive error at post-IOL exchange
| Patient | Pre-Cataract | Pseudophakic mode | Post-IOL exchange (diopters) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pt. #1 - L | -0.13 | +1.13 | -0.25 |
| Pt. #2 - R | -0.13 | -0.04 | -0.13 |
| Pt. #2 - L | -0.01 | -0.20 | -0.38 |
| Pt. #3 - L | -0.11 | -0.03 | - |
| Pt. #4 - R | -0.18 | -0.65 | - |
| Pt. #5 - R | +0.08 | -0.17 | -0.75 |
| Pt. #6 - R | -0.03 | -0.08 | -0.25 |
| Pt. #7 - L | -0.12 | -0.29 | -0.50 |
| Pt. #8 - L | -0.05 | +0.07 | -0.38 |
| Pt. #9 - L | +0.12 | +0.04 | -0.25 |
| Pt. #10 - L | +0.17 | +0.34 | +0.50 |
| Pt. #11 - R | +0.06 | +0.50 | +0.25 |
| Pt. #11 - L | +0.12 | +0.05 | +0.25 |
| Pt. #12 - R | -0.05 | -0.09 | - |
| Average | -0.02±0.11 | +0.04±0.41 | -0.19±0.09 |
| p-value∗ | 0.97 | 0.08 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download